Abstract
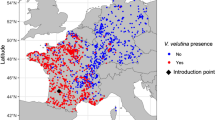
Knowledge of the native range of invasive pests is vital for understanding their biology, for ecological niche modeling to infer potential invasive distribution, and for searching of natural enemies. Standard descriptions of pest ranges frequently pass from one publication to another without verification. Our goal is to test the reliability of distributional information exemplified by the native range of one of the most destructive and most studied invasive forest insect pests of Asian origin—the emerald ash borer (EAB), Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire. Since the first detections of this notorious insect pest in North America in 2002 and European Russia in 2003, it has killed hundreds of millions of ash trees. Based on the examination of museum specimens and literature sources we compiled the most comprehensive database of records (108 localities) and the most detailed map of the native range of EAB in East Asia to date. There are documented records for 87 mainland localities of EAB in the Russian Far East (Primorskiy, Khabarovskiy Kray), China (Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Beijing, Hebei, Tianjin, Shandong and Xinjiang), and South Korea, and 21 localities in Japan. Records from Nei Mongol, Sichuan, Mongolia, and Taiwan are ambiguous since no documented records are available. The example of EAB shows that standard descriptions of pest ranges could include false or ambiguous data. Compilation of the database of documented localities is the only way to obtain reliable information on the range.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama Y, Akiyama K (1996) The Buprestid beetles (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) from Hiroshima Prefecture, southwestern Japan. Misc Rep Hiwa Mus Nat Hist 34:181–192 (in Japanese)
Akiyama K, Ohmomo S (1997) A checklist of the Japanese Buprestidae. Gekkan-Mushi (Supplement 1), Tokyo. pp. 67
Alexeev AV (1979) New, previously unknown from the territory of the USSR, and little-known species of jewel-beetles (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) of Eastern Siberia and the Far East. In: Krivolutskaya GO (ed) Beetles of the Far East and Eastern Siberia (new data on the fauna and taxonomy). Far East Scientific Center of Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Vladivostok, pp 123–139 (in Russian)
Belokobylskij SA, Yurchenko GI, Strazanac JS, Zaldivar-Riveron A, Mastro V (2012) A new emerald ash borer (Coleoptera, Buprestidae) parasitoid species of Spathius Nees (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Doryctinae) from the Russian Far East and South Korea. Ann Entomol Soc Am 105:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1603/AN11140
Bray AM, Bauer LS, Fuester RW, Choo HY, Lee DW, Kamata N, Smith JJ (2007) Expanded explorations for emerald ash borer in Asia and implications for genetic analysis. Emerald Ash Borer and Asian Longhorhed Beetle research and technology development meeting. Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team, West Virginia, pp 6–7
Bray M, Bauer LS, Poland TM, Haack RA, Cognato AI, Smith JJ (2011) Genetic analysis of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) populations in Asia and North America. Biol Invasions 13:2869–2887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-011-9970-5
Chamorro ML, Jendek E, Haack RA, Petrice TR, Woodley NE, Konstantinov AS, Volkovitsh MG, Yang X-K, Grebennikov VV, Lingafelter SW (2015) Illustrated guide to the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire and related species (Coleoptera, Buprestidae). Pensoft, Sofia-Moscow
Cipollini D (2015) White fringetree as a novel larval host for emerald ash borer. J Econ Entomol 108(1):370–375. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tou026
Cleary M, Nguyen D, Marčiulynienė D, Berlin A, Vasaitis R, Stenlid J (2016) Friend or foe? Biological and ecological traits of the European ash dieback pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in its native environment. Sci Rep 6:21895. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21895
Coleoptera collection of Siberian Zoological Museum (2017) http://szmn.eco.nsc.ru/Coleop/Coleopt.htm. Accessed 10 Apr 2017
Duan JJ, Yurchenko G, Fuester R (2012) Occurrence of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and biotic factors affecting its immature stages in the Russian Far East. Environ Entomol 41(2):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1603/EN11318
Emeljanov AF (1974) Proposals on the classification and nomenclature of areals. Entomologicheskoe Obozrenie 53(3):497–522 (in Russian)
Emereld Ash Borer Info (2017) http://www.emeraldashborer.info. Accessed 10 Apr 2017
