Abstract
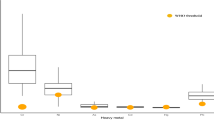
Breast milk is a complete food for the development of the newborn, but it can also be an important route for environmental pollutants transmission to the infants. This study was aimed to evaluate the status of heavy metals including lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) in the breast milk of Iranian mothers. The international databases including Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science and the Persian electronic databases including Scientific Information Database, IranMedex and Magiran were examined to find relevant articles published until July 2021. A total of 23 studies examined the levels of toxic metals in Iranian breast milk samples. According to the findings, the pooled average concentrations (µg/L) of Pb, Cd, Hg and As were 25.61, 2.40, 1.29 and 1.16, respectively. The concentration of Hg and Pb in colostrum milk was more than twice of mature milk. The Hg mean concentration in the breast milk of mothers with at least one amalgam-filled tooth was approximately three times that of mothers without amalgam-filled teeth. Risk assessment analysis indicated that the intake of Pb and Hg by infants through breastfeeding can be considered a health concern in Iran. It seems necessary to reduce the Pb exposure of pregnant and lactating women in Iran. However, more extensive studies are needed to clarify the toxic metals’ exposure status of infants through breast milk in other parts of the country.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset and statistical analysis outputs of this study are available by the author of correspondence on reasonable request.
References
Abadin HG, Hibbs BF, Pohl HR (1997) Breast-feeding exposure of infants to cadmium, lead, and mercury: a public health viewpoint. Toxicol Ind Health 13(4):495–517
Abdollahi M, Shohrati M, Nikfar S, Jalali N (1995) Monitoring of lead poisoning in bus drivers of Tehran. Irn J Med Sci 20:29–33
Abdollahi A, Tadayon F, Amirkavei M (2013) Evaluation and determination of heavy metals (mercury, lead and cadmium) in human breast milk. Paper presented at the E3S Web of Conferences.
Abtahi M, Fakhri Y, Oliveri Conti G, Keramati H, Zandsalimi Y, Bahmani Z, Hosseini Pouya R, Sarkhosh M, Moradi B, Ghasemi SM, Amanidaz N (2017) Heavy metals (As, Cr, Pb, Cd and Ni) concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa) from Iran and associated risk assessment: a systematic review. Toxin Rev 36(4):331–341
Adams SV, Newcomb PA, Shafer MM, Atkinson C, Bowles EJA, Newton KM, Lampe JW (2011) Sources of cadmium exposure among healthy premenopausal women. Sci Total Environ 409(9):1632–1637
Almeida AA, Lopes CM, Silva AM, Barrado E (2008) Trace elements in human milk: correlation with blood levels, inter-element correlations and changes in concentration during the first month of lactation. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22(3):196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2008.03.007
Al-Saleh I, Shinwari N, Mashhour A (2003) Heavy metal concentrations in the breast milk of Saudi women. Biol Trace Elem Res 96(1):21–37
Antunes Dos Santos A, Appel Hort M, Culbreth M, López-Granero C, Farina M, Rocha JB, Aschner M (2016) Methylmercury and brain development: a review of recent literature. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:99–107
Astolfi E, Maccagno A, Fernández JG, Vaccaro R, Stimola R (1981) Relation between arsenic in drinking water and skin cancer. Biol Trace Elem Res 3(2):133–143
Bahmani P, Maleki A (2018) Investigation of mercury, cadmium and arsenic levels in breast milk and their relationship with the studied parameters in Sanandaj, Iran. Zanko J Med Sci 19(62):84–97
Bahmani P, Sadeghi S, Ghahramani E, Daraei H (2018) Evaluation of lead and cadmium levels in breast milk in Sanandaj, Iran. J Adv Environ Health Res 6(3):144–151
Bassil M, Daou F, Hassan H, Yamani O, Abi Kharma J, Attieh Z, Elaridi J (2018) Lead, cadmium and arsenic in human milk and their socio-demographic and lifestyle determinants in Lebanon. Chemosphere 191:911–921
Behrooz RD, Esmaili-Sari A, Peer FE, Amini M (2012) Mercury concentration in the breast milk of Iranian women. Biol Trace Elem Res 147(1–3):36–43
