Abstract
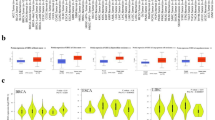
Hepatocellular carcinoma has become one of the most shared cancers in the whole world because of its high morbidity, poor survival rate, and low recovery rate. LncRNA DIO3 opposite strand upstream RNA (DIO3OS) has been reported to be obviously important in several human cancers, while its biological function in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. Here, DIO3OS gene expression data and clinical information of HCC patients were extracted from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the university of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) Xena database. In our study, the Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare DIO3OS expression between healthy individuals and HCC patients. It was found that patients with HCC had significantly lower DIO3OS expression than healthy individuals. Furthermore, Kaplan–Meier curves and Cox regression analysis showed that high DIO3OS expression tended to predict better prognosis and higher survival rate in HCC patients. In addition, the gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) assay was used to annotate the biological function of DIO3OS. It was found that DIO3OS was significantly correlated with immune invasion in HCC. This was also aided by the subsequent ESTIMATE assay. Our study provides a novel biomarker and therapeutic strategy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are from the public database. And, all experimental protocols were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines.
References
Amon L et al (2019) Transcriptional control of dendritic cell development and functions. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 349:55–151
Arneth B (2019) Tumor microenvironment. Medicina (kaunas) 56(1):15
Bindea G et al (2013) Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity 39(4):782–795
Bödder J et al (2020) Harnessing the cDC1-NK cross-talk in the tumor microenvironment to battle cancer. Front Immunol 11:631713
Böttcher JP et al (2018) NK cells stimulate recruitment of cDC1 into the tumor microenvironment promoting cancer immune control. Cell 172(5):1022-1037.e1014
Cao X et al (2007) Granzyme B and perforin are important for regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of tumor clearance. Immunity 27(4):635–646
Chen W et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132
Cui K et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA DIO3OS interacts with miR-122 to promote proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through upregulating ALDOA. Cancer Cell Int 19:202
Echarti A et al (2019) CD8+ and regulatory T cells differentiate tumor immune phenotypes and predict survival in locally advanced head and neck cancer. Cancers 11(9):1398
El-Serag HB (2011) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 365(12):1118–1127
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132(7):2557–2576
Farhood B et al (2020) TGF-β in radiotherapy: mechanisms of tumor resistance and normal tissues injury. Pharmacol Res 155:104745
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma. The Lancet 391(10127):1301–1314
Fregni G et al (2012) NK cells sense tumors, course of disease and treatments: consequences for NK-based therapies. Oncoimmunology 1(1):38–47
Global Burden of Disease Cancer C et al (2019) Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 5(12):1749–1768
Habif G et al (2019) Targeting natural killer cells in solid tumors. Cell Mol Immunol 16(5):415–422
Heilig R et al (2003) The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 14. Nature 421(6923):601–607
Hernandez A (2005) Structure and function of the type 3 deiodinase gene. Thyroid 15(8):865–874
Hernandez A et al (2004) Complex organization and structure of sense and antisense transcripts expressed from the DIO3 gene imprinted locus. Genomics 83(3):413–424
Konjević GM et al (2019) The role of cytokines in the regulation of NK cells in the tumor environment. Cytokine 117:30–40
Liu J et al (2018) An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics. Cell 173(2):400-416.e411
Marson A et al (2007) Foxp3 occupancy and regulation of key target genes during T-cell stimulation. Nature 445(7130):931–935
Nishikawa H, Sakaguchi S (2010) Regulatory T cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer 127(4):759–767
Ohue Y, Nishikawa H (2019) Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci 110(7):2080–2089
Parkin DM et al (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94(2):153–156
Peterson EE, Barry KC (2020) The natural killer-dendritic cell immune axis in anti-cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Front Immunol 11:621254
Piñeiro Fernández J et al (2019) Hepatic tumor microenvironments and effects on NK cell phenotype and function. Int J Mol Sci 20(17):4131
Reik W, Walter J (2001) Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat Rev Genet 2(1):21–32
Sakaguchi S et al (1995) Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol (baltimore, Md. : 1950) 155(3):1151–1164
Sanchez Calle A et al (2018) Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci 109(7):2093–2100
Sarhan D et al (2015) Dendritic cell regulation of NK-cell responses involves lymphotoxin-α, IL-12, and TGF-β. Eur J Immunol 45(6):1783–1793
Schleypen JS et al (2006) Cytotoxic markers and frequency predict functional capacity of natural killer cells infiltrating renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(3 Pt 1):718–725
Scott KE, Cleveland JL (2016) Lactate wreaks havoc on tumor-infiltrating T and NK cells. Cell Metab 24(5):649–650
Song M et al (2019) Large-scale analyses identify a cluster of novel long noncoding RNAs as potential competitive endogenous RNAs in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 11(22):10422–10453
Struhl K (2007) Transcriptional noise and the fidelity of initiation by RNA polymerase II. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14(2):103–105
Subramanian A et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545–15550
Sun C et al (2015) NK cell receptor imbalance and NK cell dysfunction in HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Immunol 12(3):292–302
Suuring M, Moreau A (2021) Regulatory macrophages and tolerogenic dendritic cells in myeloid regulatory cell-based therapies. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):7970
Wang Z et al (2020a) Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation play critical roles in natural killer cell receptor-mediated natural killer cell functions. Front Immunol 11:202
Wang Z et al (2020b) Long noncoding RNA DIO3OS hinders cell malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the microRNA-328/Hhip axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:3903–3914
Wang M et al (2021) Long non-coding RNA DIO3OS/let-7d/NF-kappaB2 axis regulates cells proliferation and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells. J Cell Commun Signal 15(2):237–250
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL (2009) Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev 23(13):1494–1504
Young A et al (2018) A2AR adenosine signaling suppresses natural killer cell maturation in the tumor microenvironment. Can Res 78(4):1003–1016
Zhou X et al (2015) Tissue resident regulatory T cells: novel therapeutic targets for human disease. Cell Mol Immunol 12(5):543–552
Acknowledgements
Thanks to “Xiantao Academic” for their assistance in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant nos. ZR2020MH415, ZR2021LZY033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YW; Administrative support: DZ; Provision of study materials or patients: XH, PS; Collection and assembly of data: DC, XH, PS; Data analysis and interpretation: YW, JL; Manuscript writing: All authors; Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2023_10345_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 (JPG 4106 KB). Supplement figure. Correlation analysis of multiple immune cell markers and lncRNA DIO3OS.
10528_2023_10345_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file2 (JPG 4847 KB). Supplement figure. Correlation analysis of multiple immune cell markers and lncRNA DIO3OS.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Sun, P., Hao, X. et al. Decreased DIO3OS Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and is Associated with Immune Infiltration. Biochem Genet 61, 1791–1806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10345-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10345-5