EPPO (2017) EPPO plant quarantine data retrieval system. Version 5.3.5. http://www.eppo.int/DATABASES/pqr/pqr.htm. Accessed 10 Apr 2017
Fairmaire L (1888) Notes sur les Coléoptères des environs de Pékin (2e Partie). Rev Entomol (Caen) 7:111–160
Flora USSR (1952) Fam. CXXIX. Oleaceae. In: BK Shishkin, EG Bobrov (eds) Flora of the USSR. Vol. 18. (Primulales: Primulaceae—Ebenales: Asclepiadaceae). Academy of Science of the USSR, Moscow—Leningrad, pp. 483–525 (in Russian)
Flora of China (2017) http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=210000562. Accessed 06 Apr 2017
Flora of Taiwan (1998) Second edition. Volume Four. Angiosperms—Dicoledons [Diapensiaceae—Compositae]. Taipei Taiwan: Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan
Fuester RW, Schaefer PW (2006) Research on parasitoids of buprestids in progress at the ARS beneficial insect introduction research unit. In V Mastro, D Lance, R Reardon, G Parra (eds) Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer and Asian Longhorned Beetle Research and Technology Development Meeting, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team, West Virginia, pp. 53–55
GBIF(2017) GBIF.org (29th March 2017) GBIF Occurrence Download https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.w40ocd, GBIF.org (29th March 2017) GBIF Occurrence Download https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.ydkkwi, GBIF.org (29th March 2017) GBIF Occurrence Download https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.gec4bv GBIF.org (31st March 2017) GBIF Occurrence Download https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.fxnxbx
Google maps (2017) https://www.google.ru/maps. Accessed 06 Apr 2017
Grubov VI (1955) Conspectus of the flora of Mongolian People Republic. Proceedings of Mongolian Comission, 67, Academy of Science of the USSR. Leningrad (in Russian)
Grubov VI (1982) Key to the vascular plants of Mongolia. Nauka, Leningrad (in Russian)
Haack RA, Jendek E, Liu H, Marchant KR, Petrice TR, Poland TM, Ye H (2002) The Emerald Ash Borer: a new exotic pest in North America. Newsl Mich Entomol Soc 47(3 & 4):1–5
Haack RA, Baranchikov Y, Bauer LS, Poland TM (2015) Chapter 1: Emerald ash borer biology and invasion history. In: Van Driesche RG, Reardon RC (eds) Biology and control of emerald ash borer. United States Department of Agriculture, Morgantown, pp 1–15
Herms DA, McCullough DG (2014) Emerald ash borer invasion of North America: history, biology, ecology, impacts, and management. Annu Rev Entomol 59:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-011613-162051
Holle BV, Simberloff D (2005) Ecological resistance to biological invasion overwhelmed by propagule pressure. Ecology 86(12):3212–3218
Hou T-Q (1986) Buprestidae. In: Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, editor. Agricultural Insects of China (Part A). Agriculture Press, China, pp. 438–447 (in Chinese)
Izhevskii SS (2007) Threatening findings of the emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis in the Moscow region. http://www.zin.ru/Animalia/Coleoptera/rus/agrplaiz.htm. Accessed 10 Apr 2017 (in Russian)
Jendek E (1994) Studies in the east palaearctic species of the genus Agrilus Dahl, 1823 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) Part I. Entomol Probl 25(1):9–24
Jendek E (2006) Genus Agrilus. In: Lobl I, Smetana A (eds) Catalogue of palaearctic coleoptera, vol 3. Apollo Books, Stenstrup, pp 388–403
Jendek E, Chamorro ML (2012) Six new species of Agrilus Curtis, 1825 (Coleoptera, Buprestidae, Agrilinae) from the Oriental Region related to the emerald ash borer, A. planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 and synonymy of Sarawakita Obenberger, 1924. ZooKeys 239:71–94. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.239.3966
Jendek E, Grebennikov V (2011) Agrilus (Coleoptera, Buprestidae) of East Asia. Jan Farkac, Prague
Jendek E, Polákova J (2014) Host plants of world Agrilus (Coleoptera, Buprestidae). A critical review. Springer, Dordrecht
Keever CC, Nieman C, Ramsay L, Ritland CE, Bauer LS, Lyons DB, Cory JS (2013) Microsatellite population genetics of the emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire): comparisons between Asian and North American populations. Biol Invasions 15(7):1537–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0389-4
Ko Je Ho (1969) A list of forest insect pests in Korea. Forest Research Institute, Seoul
Konstantinov AS, Korotyaev BA, Volkovitsh MG (2009) Chapter 7. Insect biodiversity in the palearctic region. In: Foottit RG, Adler PH (eds) Insect biodiversity: science and society. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 107–162