Behrooz RD, Sari AE, Mishmast-nehi A, Sepehrikia S, Barghi M (2013) Mercury concentration in the milk of mothers living near the southern coast of the Caspian Sea during different stages of lactation period. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(5):860–869. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2013.812729
Behzadifar M, Saki M, Behzadifar M, Mardani M, Yari F, Ebrahimzadeh F, Majidi Mehr H, Abdi Bastami S, Bragazzi NL (2019) Prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding practice in the first six months of life and its determinants in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr 19(1):384
Bellinger DC (2008) Very low lead exposures and children’s neurodevelopment. Curr Opin Pediatr 20(2):172–177
Björnberg KA, Vahter M, Berglund B, Niklasson B, Blennow M, Sandborgh-Englund G (2005) Transport of methylmercury and inorganic mercury to the fetus and breast-fed infant. Environ Health Perspect 113(10):1381–1385
Bolann BJ, Rahil-Khazen R, Henriksen H, Isrenn R, Ulvik RJ (2007) Evaluation of methods for trace-element determination with emphasis on their usability in the clinical routine laboratory. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 67(4):353–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365510601095281
Bose-O’Reilly S, McCarty KM, Steckling N, Lettmeier B (2010) Mercury exposure and children’s health. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care 40(8):186–215
Brahm P, Valdes V (2017) Benefits of breastfeeding and risks associated with not breastfeeding. Rev Chil Pediatr 88(1):15–21
Bulska E, Ruszczyńska A (2017) Analytical techniques for trace element determination. Inorg Trace Anal. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110366730-003
Carignan CC, Karagas MR, Punshon T, Gilbert-Diamond D, Cottingham KL (2016) Contribution of breast milk and formula to arsenic exposure during the first year of life in a US prospective cohort. J Eposure Sci Environ Epidemiol 26(5):452–457
Castro-González M, Méndez-Armenta M (2008) Heavy metals: implications associated to fish consumption. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(3):263–271
Chao H-H, Guo C-H, Huang C-B, Chen P-C, Li H-C, Hsiung D-Y, Chou Y-K (2014) Arsenic, cadmium, lead, and aluminium concentrations in human milk at early stages of lactation. Pediatr Neonatol 55(2):127–134
Cherkani-Hassani A, Slaoui M, Ghanname I, Mojemmi B, Belhaj A, Kers B, Flayou M, Mouane N (2020) Cadmium contamination in breast milk of Moroccan lactating women and the associated factors: Contamilk study. Biol Trace Elem Res 196(1):47–59
Choi AL, Cordier S, Weihe P, Grandjean P (2008a) Negative confounding in the evaluation of toxicity: the case of methylmercury in fish and seafood. Crit Rev Toxicol 38(10):877–893
Choi J, Tanaka T, Koren G, Ito S (2008b) Lead exposure during breastfeeding. Can Fam Physician 54(4):515–516
Clarkson TW, Magos L (2006) The toxicology of mercury and its chemical compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 36(8):609–662
Concha G, Vogler G, Nermell B, Vahter M (1998) Low-level arsenic excretion in breast milk of native Andean women exposed to high levels of arsenic in the drinking water. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 71(1):42–46
David M, Afzal M, Shoaib M, Aman F, Cloete KJ, Turi N, Jahan S (2020) Study of occupational exposure to brick kiln emissions on heavy metal burden, biochemical profile, cortisol level and reproductive health risks among female workers at Rawat, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(35):44073–44088
Domingo JL, Bocio A, Falcó G, Llobet JM (2007) Benefits and risks of fish consumption: part I. A quantitative analysis of the intake of omega-3 fatty acids and chemical contaminants. Toxicology 230(2–3):219–226
Drasch G, Aigner S, Roider G, Staiger F, Lipowsky G (1998) Mercury in human colostrum and early breast milk. Its dependence on dental amalgam and other factors. J Trace Elem Med Biol 12(1):23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0946-672x(98)80017-5
Drexler H, Schaller K-H (1998) The mercury concentration in breast milk resulting from amalgam fillings and dietary habits. Environ Res 77(2):124–129
