Abstract
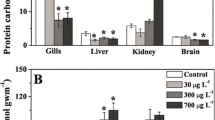
Silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) is a fish species with neotropical distribution, and is a potential model organism to study polluted environment. The aim of this study is to analyze the response of silver catfish to environmental concentrations of waterborne zinc (Zn) over 96 h. Significant metal accumulation was seen in gill, intestine and liver tissues. No significant accumulation was seen in muscle tissue. Lipid peroxidation increased in the brain, and decreased in the muscle and liver at all levels of exposure. Zinc exposure led to decreased protein carbonyl levels in the brain and increased levels in the liver. The activity of catalase in the liver was reduced for all exposed groups. Glutathione S-transferase activity decreased in the brain at the highest level of exposure and in the liver at all Zn concentrations tested. Non-protein thiols increased in the muscle and in the gills after exposure. Ascorbic acid levels increased in the brain and in the gills. Exposure to Zn also altered the metabolic parameters, causing decreased lactate and ammonia levels in the muscle, and decreased glycogen in the liver. Zinc exposure increased ammonia and amino acid levels in the liver, and increase glycogen and amino acid levels in muscle tissue. Our results demonstrate that exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of Zn led to accumulation of metals in the tissues of silver catfish, with significant changes in biochemical parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bidinotto PM, Moraes G, Souza RHS (1997) Hepatic glycogen and glucose in eight tropical fresh water teleost fish: aprocedure for field determinations of micro samples. Bol Tec CEPTA Pirassununga 10:53–60
Bradford MMA (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–309
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente) Resolução CONAMA nº 357 de 17/03/05. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codleg=459. Accessed 20 June 2018
Dural M, Göksu MZL, Özak AA (2007) Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically important fish species captured from the Tuzla lagoon. Food Chem 102:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.03.001
Eisler R (1988) Lead hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. US Fish and Wildlife Service. Biological Report 85(1.14)
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem 82:70–77
FAO/WHO (1983) Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. Fish Circ 464:764
FAO/WHO (1989) National research council recommended dietary allowances, 10th edn. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jacoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferase, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Harrower JR, Brown CH (1972) Blood lactic acid: a micro method adapted to collection of micro liter samples. J Appl Physiol 32:709–711
Ineu RP, Oliveira CS, Oliveira VA, Moraes-Silva L, Luz SCA, Pereira ME (2013) Antioxidant effect of zinc chloride against ethanol-induced gastrointestinal lesions in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 58:522–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.05.022
La Colla NS, Botté SE, Marcovecchio JE (2018) Metals in coastal zones impacted with urban and industrial wastes: insights on the metal accumulation pattern in fish species. J Mar Syst 181:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2018.01.012
Leitemperger J, Menezes C, Santi A, Murussi C, Lópes T, Costa M, Nogueira LS, Loro VL (2016) Early biochemical biomarkers for zinc in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) after acute exposure. Fish Physiol Biochem 42(3):1005–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0192-0
Loro VL, Nogueira L, Nadella SR, Wood CM (2014) Zinc bioaccumulation and ionoregulatory impacts in Fundulus heteroclitus exposed to sublethal waterborne zinc at different salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol C 166:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2014.07.004
Lowry DH, Rosenbrough NJ, Far AL, Randal RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006
McGeer JC, Szebedinszky C, McDonald DG, Wood CM (2000) Effects of chronic sublethal exposure to waterborne Cu, Cd or Zn in rainbow trout 2: tissue specific metal accumulation. Aquat Toxicol 50:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00106-X
McRae NK, Gaw S, Glover CN (2016) Mechanisms of zinc toxicity in the galaxiid fish, Galaxias maculatus. Comp Biochem Physiol C 179:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.10.010
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the auto-oxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Nelson DP, Kiesow LA (1972) Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25 °C (with molar extinction coefficients of H2O2 solution in the UV). Anal Biochem 49:474–478
Pretto A, Loro VL, Morsch VM, Moraes BS, Menezes C, Santi A, Toni C (2014a) Alterations in carbohydrate and protein metabolism in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:188–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.11.004
Pretto A, Loro VL, Silva VM, Salbego J, Menezes CC, Souza CF, Gioda CR, Baldisserotto B (2014b) Exposure to sublethal concentrations of copper changes biochemistry parameters in silver catfish, Rhamdia quelen, Quoy & Gaimard. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(4):399–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1215-8
Rahman MS, Molla AH, Saha N, Rahman A (2012) Study on heavy metals levels and its risk assessment in some edible fishes from Bangshi River, Savar, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Chem 134:1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.099
Roe JH (1954) In: Glick D (ed) Methods of biochemical analysis. Interscience Publishers, New York, pp 115–139
Romani R, Antognelli C, Baldracchini F, De Santis A, Isani G, Giovannini E, Rossi G (2003) Increased acetylcholinesterase activities in specimens of Sparus auratus exposed to sublethal copper concentrations. Chem Biol Interact 145:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2797(03)00058-9
Spies JR (1957) Colorimetric procedures for aminoacids. Methods Enzymol 3:467–477
Verdouw H, Vanechteld CJA, Deckkers EMJ (1978) Ammonia determinations based on indo phenol formation with sodium salicylate. Water Res 12:399–402
Viarengo A, Canesi L, Pertica M, Poli G, Moore MN, Orunesu M (1990) Heavy metal effects on lipid peroxidation in the tissues of Mytilus gallopro vincialis lam. Comp Biochem Phys C 97:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-8413(90)90168-9
Yan LJ, Traber MG, Packer L (1995) Spectrophotometric method for determination of carbonyls in oxidatively modified apolipoprotein B of human low-density lipoproteins. Anal Biochem 228:349–351
Yilmaz AB, Sangum MK, Yaghoglu D, Turan C (2010) Metals (major, essential to non-essential) composition of the different tissues of three demersal fish species from Iskenderun Bay, Turkey. Food Chem 123:410–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.057
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) – Programa PROEX Protocol Number: 23038.005848/2018-31. Student Jossiele Leitemperger received fellowship from CAPES under Protocol Number 88882.182137/2018-01 and student Tiago Fiuza received fellowship from CAPES under Protocol Number 88882.182157/2018-01. Vania Lucia Loro received research fellowship from CNPq under Process Number: 309314/2017-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leitemperger, J., Menezes, C., de Oliveira, V.A. et al. The bioaccumulation of waterborne zinc in tissues of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) and its effect on biochemical parameters. Biometals 32, 241–249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-019-00168-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-019-00168-6