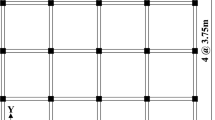
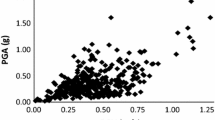
Abstract
Over the past 20 years, significant socio-economic losses have been encountered in Turkey due to several moderate to large earthquakes. The studies published after the earthquakes concurringly emphasized that multistory reinforced concrete (RC) buildings, mostly 3–7 story ones, collapsed or were heavily damaged as a result of inadequate seismic performance. Global drift ratio demands are mostly used as a representative quantity for determining the behavior of structures when subjected to earthquakes. In this study, three representative mid-rise RC buildings are analyzed by nonlinear time history analysis using code-compatible real ground motion record sets and the calculated global drift ratio demands of these buildings are statistically evaluated. Ground motion record sets compatible with the design spectrum defined for local soil classes in the Turkish Earthquake Code (TEC-2007) are used for the analyses. In order to evaluate the effect of the number of ground motions on drift ratio demands, five different ground motion record sets with 7, 11 and 15 ground motion records are used separately for each local soil class. Results of this study indicate that (1) the dispersion of global drift ratio demands calculated for individual ground motion records in record sets is high, (2) local soil class has no significant effect on dispersion. However, dispersion increases in a direct proportion to the number of ground motion records in a record set, (3) the mean of global drift ratio demands calculated for different ground motion record sets may differ although they are compatible with the same design spectrum, (4) the mean of the drift demands obtained from different ground motion record sets compatible with a particular design spectrum can be accepted as simply random samples of the same population at 95% confidence level.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalier K, Aydingun O (2001) Structural engineering aspects of the June 27, 1998 Adana-Ceyhan (Turkey) earthquake. Eng Struct 23:343–355
Akkar S, Boore DM, Gülkan P (2005a) An evaluation of the strong ground motion recorded during the May 1, 2003 Bingöl Turkey, Earthquake. J Earthq Eng 9(2):173–197
Akkar S, Yazgan U, Gulkan P (2005b) Drift estimates in frame buildings subjected to near fault ground motions. J Struct Eng 131(7):1014–1024
Akkar S, Sucuoglu H, Yakut A (2005c) Displacement based fragility functions for low- and mid-rise ordinary concrete buildings. Earthq Spectra 21(4):901–927
Ambraseys NN, Douglas J, Rinaldis D, Berge-Thierry C, Suhadolc P, Costa G, Sigbjornsson R, Smit P (2004a) Dissemination of European strong-motion data, vol 2. CD-ROM Collection, Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, Swindon
Ambraseys NN, Smit P, Douglas J, Margaris B, Sigbjornsson R, Olafsson S, Suhadolc P, Costa G (2004b) Internet site for European strong-motion data. Bollettino di Geofisica Teorica ed Applicata 45(3):113–129
Ancheta TD, Darragh RB, Stewart JP, Seyhan E, Silva WJ, Chiou BSJ, Wooddell KE, Graves RB, Kottke AR, Boore DM, Kishida T, Donahue JL (2014) NGA-West2 database. Earthq Spectra 30(3):989–1005
Araújo M, Macedo L, Marques M, Castro JM (2016) Code-based record selection methods for seismic performance assessment of buildings. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 45:129–148
Arslan MH (2010) An evaluation of effective design parameters on earthquake performance of RC buildings using neural networks. Eng Struct 32:1888–1898
ASCE 07–05 (2006) Minimum design loads for buildings and other structures. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston
ASCE 07–10 (2010) Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and other structures. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston
Askan A, Yucemen MS (2010) Probabilistic methods for the estimation of potential seismic damage: application to reinforced concrete buildings in Turkey. Struct Saf 32(4):262–271
ATC-40 (1996) Seismic evaluation and retrofit of concrete buildings, vol 1–2. Applied Technology Council, California
Bal IE, Crowley H, Pinho R, Gülay FG (2008) Detailed assessment of structural characteristics of Turkish RC building stock for loss assessment models. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 28:914–932
Bazzurro P, Luco N (2005) Accounting for uncertainty and correlation in earthquake loss estimation. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on structural safety and reliability (ICOSSAR), Rome
Bommer JJ, Acevedo AB (2004) The use of real earthquake accelerograms as input to dynamic analysis. J Earthq Eng 8(1):43–91