Dursun A, Yurdakok K, Yalcin SS, Tekinalp G, Aykut O, Orhan G, Morgil GK (2016) Maternal risk factors associated with lead, mercury and cadmium levels in umbilical cord blood, breast milk and newborn hair. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29(6):954–961. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2015.1026255
Ettinger AS, Téllez-Rojo MM, Amarasiriwardena C, González-Cossío T, Peterson KE, Aro A, Hu H, Hernández-Avila M (2004) Levels of lead in breast milk and their relation to maternal blood and bone lead levels at one month postpartum. Environ Health Perspect 112(8):926–931
European Food Safety Authority (2012) Lead dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J 10(7):2831
Fakour H, Esmaili-Sari A, Zayeri F (2010) Mercury exposure assessment in Iranian women’s hair of a port town with respect to fish consumption and amalgam fillings. Sci Total Environ 408(7):1538–1543
Fängström B, Moore S, Nermell B, Kuenstl L, Goessler W, Grandér M, Kabir I, Palm B, Arifeen SE, Vahter M (2008) Breast-feeding protects against arsenic exposure in Bangladeshi infants. Environ Health Perspect 116(7):963–969
Feizi R, Jaafarzadeh N, Akbari H, Jorfi S (2019) Evaluation of lead and cadmium concentrations in lipstick and eye pencil cosmetics. Environ Health Eng Manag J 6(4):277–282
Frkovic A, Kras M, Alebic-Juretic A (1997) Lead and cadmium content in human milk from the Northern Adriatic area of Croatia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58(1):16–21
García-Esquinas E, Pérez-Gómez B, Fernández MA, Pérez-Meixeira AM, Gil E, de Paz C, Iriso A, Sanz JC, Astray J, Cisneros M, de Santos A, Asensio A, García-Sagredo JM, García JF, Vioque J, Pollán M, López-Abente G, González MJ, Martínez M, Bohigas PA, Pastor R, Aragonés N (2011) Mercury, lead and cadmium in human milk in relation to diet, lifestyle habits and sociodemographic variables in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 85(2):268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.029
Ghaderpoori M, Kamarehie B, Jafari A, Alinejad AA, Hashempour Y, Saghi MH, Yousefi M, Oliveri Conti G, Mohammadi AA, Ghaderpoury A (2020) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in cosmetic products sold in Iran: the Monte Carlo simulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7588–7595
Ghaffarian-Bahraman A, Shahroozian I, Jafari A, Ghazi-Khansari M (2014) Protective effect of magnesium and selenium on cadmium toxicity in the isolated perfused rat liver system. Acta Med Iran 52:872–878
Ghaffarian-Bahraman A, Mohammadi S, Jafari A, Ghani-Dehkordid J, Arabnezhad M-R, Rahmdel S, Hosseini Teshnizi S (2020) Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milks of five animal species in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Rev Intl 36(7):692–712
Ghaffarian-Bahraman A, Taherifard A, Esmaeili A, Ahmadinia H, Rezaeian M (2021) Evaluation of blood lead among painters of buildings and cars. Toxicol Ind Health. https://doi.org/10.1177/07482337211042731
Ghoochani M, Rastkari N, Yunesian M, Nodehi RN, Mesdaghinia A, Houshiarrad A, Shamsipour M, Dehghani MH (2018) What do we know about exposure of Iranians to cadmium? Findings from a systematic review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1–11
Ghorban K, Dadmanesh M, Fathollahi MS, Rezai Z, Ezati P, Salmani MH, Akrami Mohajeri F, Yousefi-Daredor H, Ebrahimi H, Kazemi Arababadi M, Kennedy D (2020) IL-8 may be the target of arsenic in human breast milk. Int J Med Lab. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijml.v7i1.2470
Golmohammadi T, Ansari M, Nikzamir A, Safary-Abhari R, Elahi S (2007) The effect of maternal and fetal lead concentration on birth weight: polluted versus non-polluted areas of Iran. Tehran Univ Med J 65(8):74–78
Goudarzi M, Parsaei P, Nayebpour F, Rahimi E (2013) Determination of mercury, cadmium and lead in human milk in Iran. Toxicol Ind Health 29(9):820–823
Grzunov Letinić J, Matek Sarić M, Piasek M, Jurasović J, Varnai VM, Sulimanec Grgec A, Orct T (2016) Use of human milk in the assessment of toxic metal exposure and essential element status in breastfeeding women and their infants in coastal Croatia. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.08.002
