Abstract
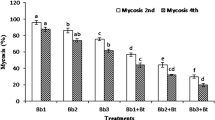
A scarabid-specific isolate (Bt 62) of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner was bioassayed against different instars of the white grub Holotrichia serrata F. (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Carrot disc contamination method was followed since preliminary tests established carrot as a suitable food material vis-à-vis potato, sugarcane root and farmyard manure for first instar grubs. In two replicated bioassays with first instar grubs, 10 mm diam. carrot discs dispensed on one side with six doses, i.e, 1, 3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 μg of toxin per disc were fed to individual grubs and their mortality was recorded at 24 h intervals. In tests with second and third instar grubs, carrot discs of 30 mm diam. were similarly contaminated with 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150 and 175 μg of toxin per disc and fed to grubs. Percentage carrot disc area consumed was assessed visually to represent feeding rates and infer on feeding inhibition. In the two replicated trials against first instar, grubs suffered mortality one day after treatment (DAT) and mortality levels increased with days of exposure. Mean mortality rates at different doses were significantly higher than that in control and they increased with time reaching a peak on third DAT. In tests with second and third instar grubs, feeding inhibition manifested on first DAT but inhibition rates decreased at a decreasing rate as feeding progressed. Mean feeding rates at different doses were significantly lower than that in control and they peaked on fourth to fifth DAT. The results of the laboratory tests and the prospects of Bt 62 in white grub control are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsopp PG (1994) An artificial diet suitable for testing antimetabolic products against sugarcane white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J Aust Entomol Soc 34:135–137
Arpaia S, Ricchiuto B (1993) Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin extracts on feeding behavior and development of Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) larvae. Environ Entomol 22(2):334–338
Arvinth S, Arun S, Selvakesavan RK, Srikanth J, Mukunthan N, Ananda Kumar P, Premachandran MN, Subramonian N (2010) Genetic transformation and pyramiding of aprotinin-expressing sugarcane with cry1Ab for shoot borer (Chilo infuscatellus) resistance. Pl Cell Rep 29(4):383–395
Christy LA, Aravinth S, Saravanakumar M, Kanchana M, Mukunthan N, Srikanth J, Thomas G, Subramonian N (2009) Engineering sugarcane cultivars with bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (aprotinin) gene for protection against top borer (Scirpophaga excerptalis Walker). Pl Cell Rep 28:175–184
Crespo ALB, Spencer TA, Nekl E, Pusztai-Carey M, Moar WJ, Siegfried BD (2008) Comparison and validation of methods to quantify Cry1Ab toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis for standardization of insect bioassays. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(1):130–135
Crickmore N, Berry C, Panneerselvam S, Mishra R, Connor TR, Bonning B (2021) A structure-based nomenclature for Bacillus thuringiensis and other bacteria-derived pesticidal proteins. J Invertebr Pathol 186:107438
David H, Ananthanarayana K (1986) White grubs. In: David H, Easwaramoorthy S, Jayanthi R (eds) Sugarcane entomology in India. Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore, pp 193–208
Easwaramoorthy S, Srikanth J, Santhalakshmi G, Geetha N (2002) Mass-culture and formulation of three entomogenous fungi, with special reference to Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch. against the white grub Holotrichia serrata F. (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Proc Annu Conv Sug Technol Assoc India 64:A126–A141
Easwaramoorthy S, Srikanth J, Santhalakshmi G, Geetha N (2004) Laboratory and field studies on Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch. against Holotrichia serrata F. (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in sugarcane. Proc Annu Conv Sug Technol Assoc India 66:A3–A19
Ghidiu GM, Collins DE, Kirfman GW (1996) Laboratory and field studies of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis as a feeding deterrent to Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Agric Entomol 13(4):349–357
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons
Gould F, Anderson A, Landis D, van Mellaert H (1991) Feeding behavior and growth of Heliothis virescens larvae on diets containing Bacillus thuringiensis formulations or endotoxins. Entomol Exp Appl 58(3):199–210
Huang DF, Zhang J, Song FP, Lang ZH (2007) Microbial control and biotechnology research on Bacillus thuringiensis in China. J Invertebr Pathol 95(3):175–180
