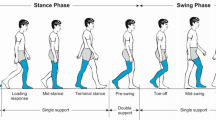
The effects of anti-orthostatic hypokinesia on the parameters of vertical posture (orthostatic and postural stability) were studied. Anti-orthostatic hypokinesia was followed by orthostatic instability manifested in a decrease in the tolerance time in the orthostatic test, a significant increase in HR and systolic BP starting from the 11th minute of the test. Significant changes in the parameters reflecting postural stability were observed starting from minutes 10-11 of the stabilometric test. Anti-orthostatic hypokinesia was shown to affect all parameters of postural stability; symmetry in paired stabilometric tests was impairmed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balin VD. Psychophysiology for Psychologist. St. Petersburg, 2008. Russian.
Dotsenko VI. Introduction into clinical posturology: the quality of vertical posture maintenance is an important indicator of general and neuropsychiatric health. Glavnyi Vrach Yuga Rossii. 2007;(2):29-32. Russian.
Kozlovskaya IB. Gravity and the tonic postural motor system. Aviakosm. Biol. Ekol. Med. 2017;51(3):5-21. Russian.
Kotov AN, Zakharov SYu, Rudenko EA, Baranov VM. The influence of prolonged head-down and head-up bed rest on orthostatic tolerance in humans. Meditsina Ekstem. Situatsii. 2016;(1):25-29. Russian.
Kotovskaya AR, Fomina GA, Alferova IV, Salnikov AV. Predicting orthostatic stability of cosmonauts in microgravity by the condition of lower extremities veins in the course of 6-month space flights. Aviakosm. Biol. Ekol. Med. 2016; 50(3):5-9. Russian.
Kubryak OV, Grokhovskii SS, Dobrorodnyi AV. Analysis of Support Reactions in Humans (Posturography, Stabilometry) and Biofeedback in the STPL Program. Moscow, 2018. Russian.
Smirnova TA, Ilyin EA. Ethics of biomedical investigations and tests. Aviakosm. Biol. Ekol. Med. 2017;51(4):59-68. Russian.
Mulavara AP, Peters BT, Miller CA, Kofman IS, Reschke MF, Taylor LC, Lawrence EL, Wood SJ, Laurie SS, Lee SMC, Buxton RE, May-Phillips TR, Stenger MB, Ploutz-Snyder LL, Ryder JW, Feiveson AH, Bloomberg JJ. Physiological and Functional Alterations after Spaceflight and Bed Rest. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018;50(9):1961-1980.
Stewart A, Marfell-Jones M, Olds T, de Ridder H. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment. Lower Hutt: International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry, 2011.
Sung PS. The ground reaction force thresholds for detecting postural stability in participants with and without flat foot. J. Biomech. 2016;49(1):60-65.
Torjesen A, Cooper LL, Rong J, Larson MG, Hamburg NM, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS, Mitchell GF. Relations of arterial stiffness with postural change in mean arterial pressure in middle-aged adults: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2017;69(4):685-690.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 1, pp. 13-16, January, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlov, D.O., Sukhostavtseva, T.V., Shpakov, A.V. et al. Effects of Anti-Orthostatic Hypokinesia on the Parameters of Vertical Posture: Orthostatic and Stabilometric Study. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 9–12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04813-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04813-w