Kurosawa Y (1956) Buprestid-fauna of Eastern Asia (3). Bull Natl Sci Mus, Tokyo, N.S. 3(38):33–41
Li Zhong H (2002) List of Chinese insects. Vol. II. Zhongshan (Sun Yat—sen) University Press, Guangzhou
Liu HP, Bauer LS, Gao R, Zhao T, Petrice TR, Haack RA (2003) Exploratory survey for emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and its natural enemies in China. The Great Lakes Entomol 36:191–204
Liu HP, Bauer LS, Miller DL, Zhao TH, Gao RT, Song L, Luan Q, Jin R, Gao C (2007) Seasonal abundance of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and its natural enemies Oobius agrili (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) and Tetrastichus planipennisi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in China. Biol Control 42:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2007.03.011
Nonnaizab NA, Qi B, Li Y (1999) Insects of inner mongolia china. People’s Publishing House in Inner Mongolia, Hu He Hao Te (in Chinese)
Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ (2013) Dramatic expansion of the range of the invasive ash pest, buprestid beetle Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera, Buprestidae) in European Russia. Entomol Rev 93(9):1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873813090042
Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ (2014) Ashes in Europe are in danger: the invasive range of Agrilus planipennis in European Russia is expanding. Biol Invasions 16(7):1345–1349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-013-0579-8
Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ, Volkovitsh MG (2014) Range expansion of Agrilus convexicollis in European Russia expedited by the invasion of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Biol Invasions 17:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-014-0762-6
Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ, Ukrainsky AS, Brown PMJ (2015) Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Asia: a re-examination of the native range and invasion to southeastern Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. Biol Invasions 17(7):1941–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0848-9
Schaefer PW (2004) Agrilus planipennis (A. marcopoli) (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in Japan and Mongolia—preliminary findings. In: Mastro V, Reardon R (eds) Emerald ash borer research and technology development meeting, 30. FHTET, Morgantown, p 13
Schütze H, Kleinfeld F (2007) Neuauflage. Die Caraben Chinas. Systematic—alle Taxa—Bibliographie—Lexicon aller literaturbekannten Fundorte. 3. völlig überarbeite Auflage. Delta-Druck + Verlag, Peks, Schwanfeld
Siegert NW, McCullough DG, Liebhold AM, Telewski FW (2014) Dendrochronological reconstruction of the epicentre and early spread of emerald ash borer in North America. Divers and Distrib 20:847–858. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12212
Sobek-Swant S, Kluza DA, Cuddington K, Lyons DB (2012) Potential distribution of emerald ash borer: what can we learn from ecological niche models using Maxent and GARP? For Ecol Manag 281:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.06.017
Straw NA, Williams DT, Kulinich O, Gninenko YI (2013) Distribution, impact and rate of spread of emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in the Moscow region of Russia. Forestry 86:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/forestry/cpt031
Urgamal M, Oyuntsetseg B, Nyambayar D, Dulamsuren Ch (2014) Conspectus of the vascular plants of Mongolia. Sanchir Ch. Jamsran Ts (eds) “Admon“Press, Ulaanbaatar
Volkovitsh MG (2007) Emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis—new extremely dangerous pest of ash in the European part of Russia. http://www.zin.ru/Animalia/Coleoptera/rus/ eab_2007.htm. Accessed 10 Apr 2017 (in Russian)
Volkovitsh MG (2009) Buprestidae. In: Storozhenko SY (ed) Insects of lazovsky nature reserve. Dalnauka, Vladivostok, pp 132–137 (in Russian)
Wang XY, Yang ZQ, Gould JR, Zhang YN, Liu GJ, Liu ES (2010) The biology and ecology of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis. China J Insect Sci 10(128):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.010.12801
Wang XY, Cao LM, Yang ZQ, Duan JJ, Gould JR, Bauer LS (2016) Natural enemies of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in northeast China, with notes on two species of parasitic Coleoptera. Can Entomol 148(3):329–342. https://doi.org/10.4039/tce.2015.57
Wei X, Reardon D, Yun W, Sun JH (2004) Emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in China: a review and distribution survey. Acta Entomol Sinica 47:679–685