Cantagallo C, Camata G, Spacone E (2014) Seismic demand sensitivity of reinforced concrete structures to ground motion selection and modification Methods. Earthq Spectra 30(4):1449–1465
Celep Z, Erken A, Taskin B, Ilki A (2011) Failures of masonry and concrete buildings during the March 8, 2010 Kovancılar and Palu (Elazığ) earthquakes in Turkey. Eng Fail Anal 18(3):868–889
D’Ambrisi A, Mezzi M (2005) A probabilistic approach for estimating the seismic response of EP SDOF systems. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 34:1737–1753
Ersoy U, Ozcebe G (2001) Reinforced concrete. Evrim, Istanbul (in Turkish)
Eurocode-8 (2004) Design provisions for earthquake resistance of structures, Part 1: General rules, seismic actions and rules for buildings. European Committee for Standardization, Brussels
FEMA-356 (2000) Prestandard and commentary for seismic rehabilitation of buildings. Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington DC
FEMA-368 (2001) NEHRP recommended provisions for seismic regulations for new buildings and other structures. Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington (DC)
FEMA-440 (2005) Improvement of nonlinear static seismic analysis procedures. Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington DC
Gamst G, Meyers LS, Guarino AJ (2008) Analysis of variance designs—a conceptual and computational approach with SPSS and SAS. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
García RJ, Miranda E (2006) Residual displacement ratios for assessment of existing structures. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 35:315–336
García RJ, Miranda E (2007) Probabilistic estimation of maximum inelastic displacement demands for performance-based design. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 9:1235–1254
García RJ, Miranda E (2010) Probabilistic estimation of residual drift demands for seismic assessment of multi-story framed buildings. Eng Struct 32:11–20
GB (2010) Code for seismic design of buildings. China Architecture and Building Press, Beijing
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76(2):60–68
Ghaffarzadeh H, Talebian N, Kohandel R (2013) Seismic demand evaluation of medium ductility RC moment frames using nonlinear procedures. Earthq Eng Eng Vib 12:399–409
Han SW, Ha SJ, Seok SW (2014) Efficient and accurate procedure for selecting ground motions matching target response spectrum. Nonlinear Dyn 78(2):889–905
Hancock J, Bommer JJ, Stafford PJ (2008) Numbers of scaled and matched accelerograms required for inelastic dynamic analyses. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 37:1585–1607
Hatzigeorgiou GD, Beskos DE (2009) Inelastic displacement ratios for SDOF structures subjected to repeated earthquakes. Eng Struct 31:2744–2755
Hatzigeorgiou GD, Liolios AA (2010) Nonlinear behaviour of RC frames under repeated strong ground motions. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:1010–1025
Hou H, Qu B (2015) Duration effect of spectrally matched ground motions on seismic demands of elastic perfectly plastic SDOFS. Eng Struct 90:48–60
Iervolino I, Maddaloni G, Cosenza E (2008) Eurocode 8 compliant real record sets for seismic analysis of structures. J Earthq Eng 12:54–90
Iervolino I, Galasso C, Cosenza E (2010a) REXEL: computer aided record selection for code-based seismic structural analysis. Bull Earthq Eng 8:339–362
Iervolino I, De Luca F, Cosenza E (2010b) Spectral shape-based assessment of SDOF nonlinear response to real, adjusted and artificial accelerograms. Eng Struct 32(9):2276–2792
Ilki A, Celep Z (2012) Earthquakes, existing buildings and seismic design codes in Turkey. Arab J Sci Eng 37:365–380
Inel M, Ozmen HB, Bilgin H (2008) Re-evaluation of building damage during recent earthquakes in Turkey. Eng Struct 30:412–427
Katsanos EI, Sextos AG (2013) ISSARS: an integrated software environment for structure-specific earthquake ground motion selection. Adv Eng Softw 58:70–85
Katsanos IE, Sextos GA, Manolis DG (2010) Selection of earthquake ground motion records: a state- of- the- art- review from a structural engineering perspective. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:157–169
Kayhan AH (2016) Scaled and unscaled ground motion sets for uni-directional and bi-directional dynamic analysis. Earthq Struct 10(3):563–588
Kayhan AH, Demir A (2016) Statistical evaluation of drift demands of rc frames using code-compatible real ground motion record sets. Struct Eng Mech 60(6):953–977
Kayhan AH, Korkmaz KA, Irfanoglu A (2011) Selecting and scaling real ground motion records using harmony search algorithm. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 31:941–953
Korkmaz S (2015) Observations on the Van earthquake and structural failures. J Perform Constr Facil 29(1):04014033
