Abstract
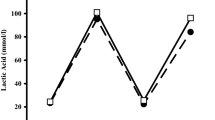
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of Citrulline/Malate supplementation with intensive training on blood lactate level in active handball players. The athletes were subjected to intense training for 4 weeks, 4 days a week, mainly pre-season strength and technique training. In this training period, stimol group (n = 11) athletes were given stimol 3 times a day as 1 g for breakfast, 1 g for lunch, and 1 g for dinner while the placebo group (n = 11) athletes were given only placebo in the same dosage and the same color at the same time. Blood lactate levels in athletes were measured 4 times, prior to and after a 1-month program as follows: rest (R), end effort (EE), recuperation 5 min (R5 m), and recuperation 20 min (R20 m). Blood lactate levels were compared both as intra-group and between the groups. In intra-group comparison, no change was observed in blood lactate levels in placebo group while a significant difference was found in the levels of stimol group as p < 0.05 with a 49.8% decrease in blood lactate level. In the measurements between groups, in the post-test measurements made after the training period, significant differences as p < 0.05 were found with a 60.7% decrease in blood lactate level EE. Considerable decline was seen especially immediately after exercise in blood lactate levels of the athletes being given stimol supplement. In this case, we can say that Citrulline/Malate supplementation may contribute positively to the performance of athletes and may help postpone fatigue at excessive or prolonged activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le GME, Cozzone PJ (2002) Citrulline/malate promotes aerobic energy production in human exercising muscle. Br J Sports Med 36:282–289
Briand J, Blehaut H, Calvayrac R, Laval-Martin D (1992) Use of a microbial model for the determination of drug effects on cell metabolism and energetics: study of citrulline-malate. Biopharm Drug Dispos 13:1–22
Commandré F (1978) Analyse de l’activité du Stimol. Essais en double aveugle sur l’asthénie. 12:1084–1085
Creff AF (1982) Controlled double-blind clinical-study against stimol placebo in the treatment of asthenia. Gazette Medicale De France 89(16):1926–1929
Crenn P et al (2000) Post-absorptive plasma citrulline concentration is a marker of intestinal failure in short bowel syndrome patients. Gastroenterology 119:1496–1505
Cutrufello PT, Gadomski SJ, Zavorsky GS (2015) The effect of l-citrulline and watermelon juice supplementation on anaerobic and aerobic exercise performance. J Sports Sci 33(14):1459–1466
Dauverchain J (1982) Méditerr Méd. 272:77
Fornaris E, Vanuxem D, Duflot J, Bernasconi P, Grimaud C (1984) Gaz Méd France 91:29
Giannesini B, Le Fur Y, Cozzone PJ, Verleye M, Le Guern ME, Bendahan D (2011) Citrulline malate supplementation increases muscle efficiency in rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 667(1–3):100–104
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE (2015) Acute citrulline malate supplementation improves upper- and lower-body submaximal weightlifting exercise performance in resistance-trained females. Eur J Nutr. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL (2016) Acute citrulline-malate supplementation improves maximal strength and anaerobic power in female, masters athletes tennis players. Eur J Sport Sci 16(8):1095–1103
Jackson DN (2004) ATP: supplement your energy. Muscle Fit 65(7):118–120
Kashani BS, Pour PT, Malekmohammad M, Behzadnia N, Sheybani-Afshar F, Fakhri M, Chaibakhsh S, Naghashzadeh F, Aidenlou S (2014) Oral l-citrulline malate in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and Eisenmenger syndrome: a clinical trial. J Cardiol 64:231–235
Perez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM (2010) Citrulline malate enhances athletic anaerobic performance and relieves muscle soreness. J Strength Cond Res 24(5):1215–1222
Perine S, Stoppani J (2010) Energize Me Flex 27(12):204–210
Sureda A, Ferrer MD, Tauler P, Maestre I, Aguiló A, Córdova A, Tur JA, Roche E, Pons A (2009) Effects of l-citrulline oral supplementation on polymorphonuclear neutrophils oxidative burst and nitric oxide production after exercise. Free Radic Res 43(9):828–835
Vanuxem D, Duflot JC, Prevot H et al (1990) Influence of an anti-asthenia agent, citrulline malate, on serum lactate and ammonia kinetics during a maximum exercise test in sedentary subjects. Actualite Therapeutique, Séminaire des Hôpitaux de Paris 66:477–481
Verleye M, Heulard I, Stephens JR, Levy RH, Gillardin JM (1995) Effects of citrulline malate on bacterial lipopolysaccharide induced endotoxemia in rats. Arzneimittelforschung 45:712–715
Wagenmakers AJ (1998) Muscle amino acid metabolism at rest and during exercise: role in human physiology and metabolism. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 26:287–314
Wax B, Kavazis AN, Luckett W (2016) Effects of supplemental citrulline-malate ingestion on blood lactate, cardiovascular dynamics, and resistance exercise performance in trained males. J Diet Suppl 13(3):269–282
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Scientific Research Projects Unit of the Ataturk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiyici, F., Eroğlu, H., Kishali, N.F. et al. The Effect of Citrulline/Malate on Blood Lactate Levels in Intensive Exercise. Biochem Genet 55, 387–394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-017-9807-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-017-9807-8