Abstract
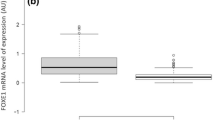
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), the most prevalent cancer of the thyroid, is more common in women than in men. To uncover the expression profile of FOXE1 gene in PTC tumor etiology. Microarray and RNA sequencing data on PTC in humans were analyzed. Eleven PTC tumor tissue samples and their neighboring normal tissue samples were collected. RT-qPCR was performed. Data normality, ROC construction, and logistic regression analysis were conducted. PTC tumors, normal tissues surrounding tumors, patients of different sexes and ages, metastasizing tumors, and tumor variants were assessed for FOXE1 expression. Eleven PTC tissues were obtained from seven women and four men. Among the PTC subtypes, there were two FV-PTCs, four C-PTCs, one microcarcinoma, and four tissues with an unknown subtype. FOXE1 gene expression was significantly increased in PTC tumors with dimensions less than 10 mm (relative expression = 14.437, p = 0.050). A significant increase in FOXE1 gene expression was observed in the normal tissue adjacent to the tumor, which was less than 10 mm in size, compared to the normal tissue adjacent to the tumor, which was larger than 10 mm (relative expression = 41.760, p = 0.0001). Females diagnosed with PTC showed a significant reduction in FOXE1 mRNA levels compared to their male counterparts (relative expression = 0.081, p = 0.042). In contrast to adjacent normal tissue, there was a significant reduction in FOXE1 gene expression in FV-PTC (relative expression = 0.044 and p = 0.0001). PTC tumors under 10mm had higher FOXE1 gene expression than larger tumors; normal tissue adjacent to smaller tumors also had higher FOXE1 expression. Females with PTC, regardless of their subtype, expressed less FOXE1 mRNA than males. FV-PTC tissues exhibited lower expression of FOXE1 mRNA than their adjacent normal tissues.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The entirety of the information provided in the manuscript can be accessed via the following URLs: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ and https://ualcan.path.uab.edu/analysis.html.
Abbreviations
- TNM:
-
Tumor-node-metastasis cancer staging system, includes T for tumor, N for lymph node spread, and M for metastasis. The number following N indicates the extent of lymphatic metastasis. For example, PTC-N0 represents tumor tissues without metastasis, while PTC-N1 represents those with metastasis
- PTC:
-
Papillary thyroid cancer, is prevalent and can develop at any age. It grows slowly, spreads to neck lymph nodes, and generally has a positive prognosis
- C-PTC:
-
Conventional or classical PTC, has papillary architecture with fibrovascular cores and psammoma bodies, and tumor cells with enlarged, overlapping nuclei, nuclear grooves, and irregularities in the nuclear membrane. It is the most common variants of PTC, accounting for 55% to 66% of cases
- FV-PTC:
-
Follicular variant-PTC, is a histological variant of PTC with follicular architecture. These tumors grossly resemble follicular carcinoma, with mean tumor size falling between C-PTC and follicular thyroid carcinoma. It is the second most common PTC subtype, accounts for 9% to 22.5% of cases
- Microcarcinoma:
-
A thyroid papillary microcarcinoma is a variant of PTC that is less than 10 millimeters in diameter
- ATC:
-
Anaplastic thyroid cancer, the most advanced and aggressive form, is uncommon, occurring in less than 2% of thyroid cancer patients, and primarily affecting individuals over 60 years old
- Microarray:
-
Is a technique used in the laboratory to assess the level of gene expression on a large scale
- RNAseq:
-
RNA sequencing, uses next-generation sequencing to assess the amount and presence of RNA in a sample, providing a snapshot of the RNA pool within the cells
- RT-qPCR:
-
Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction, is a technique used to detect and quantify RNA by transcribing mRNA into complementary DNA or cDNA
- TCGA:
-
The cancer genome atlas, is a notable cancer genomics database which has over 20,000 primary cancer and matched normal samples from 33 different types of cancer
- LogFC:
-
Log2 fold change, is employed to interpret mRNA expression levels. A logFC of 1 indicates twice the expression
- Adj. p val:
-
Adjusted p value, is the minimum significance level at which a specific comparison will be deemed statistically significant during multiple comparison testing
References
Agrawal N, Akbani R, Aksoy BA et al (2014) Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 159:676–690
American Cancer Society (2022) Cancer facts and figures. American Cancer Society, Atlanta
Armstrong MJ, Yang H, Yip L et al (2014) PAX8/PPARγ rearrangement in thyroid nodules predicts follicular-pattern carcinomas, in particular the encapsulated follicular variant of papillary carcinoma. Thyroid 24:1369–1374. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2014.0067
Dai W, Meng X, Mo S et al (2020) FOXE1 represses cell proliferation and Warburg effect by inhibiting HK2 in colorectal cancer. Cell Commun Signal 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0502-8
Ding Z, Ke R, Zhang Y et al (2019) FOXE1 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer by regulating PDGFA. Mol Cell Endocrinol 493:110420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2019.03.010
Edge SB, Compton CC (2010) The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 17:1471–1474. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I et al (2021) Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J Cancer 149:778–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33588
Fernández LP, López-Márquez A, Santisteban P (2015) Thyroid transcription factors in development, differentiation and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.186
