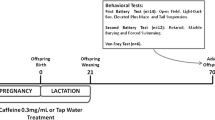
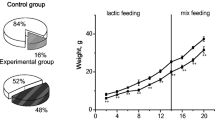
We studied the effect of long-term prenatal administration of caffeine on the behavior and learning of rats in postnatal ontogeny. Experiments were carried out on male rats born by females receiving caffeine solution as the only source of fluid throughout gestation. The control group consisted of pups obtained from females receiving drinking water throughout pregnancy. It was found that long-term caffeine intake by female rats during pregnancy determined increased locomotor activity of the offspring. Rat pups born from mothers treated with caffeine during pregnancy faster reached the underwater platform in the Morris maze, i.e. demonstrated better spatial memory formation than control animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuff-Smith KD, Schilling MA, Fisher JE, Vorhees CV. Stagespecific effects of prenatal d-methamphetamine exposure on behavioral and eye development in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1996;18(2):199-215.
Bashkatova V, Meunier J, Vanin A, Maurice T. Nitric oxide and oxidative stress in the brain of rats exposed in utero to cocaine. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2006;1074. P.632-642.
Dassesse D, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Schiffmann SN. Acute and chronic caffeine administration differentially alters striatal gene expression in wild-type and adenosine A(2A) receptordeficient mice. Synapse. 2001;42(2):63-76.
Hrebíčková I, Ševčíková M, Nohejlová K, Šlamberová R. Does effect from developmental methamphetamine exposure on spatial learning and memory depend on stage of neuroontogeny? Physiol. Res. 2016;65(Suppl. 5):S577-S589.
León D, Albasanz JL, Ruíz MA, Fernández M, Martín M. Adenosine A1 receptor down-regulation in mothers and fetal brain after caffeine and theophylline treatments to pregnant rats. J. Neurochem. 2002;82(3):625-634.
Lindsay MK, Burnett E. The use of narcotics and street drugs during pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013;56(1):133-141.
Moenk MD, Matuszewich L. Juvenile but not adult methamphetamine exposure improves performance in the Morris Water Maze in male rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2012;30(4):325-331.
Morgan S, Koren G, Bozzo P. Is caffeine consumption safe during pregnancy? Can. Fam. Physician. 2013;59(4):361-362.
Pechlivanova D, Tchekalarova J, Nikolov R, Yakimova K. Dose-dependent effects of caffeine on behavior and thermoregulation in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2010;209(2):205-211.
Soellner DE, Grandys T, Nuñez JL. Chronic prenatal caffeine exposure impairs novel object recognition and radial arm maze behaviors in adult rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2009;205(1):191-199.
Sudakov SK, Medvedeva OF, Rusakova IV, Figurina IB. Effect of short-term and chronic caffeine intake on rats with various anxiety level. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001;132(6):1177-1179.
Thompson VB, Heiman J, Chambers JB, Benoit SC, Buesing WR, Norman MK, Norman AB, Lipton JW. Long-term behavioral consequences of prenatal MDMA exposure. Physiol. Behav. 2009;96(4-5):593-601.
Yadegari M, Khazaei M, Anvari M, Eskandari M. Prenatal caffeine exposure impairs pregnancy in rats. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2016;9(4):558-562.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 165, No. 3, pp. 268-270, March, 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashkatova, V.G., Alekseeva, E.V., Bogdanova, N.G. et al. Influence of Caffeine Consumption by Pregnant Rats on Behavior and Learning in Their Offspring. Bull Exp Biol Med 165, 299–301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4154-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4154-2