Abstract
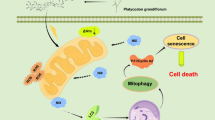
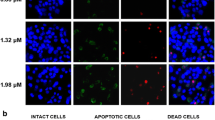
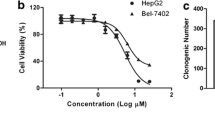
Physalin A (PA) is a bioactive withanolide with multiple pharmacological properties and has been indicated to be cytotoxic to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line HepG2. This study aims to explore the mechanisms underlying PA antitumor activity in HCC. HepG2 cells were exposed to various concentrations of PA. Cell counting kit-8 assay and flow cytometry were implemented for evaluating cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. Immunofluorescence staining was utilized for detecting autophagic protein LC3. Western blotting was employed for measuring levels of autophagy-, apoptosis- and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling-related proteins. A xenograft mouse model was established to verify the antitumor activity of PA in vivo. PA impaired HepG2 cell viability, and triggered apoptosis as well as autophagy. Inhibiting autophagy augmented PA-evoked HepG2 cell apoptosis. PA repressed PI3K/Akt signaling in HCC cells and activating PI3K/Akt reversed PA-triggered apoptosis and autophagy. PA treatment inhibited tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. PA triggers HCC cell apoptosis and autophagy by inactivating PI3K/Akt signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
03 August 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10476-9
References
Abdelrahim M et al (2022) Utilization of immunotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Peri-transplant setting: transplant oncology view. Cancers (basel) 14(7):15
Fan Q et al (2018) Autophagy promotes metastasis and glycolysis by upregulating MCT1 expression and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):9
Gao Z et al (2023) Inhibition of autophagy in macrophage promotes IL-1β-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inflammasome accumulation and self-recruitment. Biomed Pharmacother 161:114560
Hama Y, Ogasawara Y, Noda NN (2023) Autophagy and cancer: basic mechanisms and inhibitor development. Cancer Sci
Han H et al (2011) Physalins A and B inhibit androgen-independent prostate cancer cell growth through activation of cell apoptosis and downregulation of androgen receptor expression. Biol Pharm Bull 34(10):1584–1588
He H et al (2013) Physalin A induces apoptotic cell death and protective autophagy in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells. J Nat Prod 76(5):880–888
He H et al (2014) Nitric oxide induces apoptosis and autophagy; autophagy down-regulates NO synthesis in physalin A-treated A375–S2 human melanoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 71:128–135
He Y et al (2021) Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):425
He F et al. (2023) ATF4 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing SLC7A11 (xCT) to block stress-related ferroptosis. J Hepatol
Ko YC et al (2021) Physalin A, 13,14-Seco-16, 24-Cyclo-Steroid, inhibits stemness of breast cancer cells by regulation of hedgehog signaling pathway and Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1). Int J Mol Sci 22(16):456
Kotsafti A et al (2012) Autophagy and apoptosis-related genes in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol 12:118
Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A (2017) Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17(9):528–542
Liang L et al (2022) Physalis alkekengi. L. var. Franchetii (Mast) Makino: a review of the pharmacognosy, chemical constituents, pharmacological effects, quality control, and applications. Phytomedicine 105:154328
Lu R et al (2021) Physalin A inhibits MAPK and NF-κB signal transduction through integrin αVβ3 and exerts chondroprotective effect. Front Pharmacol 12:761922
Lu R et al (2023) Physalin A alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects. J Orthop Translat 39:74–87
Marahatha R et al (2021) Pharmacologic activities of phytosteroids in inflammatory diseases: mechanism of action and therapeutic potentials. Phytother Res 35(9):5103–5124
Nagaraju GP et al (2022) Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 86(Pt 3):622–632
Narayanankutty A (2021) Natural products as PI3K/ Akt inhibitors: implications in preventing hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Mol Pharmacol 14(5):760–769
Palacios C et al (2010) Autophagy inhibition sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to 17-dimethylaminoethylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin-induced apoptosis. Leuk Res 34(11):1533–1538
Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ (2014) An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(3):460–473
Shin JM et al (2019) Physalin A regulates the Nrf2 pathway through ERK and p38 for induction of detoxifying enzymes. BMC Complement Altern Med 19(1):101
Vogel A et al (2022) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 400(10360):1345–1362
Xia C et al (2022) Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J (english) 135(5):584–590
Xiao MC et al (2021) Imatinib inhibits the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing autophagy. Eur J Pharmacol 906:174217
Xie L et al (2019) Secalonic Acid-F, a novel mycotoxin, represses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via MARCH1 regulation of the PI3K/AKT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Molecules 24(3):89
Xu Z et al (2020) Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(2):575–587
Yang J, Pi C, Wang G (2018) Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 103:699–707
Zhang M et al (2019) SOCS5 inhibition induces autophagy to impair metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis 10(8):612
Zhao S et al (2012) Autophagy inhibition enhances isobavachalcone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma cells. Int J Mol Med 30(4):939–944
Zhu F et al (2016) Physalin A exerts anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by suppressing JAK/STAT3 signaling. Oncotarget 7(8):9462–9476
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Project of Medical Research Fund of Wuhan Municipal Health Commission (No.WX19Q15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XS and ZC conceived and designed the experiments. JXL, SGX, LBL, ZHY, YSC, PZR, XLP, XS and ZC carried out the experiments. XLP, XS and ZC analyzed the data. XLP, XS and ZC drafted the manuscript. All authors agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The postal code in affiliation 1 and the affiliation 3 has been corrected.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, X., Chen, Z., Liu, J. et al. Physalin A Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Inhibition of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Biochem Genet 62, 633–644 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10429-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10429-2