Guney M, Zagury GJ (2012) Heavy metals in toys and low-cost jewelry: critical review of U.S. and Canadian legislations and recommendations for testing. Environ Sci Technol 46(8):4265–4274. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203470x
Halimi L, Haghdoost AA, Alizadeh SM (2013) Prevalence of cigarette smoking among Iranian women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med J Islam Repub Iran 27(3):132
Hallen IP, Jorhem L, Lagerkvist BJ, Oskarsson A (1995) Lead and cadmium levels in human milk and blood. Sci Total Environ 166(1–3):149–155
Hashempour-Baltork F, Hosseini H, Houshiarrad A, Esmaeili M (2019) Contamination of foods with arsenic and mercury in Iran: a comprehensive review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(25):25399–25413
International Agency for Research on Cancer (1993) Beryllium, cadmium, mercury and exposures in the glass manufacturing industry. IARC, Lyon
International Agency for Research on Cancer (2012) Arsenic and arsenic compounds. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK304380/
Jafari A, Shoeibi S, Amini M, Amirahmadi M, Rastegar H, Ghaffarian A, Ghazi-Khansari M (2012) Monitoring dithiocarbamate fungicide residues in greenhouse and non-greenhouse tomatoes in Iran by HPLC-UV. Food Addit Contam B 5(2):87–92
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68(1):167–182
Jean J, Sirot V, Hulin M, Le Calvez E, Zinck J, Noël L, Vasseur P, Nesslany F, Gorecki S, Rivière G, Guérin T (2018) Dietary exposure to cadmium and health risk assessment in children—results of the French infant total diet study. Food Chem Toxicol 115:358–364
Johansson C, Castoldi AF, Onishchenko N, Manzo L, Vahter M, Ceccatelli S (2007) Neurobehavioural and molecular changes induced by methylmercury exposure during development. Neurotox Res 11(3–4):241–260
Jonidi Jafari A, Esrafili A, Moradi Y, Mahmoudi N (2020) Mercury level in biological samples of dentists in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(2):1655–1669
Karamian E (2020) Risk assessment of heavy metals (chromium, nickel, lead, copper and iron) in fast foods consumed in Isfahan, Iran. J Bioenergy Food Sci 7(4):3032020
Kelishadi R, Hasanghaliaei N, Poursafa P, Keikha M, Ghannadi A, Yazdi M, Rahimi E (2016) A randomized controlled trial on the effects of jujube fruit on the concentrations of some toxic trace elements in human milk. J Res Med Sci 21:108
Khammar S, Pourkhabbaz A, Dahmardeh Behrooz R (2017) Examination of mercury concentration in the hair and milk mothers and relation to number of dental amalgam filling and mother feeding case study:(city of Zahedan). J Nat Environ 70(1):77–86
Khanjani N, Jafari M, Mousavi EA (2018) Breast milk contamination with lead and cadmium and its related factors in Kerman, Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng 16(2):323–335
Koyashiki GA, Paoliello MM, Tchounwou PB (2010a) Lead levels in human milk and children’s health risk: a systematic review. Rev Environ Health 25(3):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh.2010.25.3.243
Koyashiki GAK, Paoliello MMB, Matsuo T, de Oliveira MMB, Mezzaroba L, de Fátima Carvalho M, Sakuma AM, Turini C, Vannuchi MT, Barbosa CSD (2010b) Lead levels in milk and blood from donors to the Breast Milk Bank in Southern Brazil. Environ Res 110(3):265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2009.12.001
Kramer MS, Kakuma R (2012) Optimal duration of exclusive breastfeeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003517.pub2
Kuivenhoven M, Mason K (2020) Arsenic toxicity StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Medeiros RJ, Santos L, Gonçalves JM, Braga A, Krauss TM, Jacob SDC (2014) Comparison of the nutritional and toxicological reference values of trace elements in edible marine fish species consumed by the population in Rio De Janeiro State, Brazil. Toxicol Rep 1:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.06.005
Mehdipour A, Zaeimdar M, Sekhavatjou MS, Jozi SA (2020) Heavy metal concentrations in the outdoor and indoor air of high-traffic areas in Tehran, Iran. J Adv Environ Health Res 8(1):25–37
Mirzakouchaki P, Rashidi F, Hasanli E, Karbalaiefar S (2013) Relationship between the number of tooth surfaces restored with amalgam and mothers’ breast milk mercury levels: a preliminary study. J Isfahan Dent Sch 8(7):645–651
