Abstract
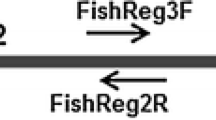
Detection and monitoring of target species is the primary strategy in the management and control of biological invasions. Traditional methods to detect invasive species are time consuming and cumbersome, with a requisite for trained taxonomists for identification of aquatic species. Environmental DNA (eDNA)-based molecular methods offer an alternative, as they are quick, cost-effective and require minimal manpower. In this study, we design and optimize a reliable eDNA-based quantitative PCR assay to detect the African Sharptooth catfish, a highly invasive and banned species in India. Here, we delineate the step-by-step processes involved in the design and optimization of the assay, and show its performance through field-testing in selected water bodies in and around the city of Hyderabad. The present workflow can be used to design assays to detect a wide range of aquatic species.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bang A, Cuthbert RN, Haubrock PJ, Fernandez RD, Moodley D, Diagne C, Turbelin AJ, Renault D, Dalu T, Courchamp F (2022) Massive economic costs of biological invasions despite widespread knowledge gaps: a dual setback for India. Biol Invasions 5:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-022-02780-z
Beng KC, Corlett RT (2020) Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers Conserv 29(7):2089–2121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-020-01980-0
Booth AJ, Traasg GR, Weyl OL (2010) Adult African sharptooth catfish, Clarias gariepinus, population dynamics in a small invaded warm-temperate impoundment. Afr Zool 45(2):299–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/15627020.2010.11657279
Dawson W, Moser D, Van Kleunen M, Kreft H, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Weigelt P, Winter M, Lenzner B, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE (2017) Global hotspots and correlates of alien species richness across taxonomic groups. Nat Ecol Evol 1(7):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-017-0186
Elberri AI, Galal-Khallaf A, Gibreel SE, El-Sakhawy SF, El-Garawani I, ElNabi SE, Mohammed-Geba K (2020) DNA and eDNA-based tracking of the North African sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus. Mol Cell Probes 51:101535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101535
Evans NT, Lamberti GA (2018) Freshwater fisheries assessment using environmental DNA: a primer on the method, its potential, and shortcomings as a conservation tool. Fish Res 197:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2017.09.013
Froese R, Pauly D (2022) FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication, version 2022-02. www.fishbase.org
Goldberg CS, Turner CR, Deiner K, Klymus KE, Thomsen PF, Murphy MA, Spear SF, McKee A, Oyler-McCance SJ, Cornman RS, Laramie MB (2016) Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol Evol 7(11):1299–1307. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12595
Gopi KC, Radhakrishnan C (2002) Impact assessment of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) infestation on indigenous fish diversity in Manalur Grama Panchayat, Thrissur District, Kerala: a case study. ENVIS Newsl Zool Surv India 9(1–2):9–12
Goyal N, Krishna S, Shah K, Rashid I, Sharma GP (2021) Integrating the biological invasion paradigm in the policy framework in India. Trop Ecol 62(1):144–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-020-00117-2
Jo T, Ikeda S, Fukuoka A, Inagawa T, Okitsu J, Katano I, Doi H, Nakai K, Ichiyanagi H, Minamoto T (2021) Utility of environmental DNA analysis for effective monitoring of invasive fish species in reservoirs. Ecosphere 12(6):e03643. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.3643
Keskin E (2014) Detection of invasive freshwater fish species using environmental DNA survey. Biochem Syst Ecol 1(56):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.05.003
Klymus KE, Merkes CM, Allison MJ, Goldberg CS, Helbing CC, Hunter ME, Jackson CA, Lance RF, Mangan AM, Monroe EM, Piaggio AJ (2020a) Reporting the limits of detection and quantification for environmental DNA assays. Environ DNA 2(3):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.29
Klymus KE, Ramos DV, Thompson NL, Richter CA (2020b) Development and testing of species-specific quantitative PCR assays for environmental DNA applications. J vis Exp 5(165):e61825. https://doi.org/10.3791/61825
Krishnakumar K, Ali A, Pereira B, Raghavan R (2011) Unregulated aquaculture and invasive alien species: a case study of the African Catfish Clarias gariepinus in Vembanad Lake (Ramsar Wetland) Kerala India. J Threat Taxa 3(5):1737–1744. https://doi.org/10.11609/JoTT.o2378.1737-44
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonák J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjöback R, Sjögreen B, Strömbom L, Ståhlberg A (2006) The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol Aspects Med 27(2–3):95–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2005.12.007
Meyerson LA, Pauchard A, Brundu G, Carlton JT, Hierro JL, Kueffer C, Pandit MK, Pyšek P, Richardson DM, Packer JG (2022) Moving toward global strategies for managing invasive alien species. In: Clements DR, Upadhyaya MK, Joshi S, Shrestha A (eds) Global plant invasions. Springer, Cham, pp 331–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89684-3_16
Mungi NA, Kaushik M, Mohanty NP, Rastogi R, Antony Johnson J, Qureshi Q (2019) Identifying knowledge gaps in the research and management of invasive species in India. Biologia 74(6):623–629. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-00186-8
Rees HC, Maddison BC, Middleditch DJ, Patmore JR, Gough KC (2014) The detection of aquatic animal species using environmental DNA—a review of eDNA as a survey tool in ecology. J Appl Ecol 51(5):1450–1459. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12306
Roshni K, Renjithkumar CR, Raghavan R, Dahanukar N, Kutty R (2020) Population dynamics and management strategies for the invasive African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) in the Western Ghats hotspot. J Threat Taxa 12(10):16380–16384. https://doi.org/10.11609/jott.6222.12.10.16380-16384
Sandilyan S (2022) Alien fish species in Indian inland wetlands: current status and future challenges. Wetlands Ecol Manage 13:1–5. Wetlands Ecol Manage 30:423–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-022-09870-8
Sandilyan S, Meenakumari B, Babu CR, Mandal R (2018) Invasive alien species of India. Centre for Biodiversity Policy and Law (CEBPOL), National Biodiversity Authority, MoEFCC, Govt. of India
Seebens H, Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Capinha C, Dawson W, Dullinger S, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, van Kleunen M, Kühn I, Jeschke JM (2021) Projecting the continental accumulation of alien species through to 2050. Global Change Biol 27(5):970–982. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15333
Singh AK, Kumar D, Srivastava SC, Ansari A, Jena JK, Sarkar UK (2013) Invasion and impacts of alien fish species in the Ganga River, India. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 16(4):408–414. https://doi.org/10.1080/14634988.2013.857974
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Hajibabaei M, Rieseberg LH (2012) Environmental DNA. Mol Ecol 21(8):1789–1793. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05542.x
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support provided by Nehru Zoological Park, Hyderabad. We thank Shivakumara Manu and Manisha Ray for their constant support and suggestions throughout the work.
Funding
The study was funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India, vide Grant No. BT/PR29032/FCB/125/4/2018 received by Govindhaswamy Umapathy. Gopi Krishnan Prabhakaran was supported by a Ph.D. fellowship from Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was carried out by complying with the institutional ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhakaran, G.K., Sunkara, M., Raghavan, R. et al. Development of a species-specific qPCR assay for the detection of invasive African sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus) using environmental DNA. Biol Invasions 25, 975–982 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-022-02969-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-022-02969-2