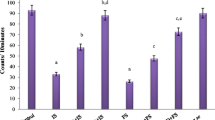
We studied the effects of Selank on morphological parameters of the liver in Wistar male rats subjected to chronic foot-shock stress. Selank was injected intraperitoneally in doses of 100, 300 and 1000 μg/kg 15 min before each stress session. Morphological and morphometrical analysis showed that chronic foot-shock stress induced hydropic degeneration of hepatocytes, an increase of the nucleus/cytoplasm ratio due to an increase in the area of nuclei and reduction of the cytoplasm area, the appearance of focal necroses, and lymphohistiocyte infiltration. Injection of Selank in all doses reduced the intensity of stress-induced degenerative changes. Administration of Selank in doses of 300 and 1000 μg/kg restored the nucleus/cytoplasm ratio in hepatocytes. The maximum stress-limiting effect was attained after administration of 300 μg/kg Selank.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belykh AE, Dudka VT, Bobyntsev II, Kryukov AA. Rats’ liver morphology in conditions of acute foot-shock stress against the background of delta sleep-inducing peptide injection. Chelovek Ego Zdorov’ie. 2016;(4):59-66. Russian.
Vasil’eva EV, Kondrakhin EA, Salimov RM, Kovalev GI. Comparison of Pharmacological Effects of Heptapeptide Selank after Intranasal and Intraperitoneal Administration to BALB/C and C57BL/6 Mice. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2016;79(9):3-11. Russian.
Zozulya AA, Neznamov GG, Syunyakov TS, Kast NV, Gabaeva MV, Sokolov OYu, Serebryakova EV, Siranchieva OA, Andryushchenko AV, Telesheva ES, Syunyakov SA, Smulevich АВ, Myasoedov NF, Seredenin SB. Efficacy and possible mechanisms of action of a new peptide anxiolytic Selank in the therapy of generalized anxiety disorders and neurasthenia. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. 2008;108(4):38-48. Russian.
Zolotarev YuA, Myasoedov NF, Sokolov OYu, Kost NV, Zozulya AA, Vaskovsky BV. Leu-enkephalin generally labeled with tritium in studying the Selank inhibiting effect on the enkephalin-degrading enzymes of human blood plasma. Rus. J. Bioorgan. Chem. 2004;30(3):207-212.
Kolomin TA, Shadrina MI, Slominsky PA, Limborska SA, Myasoedov NF. Changes in expression of the genes for chemokines, cytokines, and their receptors in response to Selank and its fragments. Rus. J. Genetics. 2011;47(5):629-631.
Pavlov TS, Samonina GE, Bakaeva ZV, Zolotarev YA, Guseva AA. Selank and its metabolites maintain homeostasis in the gastric mucosa. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007;143(1):51-53.
Petrovsky AK, Petrovskaya AYu, Kosenko MV, Andreeva LA, Smirnov NA, Fedorov VN. Adaptogenic acticity of Semax and Selang: experimental research. Med. Al’manakh. 2017;(1):114-118. Russian.
Skrebitsky VG, Kasyan AP, Povarov IS, Kondratenko RV, Slominsky PA. Biological Activity and Basic Mechanisms of Action of Selang - a Neuropeptide Product. Nervn. Bol. 2016;(4):52-57. Russian.
Khnychenko LK, Sapronov NS. Stress and its role in development of pathological processes. Obzory po Klin. Farmakol. Lek. Ter. 2003;2(3):2-15. Russian.
Caixeta DC, Teixeira RR, Peixoto LG, Machado HL, Baptista NB, de Souza AV, Vilela DD, Franci CR, Salmen Espindola F. Adaptogenic potential of royal jelly in liver of rats exposed to chronic stress. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0191889. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191889.
Chida Y, Sudo N, Motomura Y, Kubo C. Electric foot-shock stress drives TNF-alpha production in the liver of IL-6-deficient mice. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2004;11(6):419-424.
Chida Y, Sudo N, Sonoda J, Sogawa H, Kubo C. Electric foot shock stress-induced exacerbation of alpha-galactosylceramide-triggered apoptosis in mouse liver. Hepatology. 2004;39(4):1131-1140.
Fu J, Ma S, Li X, An S, Li T, Guo K, Lin M, Qu W, Wang S, Dong X, Han X, Fu T, Huang X, Wang T, He S. Longterm stress with Hyperglucocorticoidemia-induced hepatic steatosis with VLDL overproduction is dependent on both 5-HT2 receptor and 5-HT synthesis in liver. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016;12(2):219-234.
Liu YZ, Chen JK, Zhang Y, Wang X, Qu S, Jiang CL. Chronic stress induces steatohepatitis while decreases visceral fat mass in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-14-106.
Matthews DB, Morrow AL, O’Buckley T, Flanigan TJ, Berry RB, Cook MN, Mittleman G, Goldowitz D, Tokunaga S, Silvers JM. Acute mild footshock alters ethanol drinking and plasma corticosterone levels in C57BL/6J male mice, but not DBA/2J or A/J male mice. Alcohol. 2008;42(6):469-476.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 167, No. 2, pp. 257-260, February, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fomenko, E.V., Bobyntsev, I.I., Ivanov, A.V. et al. Effect of Selank on Morphological Parameters of Rat Liver in Chronic Foot-Shock Stress. Bull Exp Biol Med 167, 293–296 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04512-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04512-1