Mohammadi S, Keshavarzi M, Kazemi A, Berizi E, Mohsenpour MA, Ghaffarian-Bahraman A (2021) Occurrence of aflatoxin M 1 in yogurt of five countries in west Asia region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Food Saf 41:e12897
Motas M, Jiménez S, Oliva J, Cámara MÁ, Pérez-Cárceles MD (2021) Heavy metals and trace elements in human breast milk from industrial/mining and agricultural zones of southeastern Spain. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(17):9289
Murata K, Iwata T, Dakeishi M, Karita K (2008) Lead toxicity: does the critical level of lead resulting in adverse effects differ between adults and children? J Occup Health. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.k8003
Naalbandi H, Saeedi M, Moharrami Moghanlou O, Akbari J, Morteza-Semnani K, Alizadeh R, Esfahani-Zadeh MH, Tajbakhsh M (2016) Evaluation of heavy metal content of some lipsticks in Iran market. Pharm Biomed Res 2(3):31–37
Nazarpour S, Teymouri L, Teimoori S, Nojoumi SA, Moghimi A (2013) Investigation of Cd(II) concentrations in mother’s milk of Varamin region of Iran. Asian J Chem 25(10):5402
Nickerson K (2006) Environmental contaminants in breast milk. J Midwifery Womens Health 51(1):26–34
Nishijo M, Tawara K, Honda R, Kuriwaki J-I, Nakagawa H, Tanebe K, Saito S (2004) Cadmium and nutritional intake in pregnant Japanese women. Toxicol Lett 148(3):171–176
Norouzi E, Bahramifar N, Ghasempouri SM (2010) Determination concentration of lead in breast in lactating women in region industrial Zarinshahr and effect on infant. J Isfahan Med Sch 28(112):640–646
Norouzi E, Bahramifar N, Ghasempouri SM (2012) Effect of teeth amalgam on mercury levels in the colostrums human milk in Lenjan. Environ Monit Assess 184(1):375–380
Okati N, Sari A, Ghasempouri S (2013) Evaluation of mercury pollution in breast milk and Iranian infants’ hair. Int Res J Appl Basic Sci 4(9):2857–2864
Olang B, Farivar K, Heidarzadeh A, Strandvik B, Yngve A (2009) Breastfeeding in Iran: prevalence, duration and current recommendations. Int Breastfeed J 4(1):8
Oosthuizen J, Ehrlich R (2001) The impact of pollution from a mercury processing plant in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, on the health of fish-eating communities in the area: an environmental health risk assessment. Int J Environ Health Res 11(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603120020019638
Örün E, Yalçın SS, Aykut O, Orhan G, Morgil GK, Yurdakök K, Uzun R (2011) Breast milk lead and cadmium levels from suburban areas of Ankara. Sci Total Environ 409(13):2467–2472
Oskarsson A, Schütz A, Skerfving S, Hallén IP, Ohlin B, Lagerkvist BJ (1996) Total and inorganic mercury in breast milk and blood in relation to fish consumption and amalgam fillings in lactating women. Arch Environ Health 51(3):234–241
Oskarsson A, Hallén IP, Sundberg J, Grawé KP (1998) Risk assessment in relation to neonatal metal exposure. Analyst 123(1):19–23
Pajewska-Szmyt M, Sinkiewicz-Darol E, Gadzała-Kopciuch R (2019) The impact of environmental pollution on the quality of mother’s milk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(8):7405–7427
Pan J, Plant JA, Voulvoulis N, Oates CJ, Ihlenfeld C (2010) Cadmium levels in Europe: implications for human health. Environ Geochem Health 32(1):1–12
Park J-D, Zheng W (2012) Human exposure and health effects of inorganic and elemental mercury. J Prev Med Public Health 45(6):344
Parr RM, DeMaeyer EM, Iyengar VG, Byrne AR, Kirkbright GF, Schöch G, Niinistö L, Pineda O, Vis HL, Omololu A, Hofvander Y (1991) Minor and trace elements in human milk from Guatemala, Hungary, Nigeria, Philippines, Sweden, and Zaire. Biol Trace Elem Res 29(1):51–75
Popovic M, McNeill FE, Chettle DR, Webber CE, Lee CV, Kaye WE (2005) Impact of occupational exposure on lead levels in women. Environ Health Perspect 113(4):478–484
Rahimi E, Hashemi M, Baghbadorani ZT (2009) Determination of cadmium and lead in human milk. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6(4):671–676
Rahmani J, Fakhri Y, Shahsavani A, Bahmani Z, Urbina MA, Chirumbolo S, Keramati H, Moradi B, Bay A, Bjørklund G (2018) A systematic review and meta-analysis of metal concentrations in canned tuna fish in Iran and human health risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 118:753–765
