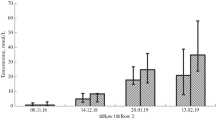
Studies of the dynamics of thyroid hormone concentrations in the blood revealed a 3-day rhythm that significantly manifested in male Wistar rats and Chinchilla rabbits during intensive growth and in common starlings (Sturnus vulgaris) during moult. Synphasic 3-day biorhythms of thyroid hormonal activities were found in these animals, which attested to an external synchronizer of this biorhythm common for mammals and birds. The maximum level of thyroid hormones coincided with the extrema of daily fluctuations of the Earth rotation velocity, as a result of which this external factor or another factor closely related to it seemed to be involved in synchronization of the 3-day infradian biorhythm of thyroid hormones in mammals and birds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belisheva NK, Zhirov VK, Kuzhevskij BM, Sigaeva EA, Panasyuk MI. Variations in the neutron intensity near the Earth’s surface modulate the functional state of the blood. Dokl. Biochem. Biophysics. 2006;407(1):83-87.
Breus TK, Halberg G, Cornelissen G. Effect of solar activity on the physiological rhythms of biological systems. Biofi zika. 1995;40(4):737-48. Russian.
Vasilik PV, Vasilega AG. Peculiarities of changes in body weight in guinea pigs as an indicator of fl uctuations in the unevenness of Earth rotation caused by the infl uence of the Moon. Geofi zich. Processy Biosfera. 2004;3(1):58-62. Russian.
Vladimirskii BM, Narmanskii VYa, Temur’yants NA. Global rhythmicity of the solar system in the terrestrial environment. Biofi zika. 1995;40(4):749-754. Russian.
Deshcherevsky AV, Lukk AA. Searching of the regular components in temporal variations of geophuysical parameters by method of decomposition in non-harmonious components. Vulkanologiya Seismologiya. 2002;(5):65-78. Russian.
Diatroptov ME. The infradian rhythm in changes of thyroxine level and related periodicity of feather replacement during the molting in passerine birds. Zh. Obshch. Biologii. 2013;74(5):379-385. Russian.
Diatroptov ME, Makarova OV, Diatroptova MA. Regularities of infradian rhythms of the esophageal epithelium proliferation activity in Japanese Quails (Coturnix Japonica) and male Vistar rats. Geofi zich. Processy Biosfera. 2014;13(4):82-96. Russian.
Diatroptov ME, Nechai VV, Diatroptova MA. Infradian modulation of circadian rhythms of proliferative activity of the esophageal and corneal epithelium. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013;155(4):498-500.
Dubrov AP. Lunar rhythms in humans. Moscow, 1990. Russian.
Matrynyuk VS, Vladimirskii BM, Temur’yants NA. Biological rhythms and electromagnetic fi elds in the habitat. Geofi zich. Processy Biosfera. 2006;5(1):5-23. Russian.
Rustembekova SA, Tliashinova AM, Buraya TI, Sel’verova NB. Age-related changes in the structure and function of the thyroid gland. Novye Issledovaniya. 2011;1(28):65-74. Russian.
Temur’yants NA, Chuyan EN, Kostyuk AS, Tumanyants KH, Demstun NA, Yarmolyuk NS. Effects of Weak Electromagnetic Factors in Invertebrate Animals. Simferopl’, 2012. Russian.
Cherry N. Schumann resonances, a plausible biophysical mechanism for the human health effects of Solar/Geomagnetic Activity. Natural Hazards. 2002;26(3):279-331.
Jozsa R, Halberg F, Cornélissen G, Zeman M, Kazsaki J, Csernus V, Katinas GS, Wendt HW, Schwartzkopff O, Stebelova K, Dulkova K, Chibisov SM, Engebretson M, Pan W, Bubenik GA, Nagy G, Herold M, Hardeland R, Hüther G, Pöggeler B, Tarquini R, Perfetto F, Salti R, Olah A, Csokas N, Delmore P, Otsuka K, Bakken E.E, Allen J, Amory-Mazaudin C. Chronomics, neuroendocrine feedsidewards and the recording and consulting of nowcasts-forecasts of geomagnetics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005;59(Suppl. 1):S24-S30.
Li J, Nguyen V, French BA, Parlow AF, Su GL, Fu P, Yuan QX, French SW. Mechanism of the alcohol cyclic pattern: role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000;279(1):G118-G125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 12, pp. 790-795, December, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diatroptov, M.Е., Diatroptova, M.A. Infradian Biorhythm of Thyroid Hormone Concentrations in Mammals and Birds. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 815–819 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3720-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3720-3