Abstract
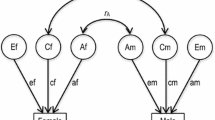
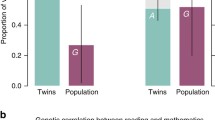
We explored the genetic and environmental influence on both stability and growth in literacy and numeracy in 1927 Australian twin pairs from Grade 3 to Grade 9. Participants were tested on reading, spelling, grammar and punctuation, writing, and numeracy. In each domain, performance across time was highly correlated and this stability in performance was primary due to genes. Key findings on growth showed that reading followed a compensatory growth pattern that was largely due to genetic effects, while variation in growth in the other literacy domains was predominantly due to environmental influences. Genes and the shared environment influenced growth in numeracy for girls, while for boys it was influenced by the shared and unique environment. These results suggest that individual differences in growth of reading are primarily due to a genetically influenced developmental delay in the acquisition of necessary skills, while environmental influences, perhaps including different schools or teachers, are more important for the other domains.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Curriculum Assessment and Reporting Authority (2015a) National assessment program—literacy and numeracy 2014: technical report. ACARA, Sydney
Australian Curriculum Assessment and Reporting Authority (2015b) National protocols for test administration. ACARA, Sydney
Baumert J, Nagy G, Lehmann R (2012) Cumulative advantages and the emergence of social and ethnic inequality: Matthew effects in reading and mathematics development within elementary schools? Child Dev 83(4):1347–1367
Betjemann R, Willcutt E, Olson R, Keenan J, DeFries J, Wadsworth S (2008) Word reading and reading comprehension: stability, overlap and independence. Read Writ 21(5):539–558
Bloom HS, Hill CJ, Black AR, Lipsey MW (2008) Performance trajectories and performance gaps as achievement effect-size benchmarks for educational interventions. J Res Educ Eff 1(4):289–328
Boker S, Neale M, Maes H, Wilde M, Spiegel M, Brick T, Spies J, Estabrook R, Kenny S, Bates T, Mehta P, Fox J (2011) Openmx: an open source extended structural equation modeling framework. Psychometrika 76(2):306–317
Byrne B, Wadsworth S, Corley R, Samuelsson S, Quain P, DeFries JC, Willcutt E, Olson RK (2005) Longitudinal twin study of early literacy development: preschool and kindergarten phases. Sci Stud Read 9(3):219–235
Byrne B, Samuelsson S, Wadsworth S, Hulslander J, Corley R, DeFries J, Quain P, Willcutt E, Olson R (2007) Longitudinal twin study of early literacy development: preschool through Grade 1. Read Writ 20(1):77–102
Byrne B, Coventry WL, Olson RK, Samuelsson S, Corley R, Willcutt EG, Wadsworth S, DeFries JC (2009) Genetic and environmental influences on aspects of literacy and language in early childhood: continuity and change from preschool to Grade 2. J Neurolinguist 22(3):219–236
Byrne B, Coventry WL, Olson RK, Wadsworth SJ, Samuelsson S, Petrill SA, Willcutt EG, Corley R (2010) “Teacher effects” in early literacy development: evidence from a study of twins. J Educ Psychol 102(1):32–42
Christopher ME, Hulslander J, Byrne B, Samuelsson S, Keenan JM, Pennington B, DeFries JC, Wadsworth SJ, Willcutt E, Olson RK (2013a) The genetic and environmental etiologies of individual differences in early reading growth in Australia, the United States, and Scandinavia. J Exp Child Psychol 115(3):453–467
Christopher ME, Hulslander J, Byrne B, Samuelsson S, Keenan JM, Pennington B, DeFries JC, Wadsworth SJ, Willcutt EG, Olson RK (2013b) Modeling the etiology of individual differences in early reading development: evidence for strong genetic influences. Sci Stud Read 17:350–368
Cooper H, Robinson JC, Patall EA (2006) Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Rev Educ Res 76(1):1–62
de Zeeuw EL, de Geus EJC, Boomsma DI (2015) Meta-analysis of twin studies highlights the importance of genetic variation in primary school educational achievement. Trends Neurosci Educ 4(3):69–76
Grasby KL, Coventry WL, Byrne B, Olson RK, Medland SE (2016) Genetic and environmental influences on literacy and numeracy performance in Australian school children in Grades 3, 5, 7, and 9. Behav Genet. doi:10.1007/s10519-016-9797-z
Harlaar N, Dale PS, Plomin R (2007) From learning to read to reading to learn: substantial and stable genetic influence. Child Dev 78(1):116–131
Hart SA, Logan JAR, Soden-Hensler B, Kershaw S, Taylor J, Schatschneider C (2013) Exploring how nature and nurture affect the development of reading: an analysis of the Florida twin project on reading. Dev Psychol 49:1971–1981
Hattie J (2008) Visible learning: a synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge, London
Kovas Y, Haworth CMA, Dale PS, Plomin R, Weinberg RA, Thomson JM, Fischer KW (2007) The genetic and environmental origins of learning abilities and disabilities in the early school years. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev 72(3):i-156
Logan JAR, Hart SA, Cutting L, Deater-Deckard K, Schatschneider C, Petrill S (2013) Reading development in young children: genetic and environmental influences. Child Dev 84(6):2131–2144