Rani A, Kumar A, Lal A, Pant M (2014) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: a review. Int J Environ Health Res 24(4):378–399
Ravanipour M, Hadi M, Rastkari N, Borji SH, Nasseri S (2021) Presence of heavy metals in drinking water resources of Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13293-y
Rebelo FM, Caldas ED (2016) Arsenic, lead, mercury and cadmium: toxicity, levels in breast milk and the risks for breastfed infants. Environ Res 151:671–688
Registry AfTSaD (2017) Lead toxicity. Available at https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/lead/docs/csem-lead_toxicity_508.pdf
Rehman K, Fatima F, Waheed I, Akash MSH (2018) Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J Cell Biochem 119(1):157–184
Reinhardt J (1992) Side-effects: mercury contribution to body burden from dental amalgam. Adv Dent Res 6(1):110–113
Reyes-Hinojosa D, Lozada-Pérez C, Cuevas YZ, López-Reyes A, Martínez-Nava G, Fernández-Torres J, Olivos-Meza A, Landa-Solis C, Gutiérrez-Ruiz MC, Martínez-Flores K, Del Castillo ER (2019) Toxicity of cadmium in musculoskeletal diseases. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 72:103219
Rompalski P, Greczichen A (2018) Measuring low mercury content in furnace waste, with ALTEC’s automatic atomic absorption spectrometer. J Sustain Min 17(4):195–201
Sadeghi N, Jannat B, Behzad M, Oveisi MR, Hajimahmoodi M, Ahmadi F (2020) Determination of zinc, copper, lead and cadmium concentration in breastmilk by anodic stripping voltammetry method and investigating their impact on infants’ growth indicators. Hum Health Halal Metr 1(2):24–30
Salehi Z, Esmaili-Sari A (2010) Hair mercury levels in pregnant women in Mahshahr, Iran: fish consumption as a determinant of exposure. Sci Total Environ 408(20):4848–4854
Salmani MH, Rezaie Z, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Ehrampoush MH (2018) Arsenic exposure to breast-fed infants: contaminated breastfeeding in the first month of birth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(7):6680–6684
Salpietro CD, Gangemi S, Minciullo PL, Briuglia S, Merlino MV, Stelitano A, Cristani M, Trombetta D, Saija A (2002) Cadmium concentration in maternal and cord blood and infant birth weight: a study on healthy non-smoking women. J Perinat Med 30(5):395–399
Samanta G, Das D, Mandal BK, Chowdhury TR, Chakraborti D, Pal A, Ahamed S (2007) Arsenic in the breast milk of lactating women in arsenic-affected areas of West Bengal, India and its effect on infants. J Environ Sci Health A 42(12):1815–1825
Samiee F, Leili M, Faradmal J, Torkshavand Z, Asadi G (2019a) Exposure to arsenic through breast milk from mothers exposed to high levels of arsenic in drinking water: infant risk assessment. Food Control 106:106669
Samiee F, Vahidinia A, Javad MT, Leili M (2019b) Exposure to heavy metals released to the environment through breastfeeding: a probabilistic risk estimation. Sci Total Environ 650:3075–3083
Sarlak Z, Hosseini H, Garavand F, Mohammadi R, Rouhi M (2021a) The occurrence of lead in animal source foods in Iran in the 2010s decade: a systematic review. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02787-y
Sarlak Z, Rouhi M, Mirza Alizadeh A, Sadeghi E, Hosseini H, Mousavi Khaneghah A (2021b) Pb exposure from plant foods in Iran: a review. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1970149
Schnaas L, Rothenberg SJ, Flores M-F, Martinez S, Hernandez C, Osorio E, Velasco SR, Perroni E (2006) Reduced intellectual development in children with prenatal lead exposure. Environ Health Perspect 114(5):791–797
Shaji E, Santosh M, Sarath K, Prakash P, Deepchand V, Divya B (2021) Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci Front 12(3):101079
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 350:g7647. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Sharafati Chaleshtori F, Rafieian Kopaei M, Sharafati Chaleshtori R (2017) A review of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa) of Iran. Toxin Rev 36(2):147–153
Sharma R, Pervez S (2005) Toxic metals status in human blood and breast milk samples in an integrated steel plant environment in Central India. Environ Geochem Health 27(1):39–45
