Abstract
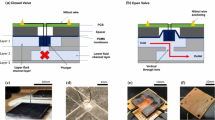
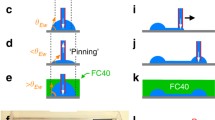
The development and optimization of many new drug therapies requires long-term local delivery with controlled, but variable dosage. Current methods for chronic drug delivery have limited utility because they either cannot deliver drugs locally to a specific organ or tissue, do not permit changes in delivery rate in situ, or cannot be used in clinical trials in an untethered, wearable configuration. Here, we describe a small, self-contained system for liquid-phase drug delivery. This system enables studies lasting several months and infusion rates can be programmed and modified remotely. A commercial miniature pump is integrated with microfabricated components to generate ultralow flow rates and stroke volumes. Solutions are delivered in pulses as small as 370 nL, with pulses delivered at any interval of 1 min or longer. A unique feature of the system is the ability to infuse and immediately withdraw liquid, resulting in zero net volume transfer while compounds are exchanged by mixing and diffusion with endogenous fluid. We present in vitro results demonstrating repeatability of the delivered pulse volume for nearly 3 months. Furthermore, we present in vivo results in an otology application, infusing into the cochlea of a guinea pig a glutamate receptor antagonist, which causes localized and reversible changes in auditory sensitivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Chen, S.G. Kujawa, M.J. McKenna, J.O. Fiering, M.J. Mescher, J.T. Borenstein, E.E.L. Swan, W.F. Sewell, J. Control. Release 110, 1–19 (2005)doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.09.003
C.E. Dubé, J.O. Fiering, M.J. Mescher, in Proc. IEEE Sensors, Orlando, (2002)
N. Galley, R. Klinke, W. Oertel, M. Pause, W.H. Storch, Brain Res. 64, 55–63 (1973)
M.C. Holley, Br. Med. Bull. 63, 157–169 (2002)
M.C. Holley, Drug Discovery Today 10, 1269–1282 (2005)
N. Inamura, A.N. Salt, Hear. Res. 61, 12–18 (1992)
D.A. LaVan, T. McGuire, R. Langer, Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1184–1191 (2003)
T. Littman, R.P. Bobbin, M. Fallon, J.L. Puel, Hear. Res. 40, 45–53 (1989)
D. Maillefer, S. Gamper, B. Frehner, P. Balmer, H. van Lintel, P. Renaud, in Proc. MEMS 2001, 14th IEEE International Conf. on, Interlaken, Switzerland, 413–417 (2001)
D.M. Merfeld, W. Gong, J. Morrissey, M. Saginaw, C. Haburcakova, R.F. Lewis, IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng. 53, 2362–2372 (2006)
M.J. Mescher, C.E. Dube, M. Varghese, J.O. Fiering, in Proc. Micro Total Analysis Systems (MicroTAS), Squaw Valley CA, 947–950 (2003)
M.J. Mescher, C.E. Dube, J.O. Fiering, D.L. Fyler, E.S. Kim, M. Hansberry, J.T. Borenstein, J.J. Bernstein, E. Gragoudas, J. Miller, in Proc. Annual Meeting Society for Biomaterials, Pittsburgh (2006)
M.R. Prausnitz, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 581–587 (2004)
J.H. Prescott, S. Lipka, S. Baldwin, N.F.J. Sheppard, J.M. Maloney, J. Coppeta, B. Yomtov, M.A. Staples, J.T.J. Santini, Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 437–438 (2006)
S.Z. Razzacki, P.K. Thwar, M. Yang, V.M. Ugaz, M.A. Burns, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 185–198 (2004)
N. Roxhed, B. Samel, L. Nordquist, P. Griss, G. Stemme, in Proc. MEMS 2006, 19th International Conf. on, Istanbul, 414–417 (2006)
W.M. Saltzman, Drug Delivery: Engineering Principles for Drug Therapy (Oxford University Press, New York, 2001)
J.T.J. Santini, M.J. Cima, R. Langer, Nature 397, 335–338 (1999)
J.T.J. Santini, A.C. Richards, R. Scheidt, M.J. Cima, R. Langer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 2396–2407 (2000)
M. Thorne, A.N. Salt, J.E. DeMott, M.M. Henson, O.W.J. Henson, S.L. Gewalt, The Laryngoscope 109, 1661–1668 (1999)
A.K. Wise, R. Richardson, J. Hardman, G. Clark, S. O'Leary, J Comp Neurol 487, 147–165 (2005)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Sarah Tao for her contributions. This research was made possible by grant number 5R01DC006848-03 from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM1
(DOC 32.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiering, J., Mescher, M.J., Leary Swan, E.E. et al. Local drug delivery with a self-contained, programmable, microfluidic system. Biomed Microdevices 11, 571–578 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9265-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9265-5