Lykken DT, Bouchard TJ, McGue M, Tellegen A (1990) The Minnesota twin family registry: some initial findings. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 39(1):35–70
MacCallum RC, Browne MW, Sugawara HM (1996) Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modeling. Psychol Methods 1(2):130–149
Masters G, Rowley G, Ainley J, Khoo S (2008) Reporting and comparing school performances. http://research.acer.edu.au/ar_misc/8
McArdle JJ, Prescott CA, Hamagami F, Horn JL (1998) A contemporary method for developmental-genetic analyses of age changes in intellectual abilities. Dev Neuropsychol 14(1):69–114
Morgan PL, Farkas G, Wu Q (2011) Kindergarten children’s growth trajectories in reading and mathematics: who falls increasingly behind? J Learn Disabil 44(5):472–488
Neale MC, Røysamb E, Jacobson K (2006) Multivariate genetic analysis of sex limitation and G × E interaction. Twin Res Hum Genet 9(4):481–489
Nye B, Konstantopoulos S, Hedges LV (2004) How large are teacher effects? Educ Eval Policy An 26(3):237–257
Olson RK, Keenan JM, Byrne B, Samuelsson S, Coventry WL, Corley R, Wadsworth SJ, Willcutt EG, DeFries JC, Pennington BF, Hulslander J (2011) Genetic and environmental influences on vocabulary and reading development. Sci Stud Read 15(1):26–46
Olson RK, Keenan JM, Byrne B, Samuelsson S (2014) Why do children differ in their development of reading and related skills? Sci Stud Read 18(1):38–54
Paris SG (2005) Reinterpreting the development of reading skills. Read Res Quart 40(2):184–202
Petrill SA, Deater-Deckard K, Thompson LA, Schatschneider C, DeThorne L, Vandenbergh DJ (2007) Longitudinal genetic analysis of early reading: the Western Reserve Reading Project. Read Writ 20(1–2):127–146
Petrill SA, Hart SA, Harlaar N, Logan J, Justice LM, Schatschneider C, Thompson LA, DeThorne LS, Deater-Deckard K, Cutting L (2010) Genetic and environmental influences on the growth of early reading skills. J Child Psychol Psyc 51(6):660–667
Pfost M, Hattie J, Dörfler T, Artelt C (2014) Individual differences in reading development: a review of 25 years of empirical research on Matthew effects in reading. Rev Educ Res 84(2):203–244
Plomin R, DeFries JC, Knopik VS, Neiderhiser JM (2013) Behavioral genetics. Worth, New York
Rijsdijk FV, Sham PC (2002) Analytic approaches to twin data using structural equation models. Brief Bioinform 3(2):119–133
Rosseel Y (2012) Lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw 48(2):1–36
Samuelsson S, Byrne B, Olson RK, Hulslander J, Wadsworth S, Corley R, Willcutt EG, DeFries JC (2008) Response to early literacy instruction in the United States, Australia, and Scandinavia: a behavioral-genetic analysis. Learn Individ Differ 18(3):289–295
Senate Standing Committee on Education and Employment (2014) Effectiveness of the national assessment program—literacy and numeracy. Canberra: Senate Printing Unit. http://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Senate/Education_and_Employment/Naplan13/Report/index
Shin T, Davison ML, Long JD, Chan C-K, Heistad D (2013) Exploring gains in reading and mathematics achievement among regular and exceptional students using growth curve modeling. Learn Individ Differ 23:92–100
Sirin SR (2005) Socioeconomic status and academic achievement: a meta-analytic review of research. Rev Educ Res 75(3):417–453
Smyth E, Whelan C, McCoy S, Quail A, Doyle E (2010) Understanding parental influence on educational outcomes among 9 year olds in Ireland: the mediating role of resources, attitudes and children’s own perspectives. Child Indic Res 3(1):85–104
Soden B, Christopher ME, Hulslander J, Olson RK, Cutting L, Keenan JM, Thompson LA, Wadsworth SJ, Willcutt EG, Petrill SA (2015) Longitudinal stability in reading comprehension is largely heritable from Grades 1 to 6. PLoS One 10(1):e0113807
Stankov L, Morony S, Lee YP (2014) Confidence: the best non-cognitive predictor of academic achievement? J Educ Psychol 34(1):9–28
Wadsworth SJ, Corley RP, Hewitt JK, DeFries JC (2001) Stability of genetic and environmental influences on reading performance at 7, 12, and 16 years of age in the Colorado Adoption Project. Behav Genet 31(4):353–359
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by an Australian Research Council Grant (DP120102414). The Australian Twin Registry is supported by an enabling Grant (628911) from the National Health and Medical Research Council. We thank the Australian Twin Registry, and all of the twins, triplets and parents involved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Katrina L. Grasby and William L. Coventry declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the University of New England (HE12-150).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Edited by Yoon-Mi Hur.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasby, K.L., Coventry, W.L. Longitudinal Stability and Growth in Literacy and Numeracy in Australian School Students. Behav Genet 46, 649–664 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-016-9796-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-016-9796-0