Siblerud R, Mutter J, Moore E, Naumann J, Walach H (2019) A hypothesis and evidence that mercury may be an etiological factor in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(24):5152
Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertz-Picciotto I, Duggan HM, Wood R, Kosnett MJ, Smith MT (1992) Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 97:259–267
Soleimani S, Shahverdy MR, Mazhari N, Abdi K, Nejad SG, Shams S, Alebooyeh E, Khaghani S (2014) Lead concentration in breast milk of lactating women who were living in Tehran, Iran. Acta Med Iran 52:56–59
Sperling M (2006) Flame and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry in environmental analysis. Encycl Anal Chem Appl Theory Instrum. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470027318.a0805
Start ABsB. Amount of milk needed by baby in 24 hours. Available at http://www.best-breastpumps.com/Milk_Intake.htm
Sternowsky H-J, Moser B, Szadkowsky D (2002) Arsenic in breast milk during the first 3 months of lactation. Int J Hyg Environ Health 205(5):405–409
Takahashi Y, Tsuruta S, Arimoto M, Tanaka H, Yoshida M (2003) Placental transfer of mercury in pregnant rats which received dental amalgam restorations. Toxicology 185(1–2):23–33
Taylor CM, Emmett PM, Emond AM, Golding J (2018) A review of guidance on fish consumption in pregnancy: is it fit for purpose? Public Health Nutr 21(11):2149–2159
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol Clin Environ Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tong M, Yu J, Liu M, Li Z, Wang L, Yin C, Ren A, Chen L, Jin L (2021) Total mercury concentration in placental tissue, a good biomarker of prenatal mercury exposure, is associated with risk for neural tube defects in offspring. Environ Int 150:106425
Ursinyova M, Masanova V (2005) Cadmium, lead and mercury in human milk from Slovakia. Food Addit Contam 22(6):579–589
Vahidinia A, Samiee F, Faradmal J, Rahmani A, Javad MT, Leili M (2019) Mercury, lead, cadmium, and barium levels in human breast milk and factors affecting their concentrations in Hamadan, Iran. Biol Trace Elem Res 187(1):32–40
Vardhan KH, Kumar PS, Panda RC (2019) A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq 290:111197
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T (2014) Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol 14:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
WHO (1989) Minor and trace elements in breast milk: report of a joint WHO/IAEA collaborative study. World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (2017) The international code of marketing of breast-milk substitutes: frequently asked questions. Retrieved from
World Health Organization (2020) 10 chemicals of public health concern. Available at https://www.who.int/news-room/photo-story/photo-story-detail/10-chemicals-of-public-health-concern
Zarandi SM, Shahsavani A, Khodagholi F, Fakhri Y (2019) Concentration, sources and human health risk of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bound PM 2.5 ambient air, Tehran, Iran. Environ Geochem Health 41(3):1473–1487
Zhang Y-L, Zhao Y-C, Wang J-X, Zhu H-D, Liu Q-F, Fan Y-G, Wang NF, Zhao JH, Liu HS, Liu AP, Ou-Yang L (2004) Effect of environmental exposure to cadmium on pregnancy outcome and fetal growth: a study on healthy pregnant women in China. J Environ Sci Health A 39(9):2507–2515
Zhou T, Guo J, Zhang J, Xiao H, Qi X, Wu C, Chang X, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Zhou Z (2020) Sex-specific differences in cognitive abilities associated with childhood cadmium and manganese exposures in school-age children: a prospective cohort study. Biol Trace Elem Res 193(1):89–99
Ziegler EE, Edwards BB, Jensen RL, Mahaffey KR, Fomon SJ (1978) Absorption and retention of lead by infants. Pediatr Res 12(1):29–34
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research project was supported by the Deputy of Research and Technology, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, S., Shafiee, M., Faraji, S.N. et al. Contamination of breast milk with lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biometals 35, 711–728 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00395-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00395-4