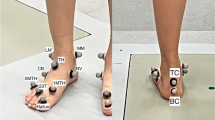
Computerized stabilometry using a four-legged stabilometric platform allows “free” positioning of the feet to be used, which is of fundamental importance for patients and subjects of different ages. The design of the stabilometric platform is important for finding the optimal positioning of the feet in controlling upright standing, treatment, and interpretation of results and comparison with other studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moscow Consensus on the Use of Stabilometry and Biocontrol in Support Reactions in Applied Healthcare and Research [in Russian], P. K. Anokhin Science Research Institute of Normal Physiology (2017).
Skvortsov, D. V., Stabilometry Research [in Russian], Maska, Moscow (2010).
Tarakanov, A. V., Tarakanov, A. A., Efremov, V. V., and Lisutina, O. A., “Computerized stabilometry in lower back pain,” Sovrem. Prob. Nauki Obraz., No. 2, 28 (2018).
Tarakanov, A. V., Chebotov, S. A., Tarakanov, A. A., and Skokova, V. Yu., “Effects of visual control on stabilometric indicators depending on age and sex,” Morsk. Med., No. 3, 32-40 (2019).
Zhil’tsova, I. I., Al’zhev, N. V., Annenkov, O. A., and Lapshina, T. A., “Effects of psychoemotional tension on postural stability in terms of measures of statokinesiogram spectra and heart rate variability,” Voen.-Med. Zh., No. 6, 61-69 (2018).
Skvortsova, V. I., Ivanova, G. E., Skvortsov, D. V., and Klimov, L. V., “Assessment of postural function in clinical practice,” Lech. Fizkult. Sport. Med., No. 6, 8-15 (2013).
Scoppa, F., Capra, R., Gallamini, M., Schiffer, R., and D’Ottavio, S., “Clinical stabilometry standardization: Feet position in the static stabilometric assessment of postural stability,” Acta Med. Medit., 33, 707-713 (2017).
User Manual for the Stabilan-01-2 [in Russian], ZAO OKB RITM, Taganrog. Methods for the Diagnosis and Training to the Balance Function. A Guideline for Doctors [in Russian], Moscow (2009).
Kubryak, O. V. and Grokhovskii, S. S., Practical Stabilometry. Static Motor-Cognitive Tests with Biological Feedback from the Support Reaction [in Russian], Maska, Moscow (2012).
Gagey, P.-M., and Weber, B., Posturology. Regulation and Impairments of Balance of the Human Body [Russian translation], SPbMAPO, St. Petersburg (2008).
Usachev, V. I., Stabilometry in Posturology [in Russian], SPbMAPO, St. Petersburg (2004).
Day, B. L., Steiger, M. J., Thompson, P. D., and Marsden, C. D., “Effect of vision and stance width on human body motion when standing: Implications for afferent control of lateral sway,” J. Physiol., 469, 479-499 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Meditsinskaya Tekhnika, Vol. 55, No. 3, May-Jun., 2021, pp. 24-27.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarakanov, A.V., Tarakanov, A.A., Chebotov, S.A. et al. Computerized Stabilometry on a Four-Legged Platform for Comparative Analysis of Foot Positioning. Biomed Eng 55, 184–188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-021-10098-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-021-10098-8