Abstract
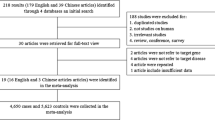
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by autoantibody production and organ involvement. The role of toll-like receptor-7 in SLE is well established. Although genetic variations in the TLR-7 gene have been associated with an increased risk of developing SLE, the findings are not consistent. We performed a meta-analysis of previously published articles on four important single nucleotide polymorphisms in the TLR-7 gene (rs3853839, rs179008, rs179019, and rs179010) to reach a valid conclusion. Various literature databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, and Scopus, were scoured for eligible reports until May 10, 2023. GPower software v.3 was used to assess the power of individual reports included in the meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-analysis v3 software was used to perform all statistics. The publication biases in each genetic comparison model were investigated using funnel plots and Egger’s regression test. To test heterogeneity, Cochrane Q statistics, probability value and I2 were used. Considering the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, the current study included a total of 10 eligible studies that included 15,472 SLE cases and 16,721 healthy controls. The meta-analysis revealed a significant association between TLR7 polymorphisms (rs179019 and rs179010) and susceptibility to SLE development. Other TLR7 polymorphisms (rs3853839 and rs179008), on the other hand, showed no significant association. Furthermore, the trial sequential analysis identified the need for additional case control studies for TLR-7 polymorphisms (rs3853839, rs179008, and rs179019) other than the rs179010 polymorphism. TLR7 variants for rs179010 and rs179019 are risk factor for the development of SLE. Further investigations are required to reach a valid conclusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azab MM, Mostafa FM, Khalil M, Salama M, Abdelrahman AA, Ali AA (2022) Association of TLR7 and TLR9 genes polymorphisms in Egyptian patients with systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Heliyon 8:e11680
Barber MR, Drenkard C, Falasinnu T, Hoi A, Mak A, Kow NY, Svenungsson E, Peterson J, Clarke AE, Ramsey-Goldman R (2021) Global epidemiology of systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol 17:515–532
Bashir MA, Afzal N, Hamid H, Kashif M, Niaz A, Jahan S (2021) Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms encompassing toll like receptor (TLR)-7 (rs179008) and (TLR)-9 (rs352140) in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Adv Life Sci 8:103–107
Bolouri N, Akhtari M, Farhadi E, Mansouri R, Faezi ST, Jamshidi A, Mahmoudi M (2022) Role of the innate and adaptive immune responses in the pathogenesis of systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Inflamm Res 71:537–554
Celhar T, Magalhaes R, Fairhurst A-M (2012) TLR7 and TLR9 in SLE: when sensing self goes wrong. Immunol Res 53:58–77
Christensen SR, Shupe J, Nickerson K, Kashgarian M, Flavell RA, Shlomchik MJ (2006) Toll-like receptor 7 and TLR9 dictate autoantibody specificity and have opposing inflammatory and regulatory roles in a murine model of lupus. Immunity 25:417–428
Dalpke A, Helm M (2012) RNA mediated toll-like receptor stimulation in health and Disease. RNA Biol 9:828–842. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.20206
Deane JA, Pisitkun P, Barrett RS, Feigenbaum L, Town T, Ward JM, Flavell RA, Bolland S (2007) Control of toll-like receptor 7 expression is essential to restrict autoimmunity and dendritic cell proliferation. Immunity 27:801–810
Deng Y, Zhao J, Sakurai D, Kaufman KM, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS, Jacob CO, Scofield RH (2013) MicroRNA-3148 modulates allelic expression of toll-like receptor 7 variant associated with systemic Lupus Erythematosus. PLoS Genet 9:e1003336
Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C (2004) Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303:1529–1531
Dos Santos B, Valverde J, Rohr P, Monticielo O, Brenol J, Xavier R, Chies J (2012) TLR7/8/9 polymorphisms and their associations in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients from southern Brazil. Lupus 21:302–309
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Elloumi N, Fakhfakh R, Abida O, Hachicha H, Marzouk S, Fourati M, Bahloul Z, Masmoudi H (2021) RNA receptors, TLR3 and TLR7, are potentially associated with SLE clinical features. Int J Immunogenet 48:250–259
Enevold C, Nielsen C, Jacobsen R, Hermansen M-LF, Molbo D, Avlund K, Bendtzen K, Jacobsen S (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes encoding toll-like receptors 7, 8 and 9 in Danish patients with systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 41:5755–5763
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang A-G (2009) Statistical power analyses using G* power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 41:1149–1160
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Kawasaki A, Furukawa H, Kondo Y, Ito S, Hayashi T, Kusaoi M, Matsumoto I, Tohma S, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H (2011) TLR7 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the 3’untranslated region and intron 2 independently contribute to systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Japanese women: a case-control association study. Arthritis Res Therapy 13:1–8
Lee YH (2015) Meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Ann Lab Med 35:283–287