Fisher KE, Jani JC, Fisher SB et al (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression is a marker for adverse pathologic features in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Surg Res 185:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.05.003
Han MA, Kim JH (2018) Diagnostic X-ray exposure and thyroid cancer risk: systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid 28:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0159
Hébrant A, Dom G, Dewaele M et al (2012) mRNA expression in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: molecular anatomy of a killing switch. PLoS ONE 7:e37807–e37807. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037807
Jögi A, Vaapil M, Johansson M, Påhlman S (2012) Cancer cell differentiation heterogeneity and aggressive behavior in solid tumors. Ups J Med Sci 117:217–224. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2012.659294
Liu H, Chen X, Lin T et al (2019) MicroRNA-524-5p suppresses the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via targeting on FOXE1 and ITGA3 in cell autophagy and cycling pathways. J Cell Physiol 234:18382–18391. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28472
Ma J, Huang X, Li Z et al (2019) FOXE1 supports the tumor promotion of Gli2 on papillary thyroid carcinoma by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol 234:17739–17748. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28399
Macchia PE (2007) FOXEI polymorphisms: a new piece in the puzzle of thyroid dysgenesis. J Endocrinol Invest 30:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347387
Majdalani P, Yoel U, Nasasra T et al (2023) Novel susceptibility genes drive familial non-medullary thyroid cancer in a large consanguineous kindred. Int J Mol Sci 24:8233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24098233
Manzella L, Stella S, Pennisi MS et al (2017) New insights in thyroid cancer and p53 family proteins. Int J Mol Sci 18:1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061325
Mishra P, Pandey CM, Singh U et al (2019) Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann Card Anaesth 22:67–72. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_157_18
Nikiforov YE, Nikiforova MN (2011) Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:569–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.142
Odate T, Oishi N, Kawai M et al (2021) Progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma to anaplastic carcinoma in metastatic lymph nodes: solid/insular growth and hobnail cell change in lymph nodes are predictors of subsequent anaplastic transformation. Endocr Pathol 32:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-021-09674-1
Perrone L, Pasca di Magliano M, Zannini M, Di Lauro R (2000) The thyroid transcription factor 2 (TTF-2) is a promoter-specific DNA-binding independent transcriptional repressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.3232
Ranjbari N, Almasi S, Mohammadi-Asl J, Rahim F (2013) BRAF mutations in iranian patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:2521–2523. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.4.2521
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Safavi A, Azizi F, Jafari R et al (2016) Thyroid cancer epidemiology in Iran: a time trend study. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 17:407–412. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.1.407
Shah JP (2015) Thyroid carcinoma: epidemiology, histology, and diagnosis. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol H&o 13:3
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Taghavi Kojidi H, Farzadfar F, Peykari N et al (2016) A comprehensive study on national and sub national trend in thyroid cancer prevalence in the Iranian Population, 1990–2010. Iran J Diabetes Metab 15:91–100
Tomorrow C (2020) Prediction of thyroid cancer epidemiology in 2040
Yu WS, Zhou ZP, Zeng JF et al (2023) Expression and clinical significance of Golgi phosphoprotein 3 (GOLPH3) in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 31:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000001117
Acknowledgements
Volunteers are thanked for their time and effort by the author. Funding for this study was provided by the Departments of Research, Technology, and Graduate Offices of the University of Isfahan, Iran. A sincere thank you is extended to Dr. Mohsen Kolahdouzan, thoracic surgeon, for his kindness, patience and responsibility in the acquisition of thyroid tissues. It is also appropriate to express gratitude to Dr. Keivan Shirneshan for approving the pathological results.
Funding
This study was conducted at Isfahan University of Iran and was supported financially by the Departments of Research, Technology and Graduate Offices (Grant Number: A\98\5727).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RH: Design, data analysis, interpretation, manuscript drafting, and final approval of the manuscript. S-MJ: Conceptualization, design, data analysis, interpretation, financial support, manuscript drafting, critical revision for critical intellectual contents, and final approval of the manuscript. MK, S-MJ: Conceptualization, design, interpretation, manuscript drafting, and final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All patients recommended for thyroid surgery at Al-Zahra and Sina hospitals in Isfahan had to sign a consent form. Isfahan University’s institutional review board (IR.UI.REC.1398.060) approved the acquisition of human tissues. All the experiments and procedures performed in this study specially but not limited to human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Authors sincerely thank the volunteers for their participation.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hajian, R., Javadirad, SM. & kolahdouzan, M. FOXE1 Gene is a Probable Tumor Suppressor Gene with Decreased Expression as Papillary Thyroid Cancers Grow, and is Absent in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancers. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10642-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10642-z