Abstract
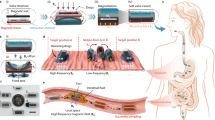
To establish a reliable, reproducible and accurate release of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract, a novel release mechanism for a controllable drug-delivery system has been investigated. The release mechanism, consisting of a one-way valve for drug release, a drug chamber, two axially magnetized cylindrical permanent magnets and a multi-layer solenoid coil, is hosted in the capsule-shaped shell with diameter 11 mm and length 30 mm. To actuate the coil piston, the two static magnetic fields produced by the two magnets are aligned along the same axis, having the same magnitude, but opposite directions. Based on the principle of the electromagnetic force and the Bernoulli equation, the actuating force can be expressed as a function of the coil stroke and the excitation current, which was modeled and experimentally verified. Thus the actuating force can be controlled by adjusting the activated period and intensity of the coil, resulting in the reproducible release with different doses and mean rates. Then, a prototype of the drug-delivery system has been developed, which consists of a drug-delivery capsule, a radio frequency transmission module, an interface circuit, and an instruction setting and triggering platform. All the drug release parameters, including the release mode, times, dose and mean flow rate, can be set by the platform. The experiment verifies that the drug-delivery capsule can deliver a predetermined dose with different flow rates and dip angles of the capsule. The relative error of the releasing dose becomes larger with increasing releasing rate and decreasing releasing dose.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.N. Antipina, G.B. Sukhorukov, Remote control over guidance and release properties of composite polyelectrolyte based capsules. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 716–729 (2011)
M. Beccani, C.D. Natali, G. Aiello, C. Benjamin, E. Susilo, P. Valdastri, A magnetic drug delivery capsule based on a coil actuation mechanism. Procedia Eng. 120, 53–56 (2015)
M. Beccani, G. Aiello, N. Gkotsis, et al., Component based design of a drug delivery capsule robot. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 245, 180–188 (2016)
D. Becker, J. Zhang, T. Heimbach, et al., Novel orally swallowable IntelliCap® device to quantify regional drug absorption in human GI tract using diltiazem as model drug. AAPS PharmSciTech 15, 1490–1497 (2014)
L. Cheong, C. Hyunchul, G. Gwangjun, et al., Active locomotive intestinal capsule endoscope (ALICE) system: A prospective feasibility study, mechatronics. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20, 2067–2074 (2015)
I. De Falco, G. Tortora, P. Dario, et al., An integrated system for wireless capsule endoscopy in a liquid-distended stomach. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61, 794–804 (2014)
T. Dietzel, H. Richert, S. Albert, U. Merkel, M. Hippius, A. Stallmach, Magnetic active agent release system (MAARS): Evaluation of a new way for a reproducible, externally controlled drug release into the small intestine. J. Control. Release 161, 722–727 (2012)
K.J. Filipsky, M.V. Varma, A.F. El-Kattan, C.M. Ambler, R.B. Ruggeri, T.C. Goosen, K.O. Cameron, Intestinal targeting of drugs: Rational design approaches and challenges. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 13, 776–802 (2013)
R. Goffredo, D. Accoto, E. Guglielmelli, Swallowable smart pills for local drug delivery: Present status and future perspectives. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 12, 585–599 (2015)
X. Guo, Z. Lu, H. Cui, et al., Modelling and solving the position tracking problem of remote-controlled gastrointestinal drug-delivery capsules. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 39, 213–218 (2018)
D. Hosokawa, T. Ishikawa, Development of a biologically inspired locomotion system for a capsule endoscope. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. 5, 471–478 (2009)
B. Kim, M.G. Lee, Y.P. Lee, et al., An earthworm-like micro robot using shape memory alloy actuator. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 125, 429–437 (2006)
H.M. Kim, S. Yang, J. Kim, et al., Active locomotion of a paddling-based capsule endoscope in an in vitro and in vivo experiment (with videos). Gastointest. Endosc. 72, 381–387 (2010)
J.Y. Lai, N.C. Tsai, H.L. Chiu, Theoretical analysis and simulations of micro-dosing locomotive robot with drug-release mechanism. Robot. Auton. Syst. 62, 177–187 (2014)
V.H. Le, H.L. Rodriguez, C. Lee, G. Go, et al., A soft-magnet-based drug-delivery module for active locomotive intestinal capsule endoscopy using an electromagnetic actuation system. Sensors Actuators A Phys 243, 81–89 (2016)
G.S. Lien, C.W. Liu, J.A. Jiang, et al., Magnetic control system targeted for capsule endoscopic operations in the stomach–design, fabrication, and in vitro and ex vivo evaluations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 2068–2079 (2012)
Z. Lu, X. Guo, T. Xu, et al., Optimum design of remote delivery capsule’s driving mechanism based on electromagnetic-permanent magnet. J. Syst. Simul. 30, 747–752 (2018)
S.S. Mapara, V.B. Patravale, Medical capsule robots: A renaissance for diagnostics, drug delivery and surgical treatment. J. Control. Release 261, 337–351 (2017)
F. Munoz, G. Alici, W. Li, Design optimization of a magnetomechanical system for drug delivery in wireless capsule endoscopy. IEEE/ASME Int. Conf. Adv. Intell. Mech. (2014) pp. 1097–1102
F. Munoz, G. Alici, H. Zhou et al., Analysis of the magnetic torque on a tilted permanent magnet for drug delivery in capsule robots. IEEE/ASME Int. Conf. Adv. Intell. Mech. (2016) pp. 1386–1391
S. Murad, J. Murad, H. Khan, A smarter SMA technology for the realization of drug delivering endoscopic capsule. Rawal Med. J. 38, 66–74 (2013)
D.A. Parasrampuria, T. Kanamaru, A. Connor, et al., Evaluation of regional gastrointestinal absorption of edoxaban using the Enterion capsule. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 55, 1286–1292 (2015)
M. Quirini, A. Menciassi, S. Scapellato, et al., Feasibility proof of a legged locomotion capsule for the GI tract. Gastointest. Endosc. 67, 1153–1158 (2008)
M. Rasouli, L. Lin, A.P. Kencana, et al., Therapeutic capsule endoscopy: Opportunities and challenges. J. Healthc. Eng. 2, 459–471 (2016)
M. Simi, P. Valdastri, C. Quaglia, et al., Design, fabrication, and testing of a capsule with hybrid locomotion for gastrointestinal tract exploration. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 15, 170–180 (2010)
P.J. van der Schaar, J.F. Dijksman, H. Broekhuizen-de Gast, J. Shimizu, N. van Lelyveld, H. Zou, V. Lordanov, C. Wanke, P.D. Siersema, A novel ingestible electronic drug delivery and monitoring device. Gastrointest. Endosc. 78, 520–528 (2013)
S.P. Woods, T.G. Constandinou, Wireless capsule endoscope for targeted drug delivery: Mechanics and design considerations. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60, 945–953 (2013)
S. Yim, K. Goyal, M. Sitti, Magnetically actuated soft capsule with themultimodal drug release function. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 18, 1413–1418 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai [grant number 15ZR1428200]; and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 61001164].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Luo, Z., Cui, H. et al. A novel and reproducible release mechanism for a drug-delivery system in the gastrointestinal tract. Biomed Microdevices 21, 25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0383-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0383-z