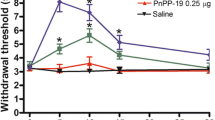
Activity of a peptide tuftsin analogue Selank was studied in outbred rats using the naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal model. Single intraperitoneal injection of Selank in an anxiolytic dose of 0.3 mg/kg reduced the total index of morphine withdrawal syndrome by 39.6%, significantly (р<0.0001) attenuated convulsive reactions, ptosis, and posture disorders, and 9-fold increased the tactile sensitivity threshold in morphine-dependent rats in comparison with the group of active control; at the same time, Selank was slightly inferior to diazepam in a dose of 2 mg/kg by pharmacological activity (the decrease in total index of morphine withdrawal syndrome by 49.3% and 13-fold increase in sensitivity threshold). Thus, Selank, like diazepam, weakens the aversive signs of morphine withdrawal in rats with opiate dependence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nylander I, Vlaskovska M, Terenius L. Brain dynorphin and enkephalin systems in Fischer and Lewis rats: effects of morphine tolerance and withdrawal. Brain Res. 1995;683(1):25-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(95)00279-y
Zolotarev YuA, Myasoedov NF, Sokolov OYu, Kost NV, Zozulya AA, Vaskovsky BV. Leu-enkephalin generally labeled with tritium in studying the Selank inhibiting effect on the enkephalin-degrading enzymes of human blood plasma. Rus. J. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2004;30(3):207-212. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUBI.0000030126.09208.c3
Fukunaga Y, Kishioka S. Enkephalinergic neurons in the periaqueductal gray and morphine withdrawal. Jpn J. Pharmacol. 2000;82(3):175-180. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.82.175
Fricker LD, Margolis EB, Gomes I, Devi LA. Five decades of research on opioid peptides: current knowledge and unanswered questions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020;98(2):96-108. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.120.119388
Sribanditmongkol P, Sheu MJ, Tejwani GA. Inhibition of morphine tolerance and dependence by diazepam and its relation to the CNS Met-enkephalin levels. Brain Res. 1994;645(1-2):1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(94)91631-4
Solov’ev BV, Gengin MT, Latynova IV, Zhigaeva LV, Sollertinskaya TN. Effect of selank on the main carboxypeptidases in the rat nervous tissue. J. Evolution. Biochem. Physiol. 2012;48(3):306-309. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093012030073
Zozulya AA, Neznamov GG, Syunyakov TS, Kast NV, Gabaeva MV, Sokolov OY, Serebryakova EV, Siranchieva OA, Andryushchenko AV, Telesheva ES, Syunyakov SA, Smulevich АВ, Myasoedov NF, Seredenin SB. Efficacy and possible mechanisms of action of a new peptide anxiolytic selank in the therapy of generalized anxiety disorders and neurasthenia. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. 2008;108(4):38-48. Russian.
Kolik LG, Konstantinopolsky MA. Comparative assessment of the effectiveness of noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists amantadine and hemantane in morphine withdrawal syndrome model. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019;166(6):739-743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04430-2
Aronowski J, Wleklik M, Gumulka SW, Luczak M, Konopinska D. Modification of morphine withdrawal: effect of tuftsin, [Lys4]-tuftsinyltuftsin, tetrapeptide fragment (1-4) of substance P and its amide. Life Sci. 1985;37(17):1649-1653. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(85)90485-0
Kolik LG, Nadorova AV, Kozlovskaya MM. Efficacy of peptide anxiolytic selank during modeling of withdrawal syndrome in rats with stable alcoholic motivation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014;157(1):52-55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2490-4
Larrinaga G, Gil J, Meana JJ, Ruiz F, Callado LF, Irazusta J. Aminopeptidase activity in the postmortem brain of human heroin addicts. Neurochem. Int. 2005;46(3):213-219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2004.10.001
Kozlovskii II, Andreeva LA, Kozlovskaya MM, Nadorova AV, Kolik LG. The role of opioid system in peculiarities of anti-anxiety effect of peptide anxiolytic Selank. Eksper. Klin. Farmakol. 2012;75(2):10-13. Russian.
Sokolov OYu, Meshavkin VK, Kost NV, Zozulya AA. Effects of Selank on behavioral reactions and activities of plasma enkephalin-degrading enzymes in mice with different phenotypes of emotional and stress reactions. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002;133(2):133-135. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015582302311
Eisenstein TK, Rahim RT, Feng P, Thingalaya NK, Meissler JJ. Effects of opioid tolerance and withdrawal on the immune system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006;1(3):237-249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-006-9019-1
Siebert A, Gensicka-Kowalewska M, Cholewinski G, Dzierzbicka K. Tuftsin – properties and analogs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017;24(34):3711-3727. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170725140826
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 173, No. 6, pp. 714-718, June, 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantinopolsky, M.A., Chernyakova, I.V. & Kolik, L.G. Selank, a Peptide Analog of Tuftsin, Attenuates Aversive Signs of Morphine Withdrawal in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 173, 730–733 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-022-05624-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-022-05624-x