Abstract
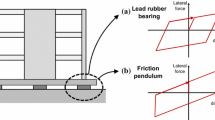
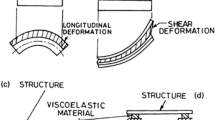
A fractional derivative Zener (FDZ) model connected in parallel with a linear viscous damper and a Coulomb friction slider is used to numerically simulate the mechanical behavior of a base isolated (BI) building tested under free vibration conditions in Solarino, Sicily. This hybrid BI system comprises high damping rubber bearings in combination with low friction sliding bearings. A comparison study of the present model with previous ones appearing in the literature, namely the bi-linear and the tri-linear models defined in the time domain, is carried out here. Furthermore, the linear viscoelastic solid, namely the classical Zener model, is also implemented and evaluated. The rheological models representing all the above BI systems are analyzed and, for the first time, the rheological formulation for the tri-linear model is presented. The present comparison study shows that the FDZ model is capable of describing the complex nonlinear response of BI systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanackovic TM, Spasic DT (2004) On viscoelastic compliant constant-impact models. J Appl Mech ASME 71:134–138
Athanasiou A, Oliveto G (2011) Modeling hybrid base isolation systems for free vibration simulations. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on Urban Earthquake Engineering , Tokyo
Athanasiou A, De Felice M, Oliveto G, Oliveto PS (2013) Dynamical modeling and parameter identification of seismic isolation systems by evolution strategies. Comput Intell 465:101–118
Braga F, Faggella M, Gigliotti R, Laterza M (2005) Nonlinear dynamic response of HDRB and hybrid HDRB-friction sliders base isolation systems. Bull Earthq Eng 3:333–353
Christopoulos C, Filiatrault A (2006) Principles of passive supplemental damping and seismic isolation. IUSS Press, Pavia
Durbin F (1974) Numerical inversion of Laplace transforms: an efficient improvement to Dubner and Abate’s method. Comput J 17(4):371–376
Flügge W (1975) Viscoelasticity. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Hansen N (2011) The CMA evolution strategy: a tutorial. https://www.lri.fr/~hansen/cmatutorial
Hudson RC, Finfgeld CR (1971) Laplace transform solution for the oscillator damped by dry friction. Amer J Phys 39:568–570
Hwang JS, Ku SW (1997) Analytical modeling of high damping rubber bearings. J Struct Eng ASCE 123:1029–1036
Hwang JS, Wang JC (1998) Seismic response of HDR bearings using fractional derivative Maxwell model. Eng Struct 20:849–856
Jumarie G (2008) Fourier’s transform of fractional order via Mittag-Leffler function and modified Riemann-Liouville derivative. J Appl Math Inform 26:1011–1021
Koh CG, Kelly JM (1990) Application of fractional derivatives to seismic analysis of base-isolated models. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 19:229–241
Markou AA, Athanasiou A, Oliveto G (2012) Recent advances in dynamic identification and response simulation of hybrid base isolation systems. In: Proceedings of the 15th world conference on earthquake engineering, paper no. 3023, Lisbon
Narayanan GV, Beskos DE (1982) Numerical operational methods for time-dependent linear problems. Int J Numer Meth Eng 18:1829–1854
Oliveto G, Granata M, Buda G, Sciacca P (2004) Preliminary results from full-scale free vibration test on a four story reinforced concrete building after seismic rehabilitation by base isolation. In: Proceedings of the JSSI 10th anniversary symposium on performance of response controlled buildings, Yokohama
Oliveto ND, Scalia D, Oliveto G (2008) Dynamic identification of structural systems with viscous and friction damping. J Sound Vib 318:911–926
Oliveto ND, Scalia D, Oliveto G (2010) Time domain identification of hybrid base isolation systems using free vibration tests. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 39:1015–1038
Oliveto G, Athanasiou A, Oliveto ND (2012) Analytical earthquake response of 1D hybrid base isolation systems. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 43:1–15
Oliveto G, Oliveto ND, Athanasiou A (2014) Constrained optimization for 1-D dynamic and earthquake response analysis of hybrid base-isolation systems. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 67:44–53
Weilbeer M (2005) Efficient numerical methods for fractional differential equations and their analytical background. Doctoral dissertation, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Professor Giuseppe Oliveto of UNICT for providing the experimental results. The first author also wishes to acknowledge financial support provided by the ‘Anastasios Anastasiadis’ grant from AUTH that allowed him to do part of his Ph.D. studies at UNICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markou, A.A., Manolis, G.D. A fractional derivative Zener model for the numerical simulation of base isolated structures. Bull Earthquake Eng 14, 283–295 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-015-9801-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-015-9801-7