Lin L (2008) Development of improved intensity measures for probabilistic seismic demand analysis. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Ottawa, Canada
Lin Y, Miranda E (2009) Estimation of maximum roof displacement demands in regular multistory buildings. J Eng Mech 136:1–11
Luzi L, Puglia R, Russo E, ORFEUS WG5 (2016) Engineering strong motion database, version 1.0. Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Observatories and Research Facilities for European Seismology. https://doi.org/10.13127/esm
Macedo L, Castro JM (2017) SelEQ: an advanced ground motion record selection and scaling framework. Adv Eng Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.05.005
Mander JB (1984) Seismic design of bridge piers, research report 84-2. Department of Civil Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch
Medina AR, Krawinkler H (2005) Evaluation of drift demands for the seismic performance assessment of frames. J Struct Eng 7:1003–1013
Mitseas IP, Kougioumtzoglou IA, Beer M (2016) An approximate stochastic dynamics approach for nonlinear structural system performance-based multi-objective optimum design. Struct Saf 60:67–76
Naeim F, Alimoradi A, Pezeshk S (2004) Selection and scaling of ground motion time histories for structural design using genetic algorithm. Earthq Spectra 20(2):413–426
Palanci M, Kalkan A, Senel SM, Yilmaz Y (2014) Investigation of effect of different modeling techniques on existing buildings performance. In: 11th international congress on advances in civil engineering, Oct 21–25, Istanbul
Palanci M, Kalkan A, Senel SM (2016) Investigation of shear effects on the capacity and demand estimation of RC buildings. Struct Eng Mech 60(6):1021–1038
Priestley MJN, Calvi GM, Kowalsky MJ (2007) Displacement-based seismic design of structures. IUSS Press, Pavia
Reyes JC, Kalkan E (2012) How many records should be used in an ASCE/SEI-7 ground motiom scaling procedure. Earthq Spectra 28(3):1223–1242
SAP2000 (2009) Integrated solution for structural analysis and design. Computers and Structures, Berkeley
Scott BD, Park R, Priestley MJN (1982) Stress–strain behavior of concrete confined by overlapping hoops at low and high strain rates. ACI Struct J 76(1):13–27
SEAOC Vision Committee 2000 (1995) Performance-based seismic engineering. Report prepared by Structural Engineers Association of California, Sacramento
Sextos AG, Katsanos EI, Manolis GD (2011) EC8-based earthquake record selection procedure evaluation: validation study based on observed damage of an irregular R/C building. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 31:583–597
Sezen H, Elwood KJ, Whittaker AS, Mosalam KM, Wallace JW, Stanton JF (2000) Structural engineering reconnaissance of the August 17, 1999 earthquake: Kocaeli (Izmit), Turkey. Report 2000-09, Pasific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California, Berkeley
Shome N, Cornell AC, Bazzurro P, Carballo JE (1998) Earthquakes, records and nonlinear responses. Earthq Spectra 14:469–500
Taskin B, Sezen A, Tugsal UM, Erken A (2013) The aftermath of 2011 Van earthquakes: evaluation of strong motion, geotechnical and structural issues. Bull Earthq Eng 11(1):285–312
TEC-1975 (1975) Specification for structures to be built in disaster areas, Turkish earthquake code. Ministry of Public Works and Settlement, Ankara (in Turkish)
TEC-1997 (1997) Specification for structures to be built in disaster areas. Ministry of Public Works and Settlement, Ankara, Turkish Earthquake Code
TEC-2007 (2007) Specification for structures to be built in disaster areas, Turkish earthquake code. Ministry of Public Works and Settlement, Ankara
TS-500 (2000) Requirements for design and construction of reinforced concrete structures. Turkish Standards Institute, Ankara
Watson-Lamprey J, Abrahamson N (2006) Selection of ground motion time series and limits on scaling. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 26:477–482
Yamin LE, Hurtado A, Rincon R, Dorado JF, Reyes JC (2017) Probabilistic seismic vulnerability assessment of buildings in terms of economic losses. Eng Struct 138:308–323
Yon B, Sayin E, Koksal TS (2013) Seismic response of buildings during the May 19, 2011 Simav, Turkey earthquake. Earthq Struct 5(3):343–357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A1
See Table 6.
Appendix A2
See Table 7.
Appendix A3
See Table 8.
Appendix B
See Table 9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palanci, M., Kayhan, A.H. & Demir, A. A statistical assessment on global drift ratio demands of mid-rise RC buildings using code-compatible real ground motion records. Bull Earthquake Eng 16, 5453–5488 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-018-0384-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-018-0384-y