Abstract
Objectives
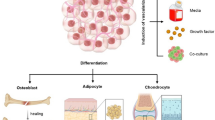
The secretome of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), also called MSC-conditioned media (MSC-CM), represents one of the promising strategies for cellular therapy and tissue repair and regeneration. MSC-CM contains growth factors and cytokines that control many cellular responses during development and regeneration. Traditional 2D cell culture (2DCC) has previously been used to generate MSC-CM while evidence has proved that the physiological and biological behaviors of cells in 2DCC are significantly different from those in 3D cell culture (3DCC). Therefore, the objective is to compare the content of MSC-CM generated from traditional 2DCC and 3DCC using a 3D scaffold.
Methods
Adipose tissue-derived MSCs (AT-MSCs) were isolated from four donors (N = 4) and characterized according to the criteria stipulated by the International Society for Cell Therapy (ISCT). MSCs at passage 3 were grown in traditional 2DCC until 70% confluence and MSC-CM were collected at 24, 48, and 94 h. On the other hand, MSCs at passage 3 were grown on a polystyrene scaffold for 10 days to generate a 3D model of MSCs, and then MSC-CM was collected at 24, 48, and 94 h. MSC-CM from both 2DCC and 3DCC were analyzed for protein content using ELISA. Haematoxylin eosin (HE) staining and immunofluorescence (IF) were used to characterize the 3DCC of MSCs.
Results
MSCs from 2DCC were fibroblast like cells, and flow cytometry showed they were positive for CD73 and CD105 while being negative for CD14, CD19, and HLA-DR. They were also able to differentiate into adipocytes, osteoblasts, and chondrocytes. HE and IF showed that MSCs formed 3D model structures on the polystyrene scaffold. MSC-CM collected from both 2DCC and 3DCC contained growth factors, e.g., platelet derived growth factor (PDGF-AB), transforming growth factor-1 (TGF-1), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1), interleukin 1 (IL-1), and interleukin 6 (IL-6). Concentrations of biomolecules secreted by MSCs in 3DCC were significantly higher than in 2DCC.
Conclusion
It could be concluded that 3DCC of MSCs using a polystyrene scaffold is a novel approach to generate MSC secretome for therapeutic applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama K, You Y-O, Yamaza T et al (2012) Characterization of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in suspension. Stem Cell Res Ther 3(5):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt131
Al-Shaibani MBH, Dickinson A, Nong-Wang X et al (2016) Effect of conditioned media from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC-CM) on wound healing using a prototype of a fully humanised 3D skin model. Cytotherapy 19(5):e23–e24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.03.062
Al-Shaibani MBH (2020) Manufacturing of a Novel scaffold to culture human and animal cells in 3 dimensional microenvironment. paper presented at the international Eurasian conference on biotechnology and biochemistry (BioTechBioChem), Ankara, Turkey. https://www.biotechbiochem.org
Baharvand H, Hashemi SM, Kazemi Ashtiani S, Farrokhi A (2006) Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into hepatocytes in 2D and 3D culture systems in vitro. Int J Dev Biol 50(7):645–652. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.052072hb
Bartosh TJ, Ylostalo JH, Mohammadipoor A et al (2010) Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(31):13724–13729. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008117107
Bernacki SH, Wall ME, Loboa EG (2008) Isolation of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone and adipose tissue. Methods Cell Biol 86:257–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-679X(08)00011-3
Bhadriraju K, Chen CS (2002) Engineering cellular microenvironments to improve cell-based drug testing. Drug Discov Today 7(11):612–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6446(02)02273-0
Birgersdotter A, Sandberg R, Ernberg I (2005) Gene expression perturbation in vitro: a growing case for three-dimensional (3D) culture systems. Semin Cancer Biol 15(5):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.06.009
Bresciani G, Hofland LJ, Dogan F et al (2019) Evaluation of spheroid 3D culture methods to study a pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm cell line. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00682
Campuzano S, Pelling AE (2019) Scaffolds for 3D cell culture and cellular agriculture applications derived from non-animal sources. Front Sustain Food Syst. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2019.00038
Desrochers TM, Palma E, Kaplan DL (2014) Tissue-engineered kidney disease models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 69–70:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.12.002
