Abstract
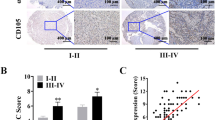
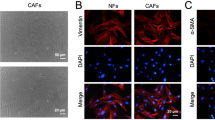
Despite the dominant roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) have attached much attention in tumorigenesis, the CAFs-derived molecular determinants that regulate renal cell carcinoma (RCC) development remains elusive. Our previous study uncovered an oncogenic SNHG1 in the immune escape of RCC, whereas CAFs-derived exosomes could be a source accounting for increasing SNHG1 in RCC cells, this is still a mystery. The obtained CAFs and normal fibroblast (NFs) from fresh RCC and adjacent tissues were firstly identified using western blot and immunofluorescent staining. The enrichment of SNHG1 was validated by RT-qPCR. CAFs-derived exosomes were isolated from conditioned medium using ultracentrifugation method and ExoQuick-TC system. The internalization of exosomes, transfer of SNHG1, was measured by immunofluorescence. Regulation of conditioned medium or exosomal SNHG1 from CAFs on RCC biological functions was evaluated by CCK-8, EdU incorporation, colony formation, and transwell assays to assess the RCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. SNHG1 was significantly upregulated in CAFs isolated from RCC stroma. Exosomes derived from CAFs transferred SNHG1 to RCC cells and resulted in an increased SNHG1 expression in RCC cells. The exosomes excreted by CAFs promoted RCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, whereas the promotion effect of CAFs-exosomes on RCC progression was attenuated by SNHG1 knockdown. The present study revealed a new mechanism of exosomal SNHG1 extracted from CAFs enhanced RCC progression and may provide a potential target for the treatment of RCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- CAFs:
-
Tumor-associated fibroblasts
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell RCC
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- lncRNAs:
-
Long-noncoding RNAs
- NAT:
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
- NFs:
-
Normal fibroblasts
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time polymerase chain reaction
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
References
Alzubaidi AN et al (2022) Incidence and distribution of new renal cell carcinoma cases: 27-year trends from a statewide cancer registry. J Kidney Cancer VHL 9(2):7–12
Baghban R et al (2020) Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Commun Signal 18(1):59
Chen B et al (2021) Exosomal miR-500a-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting USP28. Theranostics 11(8):3932–3947
Chin AI et al (2006) Surveillance strategies for renal cell carcinoma patients following nephrectomy. Rev Urol 8(1):1–7
De Raffele E et al (2020) Twenty-year survival after iterative surgery for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 8(19):4450–4465
Denton AE, Roberts EW, Fearon DT (2018) Stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 1060:99–114
Feng X et al (2019) Frequency, incidence and survival outcomes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in the United States from 1973 to 2014: a SEER-based analysis. Medicine 98(31):e16684
Fu W et al (2022) Exosomes derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate cell progression in clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. Nephron 146(4):383–392
Hasan S et al (2018) Renal cell carcinoma presenting as an ampullary mass: a case report and review of literature. Gastroenterol Res 11(3):231–234
Hong Y et al (2020) The long noncoding RNA EMBP1 inhibits the tumor suppressor miR-9-5p and promotes renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. Nefrologia 40(4):429–439
Hsieh JJ et al (2017) Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17009
Li C et al (2021) Cancer associated-fibroblast-derived exosomes in cancer progression. Mol Cancer 20(1):154
Pathania AS, Challagundla KB (2021) Exosomal long non-coding RNAs: emerging players in the tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 23:1371–1383
Qian Y, Shi L, Luo Z (2020) Long non-coding RNAs in cancer: implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Front Med 7:612393
Ren J et al (2018) Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 8(14):3932–3948
Sahai E et al (2020) A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer 20(3):174–186
Sha M et al (2018) Isolation of cancer-associated fibroblasts and its promotion to the progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Med 7(9):4665–4677
Sun LP et al (2019) Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 42(4):1319–1328
Tian P et al (2021) LncRNA SNHG1 regulates immune escape of renal cell carcinoma by targeting miR-129-3p to activate STAT3 and PD-L1. Cell Biol Int 45(7):1546–1560
Wang J et al (2022) Long non-coding RNA-TMPO-AS1 as ceRNA binding to let-7c-5p upregulates STRIP2 expression and predicts poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 12:921200
Wijesinghe SN et al (2021) Involvements of long noncoding RNAs in obesity-associated inflammatory diseases. Obes Rev 22(4):e13156
Xing F, Saidou J, Watabe K (2010) Cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor microenvironment. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 15(1):166–179
Xu Y et al (2015) Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote renal cell carcinoma progression. Tumour Biol 36(5):3483–3488
Xu C et al (2021) CD248(+) cancer-associated fibroblasts: a novel prognostic and therapeutic target for renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:773063
Yang X et al (2019) Role of exosomes in crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells. Front Oncol 9:356
Ye ZH et al (2022) LncRNA SNHG1 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression through regulation of HMGA2 via sponging miR-103a. J Clin Lab Anal 36(6):e24422
Zhang Y et al (2019) Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci 9(1):19
Zhang J et al (2021) Long noncoding RNA LINC00641 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via sponging microRNA-340-5p. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):210
Zhao S et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 (SNHG1) promotes renal cell carcinoma progression and metastasis by negatively regulating miR-137. Med Sci Monit 24:3824–3831
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to give our sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fund program: Henan provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Project (LHGJ20220192, LHGJ20220193) and Henan provincial Science and Technology Research Project (222102310629).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH: Conception and design of study. PT, JL: Acquisition of data. JW, JR: Analysis and interpretation of data. PT, JW: Drafting the manuscript. CH: Revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committees of the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital and the patient’s written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
All participants were informed and gave written consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, P., Wei, J., Li, J. et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Boost Tumorigenesis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via Exosome-Mediated Paracrine SNHG1. Biochem Genet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10512-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10512-8