Abstract
Objectives
Microbial biofilms have become one of the most significant causes of nosocomial infections. The aim of this study was to examine the potential quorum sensing inhibitor activities of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules.
Results
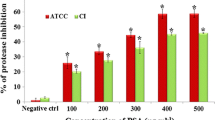
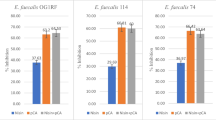
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules effectively inhibited initial biofilm formation at a concentration of 2.5 × 108 CFU/mL. Furthermore, the inhibition rate was increased to 79% in the Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules group, resulting in a reduction in the biofilm maturation stage. In addition, real-time PCR analysis revealed that the LGG microcapsules can act as effective inhibitors of transcriptional activators of the quorum sensing circuit in E.coli, luxS, lsrK, and lsrR.
Conclusions
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules can effectively inhibit biofilm formation and disturb mature biofilms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algarni AA, Yassen GH, Gregory RL (2015) Inhibitory effects of gels loaded with a low concentration of antibiotics against biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis and Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Oral Sci 57:213–218
Capurso L (2019) Thirty years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: a review. J Clin Gastroenterol Suppl 1:S1–S41
Cook MT, Tzortzis G, Charalampopoulos D et al (2012) Microencapsulation of probiotics for gastrointestinal delivery. J Control Release 162:56–67
Dekeersmaecker SC, Vanderleyden J (2003) Constraints on detection of autoinducer-2 (AI-2) signaling molecules using Vibrio harveyi as a reporter. J Microbiol 149:1953–1956
Ding WY, Sun J, Lian H et al (2018) The influence of shuttle-shape emodin nanoparticles on the Streptococcus suis biofilm. Front Pharmacol 9:227
Gao M, Song HY, Zheng HZ et al (2016a) Culture of low density E. coli cells in alginate-chitosan microcapsules facilitates stress resistance by up-regulating luxS/AI-2 system. Carbohydr Polym 141:160–165
Gao M, Song HY, Liu XD et al (2016b) Improved quorum sensing capacity by culturing Vibrio harveyi in microcapsules. J Biosci Bioeng 121:406–412
Guerin J, Burgain J, Borges F et al (2017) Use of imaging techniques to identify efficient controlled release systems of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG during in vitro digestion. Food Funct 8:1587–1598
Khan MS, Zahin M, Hasan S et al (2009) Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:354–360
Kotzé M, Eloff JN (2002) Extraction of antibacterial compound from Combretum microphyllum (Combretaceae). S Afr J Bot 68:62–67
Li HD, Li XY, Wang ZL et al (2015) Autoinducer-2 regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm formation and virulence production in a dose-dependent manner. BMC Microbiol 15:192
Marques CNH, Davies DG, Sauer K (2015) Control of biofilms with the fatty acid signaling molecule cis-2-decenoic acid. Pharmaceuticals 8:816–835
Matsuda Y, Cho O, Sugita T et al (2018) Culture supernatants of Lactobacillus gasseri and L. crispatus inhibit Candida albicans biofilm formation and adhesion to HeLa cells. Mycopathologia 183:691–700
Mehta DK, Das R (2018) Microbial biofilm and quorum sensing inhibition: endowment of medicinal plants to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Curr Drug Targets 19:1916–1932
Novais JS, Moreira CS, Silva ACJA et al (2018) Antibacterial naphthoquinone derivatives targeting resistant strain Gram-negative bacteria in biofilms. Microb Pathog 118:105–114
Petrova MI, Imholz NC, Verhoeven TL et al (2016) Lectin-like molecules of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG inhibit pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 11:e0161337
Radzig MA, Nadtochenko VA, Koksharova OA et al (2013) Antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles on gram-negative bacteria: influence on the growth and biofilms formation, mechanisms of action. Colloids Surf B 102:300–306
Song HY, Yu WT, Liu XD et al (2014) Improved probiotic viability in stress environments with post-culture of alginate-chitosan microencapsulated low density cells. Carbohydr Polym 108:10–16
Spacova I, Lievens E, Verhoeven T et al (2018) Expression of fluorescent proteins in Lactobacillus rhamnosus to study host-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions. Microb Biotechnol 11:317–331
Vieco-Saiz N, Belguesmia Y, Raspoet R et al (2019) Benefits and inputs from lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters during food-animal production. Front Microbiol 11:57
Wang L, Li J, March JC et al (2005) luxS-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli K-12 revealed by genomic expression profiling. J Bacteriol 187:8350–8360
Xue WM, Yu WT, Liu XD et al (2004) Chemical method of breaking the cell-loaded sodium alginate/chitosan microcapsule. Chem J Chin Univ 25:1342–1346
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81601734), Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20180530062) and a Basic Research Projects Grant of the Key Laboratory of the Education Department of Liaoning Province (Grant No. LZ2015028).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1―PCR primer sequences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Zhang, J., Qu, J. et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules inhibit Escherichia coli biofilm formation in coculture. Biotechnol Lett 41, 1007–1014 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02694-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02694-2