Kumari M, Manjulakumari D, Kumar ARV (2013) Evaluation of local Bacillus thuringiensis from the soils of Western Ghats, Karnataka and their biocontrol potential against white grub, Holotrichia serrata (F.) (Coleoptera) and house fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera). Asian J BioSci 8(2):221–224
Mashtoly TA, El-Zemaity ME, Hussien MI, Alm SR (2009) LC and LD50 values of Bacillus thuringiensis serovar japonensis strain Buibui toxin to oriental beetle and northern masked chafer larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J Econ Entomol 102(5):1891–1895
Murthy KS, Lubna S, Kumar ARV, Venkatesan T, Jalali SK, Verghese A (2015) Laboratory rearing of root grubs. Int J Curr Res 7(12):24650–24655
Naveenarani M, Suresha GS, Srikanth J, Hari K, Sankaranarayanan C, Mahesh P, Nirmala R, Clarancia PS, Crickmore N, Ram B, Appunu C, Singaravelu B (2022) Whole genome analysis and functional characterization of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt 62) isolate against sugarcane white grub Holotrichia serrata (F). Genomics 114:185–195
Nayimabanu T, Kumar ARV (2015) Characterization and toxicity studies of Bacillus thuringiensis against white grub Holotrichia serrata. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci 17:209–214
Nowatzki TM, Zhou X, Meinke LJ, Vaughn TY, Siegfried BD (2006) Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb1 protein on the feeding behavior and longevity of adult western corn rootworms (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Econ Entomol 99(3):927–930
Sankaranarayanan C, Singaravelu B, Rajeshkumar M (2019) Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPN): diversity in Indian tropical sugarcane ecosystem and its biocontrol potential against white grub Holotrichia serrata F. on sugarcane. Sugar Tech 21(3):371–382
Singaravelu B, Crickmore N, Srikanth J, Hari K, Sankaranarayanan C, Nirmala R, Radesh Krishnan S, Meghna M (2013) Prospecting for scarabid specific Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin cry8 gene in sugarcane ecosystem of Tamil Nadu, India. J Sugarcane Res 3(2):141–144
Singaravelu B, Mahesh P, Srikanth J, Nirmala R (2015) First report of occurrence of Brahmina mysoreensis Frey (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in sugarcane. J Sugarcane Res 5(2):87–90
Singaravelu B, Appunu C, Suresha GS, Srikanth J, Sankaranarayanan C, Mahesh P, Nirmala R, Rajeshkumar M, Naveenarani M (2017) Screening of indigenous Bacillus thuringiensis isolates for novel cry1 crystal toxin gene for use against lepidopteran sugarcane borers. J Sugarcane Res 7(2):121–125
Srikanth J, Easwaramoorthy S, Santhalakshmi G (2010) Field efficacy and persistence of Beauveria brongniartii (Sacc.) Petch applied against Holotrichia serrata F. (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) infesting sugarcane in southern India. Sugar Cane Int 28(4):151–156
Srikanth J, Santhalakshmi G, Nirmala R (2011a) An improved bioassay method for entomopathogenic fungi of sugarcane pests and its evaluation in studies of virulence in subcultures. Sugar Tech 13(2):156–165
Srikanth J, Subramonian N, Premachandran MN (2011b) Advances in transgenic research for insect resistance in sugarcane. Trop Pl Biol 4:52–61
StatSoft, Inc. (2004) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7. http://www.statsoft.com.
Thamarai Chelvi C, Rhichard Thilagaraj W, Kandasamy R (2010) Laboratory culture and virulence of Beauveria brongniarti (Metschinikoff) isolates on sugarcane white grub, Holotrichia serrata F (Coleoptera: Scarabidae). J Biopest 3(1):177–179
Veenakumari K, Veeresh GK (1982) Evaluation of different methods of inoculation for the production of the milky white disease caused by the bacterium, Bacillus popilliae Dutky on the white grub, Holotrichia serrata Fabricius. J Soil Biol Ecol 2(1):1–7
Wang K, Shu C, Zhang J (2019) Effective bacterial insecticidal proteins against coleopteran pests: a review. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 102:e21558
Yu H, Zhang J, Huang D, Gao J, Song F (2006) Characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis strain Bt185 toxic to the Asian cockchafer: Holotrichia parallela. Curr Microbiol 53(1):13–17
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the director of the Institute for academic encouragement and logistic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Human and animal rights
No Human\animal participation was involved in the study.
Informed consent
Informed consent not applicable since there was no human participation. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Éverton Kort Kamp Fernandes
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srikanth, J., Singaravelu, B., Crickmore, N. et al. Laboratory evaluation of a scarabid-specific isolate of Bacillus thuringiensis against white grub Holotrichia serrata. BioControl 69, 53–64 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-023-10220-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-023-10220-7