Lee YH, Lee HS, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2012) Associations between TLR polymorphisms and systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:262–265
Lee YH, Choi S, Ji J, Song G (2016) Association between toll-like receptor polymorphisms and systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a meta-analysis update. Lupus 25:593–601
Lund JM, Alexopoulou L, Sato A, Karow M, Adams NC, Gale NW, Iwasaki A, Flavell RA (2004) Recognition of single-stranded RNA viruses by toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5598–5603
Lyn-Cook BD, Xie C, Oates J, Treadwell E, Word B, Hammons G, Wiley K (2014) Increased expression of toll-like receptors (TLRs) 7 and 9 and other cytokines in systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) patients: ethnic differences and potential new targets for therapeutic Drugs. Mol Immunol 61:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2014.05.001
Melsen WG, Bootsma MCJ, Rovers MM, Bonten MJM (2014) The effects of clinical and statistical heterogeneity on the predictive values of results from meta-analyses. Clin Microbiol Infect 20:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-0691.12494
Pacheco GV, Nakazawa Ueji YE, Bello JR, Cobos B, Jiménez RE, Becerra ED, González Herrera LJ, Pérez Mendoza GJ, Rivero Cárdenas NA, Angulo Ramírez AV, López Villanueva RF (2022) Copy number variation and frequency of rs179008 in tlr7 gene associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in two mexican populations. J Immunol Res 2022
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ, Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB, Bolland S (2006) Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 312:1669–1672
Raafat I, Guindy E, Shahin N, Samy R, Refai LE, R (2018) Toll-like receptor 7 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk for systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a case-control study. Z Rheumatol 77:416–420
Roers A, Hiller B, Hornung V (2016) Recognition of endogenous nucleic acids by the innate immune system. Immunity 44:739–754
Sakata K, Nakayamada S, Miyazaki Y, Kubo S, Ishii A, Nakano K, Tanaka Y (2018) Up-regulation of TLR7-mediated IFN-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 9:1957
Sánchez E, Callejas Rubio J, Sabio JM, González Gay M, Jiménez Alonso J, Mico L, Ramón Ed, Camps M, Suárez Díaz AM (2009) Investigation of TLR5 and TLR7 as candidate genes for susceptibility to systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, p 27. Gutiérrez Martín, M.d.C
Santiago-Raber M-L, Dunand-Sauthier I, Wu T, Li Q-Z, Uematsu S, Akira S, Reith W, Mohan C, Kotzin BL, Izui S (2010) Critical role of TLR7 in the acceleration of systemic Lupus Erythematosus in TLR9-deficient mice. J Autoimmun 34:339–348
Shaul O (2017) How introns enhance gene expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 91:145–155
Shen N, Fu Q, Deng Y, Qian X, Zhao J, Kaufman KM, Wu YL, Yu CY, Tang Y, Chen J-Y (2010) Sex-specific association of X-linked Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) with male systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15838–15843
Skonieczna K, Woźniacka A, Czajkowski R, Styczyński J, Krenska A, Robak E, Gawrych M, Kaszewski S, Wysocki M, Grzybowski T (2018) X-linked TLR7 gene polymorphisms are associated with diverse immunological conditions but not with discoid lupus erythematosus in polish patients. Adv Dermatol Allergol/Postępy Dermatol i Alergol 35:26–32
Soni C, Wong EB, Domeier PP, Khan TN, Satoh T, Akira S, Rahman ZS (2014) B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is essential for the development of spontaneous germinal centers. J Immunol 193:4400–4414. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1401720
Tian J, Ma Y, Li J, Cen H, Wang D-G, Feng C-C, Li R-J, Leng R-X, Pan H-F, Ye D-Q (2012) The TLR7 7926A > G polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Mol Med Rep 6:105–110
Wang C-M, Chang S-W, Wu Y-JJ, Lin J-C, Ho H-H, Chou T-C, Yang B, Wu J, Chen J-Y (2014) Genetic variations in toll-like receptors (TLRs 3/7/8) are associated with systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Taiwanese population. Sci Rep 4:1–9
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P (2000) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Oxford
Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C (2008) Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 61:64–75
Wetterslev J, Jakobsen JC, Gluud C (2017) Trial sequential analysis in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol 17:1–18
Youinou P, Semana G, Piette J-C, Muller S, Kalsi J, Isenberg DA, Guillevin L, Salmon D, Viard J-P, Bach J-F (1994) Genetic and environmental factors in systemic lupus erythematosus: experimental aspects. Springer, Autoimmunity, pp 221–227
Zintzaras E (2010) Impact of hardy–Weinberg equilibrium deviation on allele-based risk effect of genetic association studies and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol 25:553–560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR: literature search, analysis and preparation of first draft of the mansucript. AKP: overall supervision, finalization of the mansucript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, S., Panda, A.K. Association of Toll-Like Receptor 7 (TLR7) Polymorphisms with Predisposition to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Meta and Trial Sequential Analysis. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10600-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10600-9