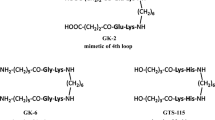
We compared the effects of GK-2 (dimeric dipeptide mimetic of nerve growth factor) and Mexidol (standard preparation for the therapy of stroke) on rat model of transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. GK-2 and Mexidol were administered intraperitoneally in the most active doses (1 and 100 mg/kg, respectively) 6 h after surgery and then once a day for 6 days. The preparations reduced the volume of cerebral infarction (by 60 and 30%, respectively). At the same time, GK-2 had a pronounced and statistically more reliable effect in a dose that is lower by two orders of magnitude. In addition, GK-2 significantly reduced the neurological deficit in the limb placement test, while Mexidol was ineffective in this test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antipova TA, Gudasheva TA, Seredenin SB. In vitro study of neuroprotective properties of GK-2, a new original nerve growth factor mimetic. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011;150(5):607-609.
Voronina TA. Mexidol: the main neuropsychotropic effects and mechanism of action. Farmateka 2009;(6):35-38. Russian.
Gudasheva TA, Antipova TA, Seredenin SB. Novel low-molecular-weight mimetics of the nerve growth factor. Dokl. Biochem. Biophysics 2010;434(1):262-265.
Seredenin SB, Gudasheva TA. The development of a pharmacologically active low-molecular mimetic of the nerve growth factor. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. 2015;115(6-1):63-70. Russian.
Yasnetsov VV, Voronina TA. Effect of Semax and Mexidol on brain ischemia models in rats. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2009;72(1):68-70. Russian.
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 1986;17(6):1304-1308.
Gudasheva TA, Povarnina PY, Antipova TA, Firsova YN, Konstantinopolsky MA, Seredenin SB. Dimeric dipeptide mimetics of the nerve growth factor Loop 4 and Loop 1 activate TRKA with different patterns of intracellular signal transduction. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015;22:106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-015-0198-z.
Hassanzadeh P, Arbabi E, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R. Nerve growth factor-carbon nanotube complex exerts prolonged protective effects in an in vitro model of ischemic stroke. Life Sci. 2016. Dec 2. pii: S0024-3205(16):30681-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.029.
Jiang H, Tian S, Zeng Y, Shi J. Nerve growth factor inhibits Gd(3+)-sensitive calcium influx and reduces chemical anoxic neuronal death. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2008;28(4):379-382.
Jolkkonen J, Puurunen K, Rantakömi S, Härkönen A, Haapalinna A, Sivenius J. Behavioral effects of the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist, atipamezole, after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;400(2-3):211-219.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989;20(1):84-91.
Oliveira SL, Pillat MM, Cheffer A, Lameu C, Schwindt TT, Ulrich H. Functions of neurotrophins and growth factors in neurogenesis and brain repair. Cytometry A. 2013 Vol. 83(1):76-89.
Park JH, Kang SS, Kim JY, Tchah H. Nerve growth factor attenuates apoptosis and inflammation in the diabetic cornea. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016;57(15):6767-6775.
Yang JP, Liu HJ, Yang H, Feng PY. Therapeutic time window for the neuroprotective effects of NGF when administered after focal cerebral ischemia. Neurol. Sci. 2011;32(3):433-441.
Zhu W, Cheng S, Xu G, Ma M, Zhou Z, Liu D, Liu X. Intranasal nerve growth factor enhances striatal neurogenesis in adult rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Drug. Deliv. 2011;18(5):338-343.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 164, No. 8, pp. 201-204, August, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Povarnina, P.Y., Volkova, A.A., Gudasheva, T.A. et al. Comparison of the Pharmacological Effects of Dimeric Dipeptide Nerve Growth Factor Mimetic GK-2 and Mexidol on the Model of Ischemic Stroke in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 164, 173–176 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3951-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3951-3