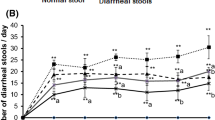
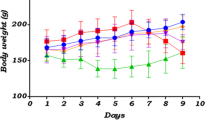
We studied the effect of turmeric extract in the composition of rectal suppositories on the level of LPO products and oxidative modification of proteins in the colon mucosa of Wistar rats with experimental Crohn’s disease modeled by rectal administration of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. The suppositories containing turmeric extract were administered 12 h after disease induction. On days 3, 5, and 7 of the experiment, clinical parameters of the disease were scored using disease activity scale (DAI) and the concentration of LPO products and intensity of oxidative modification of proteins were measured by the extraction-spectrofluorimetric method. Administration turmeric extract in rectal suppositories reduced the severity of clinical symptoms, the level of LPO products (mostly in the isopropanol phase of the lipid extract), and the total content of products of oxidative modification of proteins. Moreover, correlations between DAI and concentration of LPO products in the colon were found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaydarova AP, Koroschenko GA, Ayzman RI. Influence of turmeric and curcumin on carbohydrate metabolism in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Sovremen. Probl. Nauki Obrazovaniya. 2014;(5):597. Russian.
Фомина М.А, Абаленихина Ю.В. Способ комплексной оценки содержания продуктов окислительной модификации белков в тканях и биологических жидкостях: методические рекомендации. Рязань, 2014.
Volchegorskii IA, Dolgushin II, Kolesnikov OL, Tseilik-man VE. Experimental modeling and laboratory evaluation of adaptive responses of the body. Chelyabinsk, 2000. Russian.
Anthwal A, Thakur BK, Rawat MS, Rawat DS, Tyagi AK, Aggarwal BB. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of C-5 curcumin analogues with potential to inhibit TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014;2014. 524161. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/524161
Čolak E. New markers of oxidative damage to macromolecules. J. Med. Biochem. 2008;27(1):1-16. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10011-007-0049-x
Curkovic I, Egbring M, Kullak-Ublick GA. Risks of inflammatory bowel disease treatment with glucocorticosteroids and aminosalicylates. Dig. Dis. 2013;31(3-4):368-73. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000354699
Gupta SC, Tyagi AK, Deshmukh-Taskar P, Hinojosa M, Prasad S, Aggarwal BB. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor and other proinflammatory biomarkers by polyphenols. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014;559:91-99. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2014.06.006
Iborra M, Moret I, Rausell F, Bastida G, Aguas M, Cerrillo E, Nos P, Beltrán B. Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in Grohn’s disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011; 39(4):1102-1106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0391102
Kocaadam B, Şanlier N. Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017;57(13):2889-2895. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1077195
Murthy S, Cooper HS, Yoshitake H, Meyer C, Meyer CJ, Murthy NS. Combination therapy of pentoxifylline and TNFalpha monoclonal antibody in dextran sulphate-induced mouse colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999;13(2):251-260.
Muthupalani S, Ge Z, Feng Y, Rickman B, Mobley M, McCabe A, Van Rooijen N, Fox JG. Systemic macrophage depletion inhibits Helicobacter bilis-induced proinflammatory cytokine-mediated typhlocolitis and impairs bacterial colonization dynamics in a BALB/c Rag2-/- mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease. Infect. Immun. 2012;80(12):4388-4397. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00530-12
Randhawa PK, Singh K, Singh N, Jaggi AS. A review on chemical-induced inflammatory bowel disease models in rodents. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014;18(4):279-288. doi: https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.4.279
Sales-Campos H, Basso PJ, Alves VB, Fonseca MT, Bonfá G, Nardini V, Cardoso CR. Classical and recent advances in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015;48(2):96-107. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X20143774
Senhaji N, Kojok K, Darif Y, Fadainia C, Zaid Y. The contribution of cd40/cd40l axis in inflammatory bowel disease: an update. Front. Immunol. 2015;6:529. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00529
Trujillo J, Chirino YI, Molina-Jijón E, Andérica-Romero AC, Tapia E, Pedraza-Chaverrí J. Renoprotective effect of the antioxidant curcumin: Recent findings. Redox Biol. 2013;1:448-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2013.09.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 3, pp. 314-319, March, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osikov, M.V., Simonyan, E.V., Bakeeva, A.E. et al. Antioxidant Effects of Turmeric Extract in Rectal Suppositories of Original Composition in Experimental Crohn’s Disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 342–346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04883-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04883-w