Dominic M, Le-Blanc K, Mueller I et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Int Soc Cell Therapy Position Statement Cytotherapy 8(4):315–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240600855905
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF, Yang L (2014) Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(4):207–218. https://doi.org/10.1089/adt.2014.573
Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, Frolova GP (1968) Heterotopic of bone marrow. Anal Precursor Cells Osteogenic Hematopoietic Tissues Transpl 6(2):230–247
Friedrich J, Seidel C, Ebner R, Kunz-Schughart LA (2009) Spheroid-based drug screen: considerations and practical approach. Nat Protoc 4(3):309–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.226
Hass R, Kasper C, Bohm S, Jacobs R (2011) Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal 9:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-9-12
Hickey RJ, Modulevsky DJ, Cuerrier CM, Pelling AE (2018) Customizing the shape and microenvironment biochemistry of biocompatible macroscopic plant-derived cellulose scaffolds. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00178
Hwang JH, Shim SS, Seok OS et al (2009) Comparison of cytokine expression in mesenchymal stem cells from human placenta, cord blood, and bone marrow. J Korean Med Sci 24(4):547–554. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.547
Kapałczyńska M, Kolenda T, Przybyła W et al (2018) 2D and 3D cell cultures: a comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch Med Sci 14(4):910–919. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2016.63743
Kouroupis D, Correa D (2021) Increased mesenchymal stem cell functionalization in three-dimensional manufacturing settings for enhanced therapeutic applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.621748
Lv D, Hu Z, Lu L et al (2017) Three-dimensional cell culture: A powerful tool in tumor research and drug discovery (Review). Oncol Lett 14(6):6999–7010. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7134
Marushima H, Shibata S, Asakura T et al (2011) Three-dimensional culture promotes reconstitution of the tumor-specific hypoxic microenvironment under TGFβ stimulation. Int J Oncol 39(5):1327–1336. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2011.1142
Miranda JP, Camões SP, Gaspar MM et al (2019) The secretome derived from 3D-cultured umbilical cord tissue MSCs counteracts manifestations typifying rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00018
Mirbagheri M, Adibnia V, Hughes BR et al (2019) Advanced cell culture platforms: a growing quest for emulating natural tissues. Mater Horiz 6(1):45–71. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00803E
Qiu X, Liu S, Zhang H et al (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular matrix scaffold promote muscle regeneration by synergistically regulating macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype. Stem Cell Res Ther 9(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0821-5
Redondo-Castro E, Cunningham CJ, Miller J et al (2018) Generation of human mesenchymal stem cell 3D spheroids using low-binding plates. Bio-Protoc 8(16):2968. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2968
Sandell L, SakaiD (2008) Mammalian cell culture. In: Current protocols essential laboratory techniques. Wiley
Shi Y, Wang Y, Li Q et al (2018) Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 14(8):493–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-018-0023-5
Tietze S, Kräter M, Jacobi A, Taubenberger A et al (2019) Spheroid culture of mesenchymal stromal cells results in morphorheological properties appropriate for improved microcirculation. Adv Sci 6(8):1802104. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201802104
Trzyna A, Banaś-Ząbczyk A (2021) Adipose-derived stem cells secretome and its potential application in “stem cell-free therapy.” Biomolecules 11(6):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060878
Weiss ARR, Dahlke MH (2019) Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): mechanisms of action of living, apoptotic, and dead MSCs. Front Immunol 10:1191. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01191
Ylöstalo JH, Bartosh TJ, Coble K, Prockop DJ (2012) Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells cultured as spheroids are self-activated to produce prostaglandin E2 that directs stimulated macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Stem Cells 30(10):2283–2296. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shaibani, M.B.H. Three-dimensional cell culture (3DCC) improves secretion of signaling molecules of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Biotechnol Lett 44, 143–155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03216-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03216-9