Wei X, Wu Y, Reardon R, Sun T-H, Lu M, Sun JH (2007) Biology and damage traits of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) in China. Insect Sci 14:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2007.00163.x
Williams D, Lee H-P, Jo Y-S (2006) Exploration for emerald ash borer and its natural enemies in South Korea during May–June 2005. In: V Mastro, D Lance, R Reardon, G Parra (eds) Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer and Asian Longhorned Beetle Research and Technology Development Meeting, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team, West Virginia, p 52
Williams D, Lee HP, Jo YS, Yurchenko GI, Mastro VC (2010) Exploration for emerald ash borer and its natural enemies in South Korea and the Russian Far East 2004–2009. In: D Lance, J Buck, D Binion, R Reardon, V Mastro (eds) Proceedings of the Emerald Ash Borer and Asian Longhorned Beetle Research and Technology Development Meeting, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team, West Virginia, pp. 94–95
Yan CJ, He JH, Chen XX (2013) The genus Brulleia Szépligeti (Hymenoptera, Braconidae, Helconinae) from China, with descriptions of four new species. ZooKeys 257:17–31. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.257.3832
Yu C (1992) Agrilus marcopoli obenberger. In: Xiao G (ed) Forest Insects of China, 2nd edn. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 400–401 (in Chinese)
Yurchenko GI (2009) About ash-trees and emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) in Khabarovsk and its vicinity. In: Far Eastern forests condition and actual problems of forest management. Materials of all-Russian conference with international participation, FEFRI, Khabarovsk, pp. 289–292 (in Russian)
Yurchenko GI (2010) Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire on natural and introduced ashes in southern part of Far East. News of the Saint Petersb State For Tech Acad 192:269–276 (in Russian)
Yurchenko GI (2016) Emerald ash borer in Russian Far East. In: Gninenko Yu (ed) Emerald ash borer—occurrence and protection operatiobns in the USA and Russia. Pushkino, VNIILM, pp 5–10 (in Russian)
Yurchenko GI, Turova GI, Kuzmin EA (2007) To distribution and ecology of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) in the Russian Far East. In: AI Kurentsov’s Annual Memorial Meetings, 18, pp. 94–98 (in Russian)
Yurchenko GI, Williams DW, Kuzmin EA (2013a) Monitoring of populations of Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) and its parasitoids in the south part of Russian Far East. In: Far Eastern forests condition and actual problems of forest management. «Dal’NIILKh» , Khabarovsk, pp 440–444 (in Russian)
Yurchenko GI, Kuzmin EA, Burde PB (2013b) Biology of the Emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) and its parasitoids in the south part of Prinorskii krai. AI Kurentsov’s Annual Memorial Meetings, 24, Dal’nauka, Vladivostok. pp. 174–178 (in Russian)
Zhang YZ, Huang DW, Zhao TH, Liu HP, Bauer LS (2005) Two new species of egg parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) of wood-boring beetle pests from China. Phytoparasitica 53:253–260
Zhao TH, Gao RT, Liu HP, Bauer LS, Sun LQ (2005) Host range of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, its damage and the countermeasures. Acta Entomol Sinica 48(4):594–599 (in Chinese with English summary)
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Russian Science Foundation, Project No 16-14-10031. We would like to thank E. Jendek (Bratislava, Slovakia) for the valuable information and comments on EAB distribution and providing us with missing literature; we are also grateful to V. Kubàň (Šlapanice near Brno, Czech Republic), G. I. Yurchenko (The Far East Forest Research Institute, Forest Management Agency of the Russian Federation, Khabarovsk, Russia), Zhaozhi Lu (Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences), and M. Yu. Proschalykin (FSCB) for valuable information used in this paper; to M. Yu. Kalashian (Institute of Zoology, Scientific Center of Zoology and Hydroecology, National Academy of Sciences of Armenia, Yerevan, Armenia), and S. N. Ivanov (private collector, Vladivostok, Russia) for providing the exact locations for EAB specimens in their collections for this study; to A. A. Gusakov (ZMUM), K. V. Makarov (MSPU), and S. A. Shabalin (FSCB) for checking the presence of EAB specimens in corresponding collections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J., Volkovitsh, M.G. Are native ranges of the most destructive invasive pests well known? A case study of the native range of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Biol Invasions 20, 1275–1286 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1626-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1626-7