Abstract
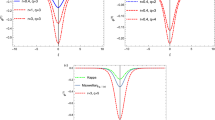
Dynamics of nonlinear ion-acoustic waves (IAWs) are studied for Venus’ lower atmosphere at an altitude of \(200-1000\) km. Two-soliton, nonlinear solitary and periodic waves in a three-component plasma consisting of \(H^{+}\) and \(O^{+}\) ions with kappa distributed electrons are studied. Using the reductive perturbation technique (RPT), the Korteweg-de Vries (KdV) equation is derived and a Planar dynamical system is formed for the KdV equation using a travelling wave transformation. A phase portrait is drawn to analyze nonlinear wave behaviors by adjusting the parameters \(\kappa \) (spectral index), \(\gamma \) (unperturbed number density ratio), and \(V\) (travelling wave speed). Increasing values of \(\kappa \) amplify amplitudes for solitary and periodic waves, narrow down the width of the solitary wave, and broaden the width of the periodic wave. Increasing value of \(\gamma \) boosts amplitude of the solitary wave with unchanged width, while amplitude of the nonlinear periodic wave decreases and width widens. Increasing value of \(V\) enhances amplitudes and reduces widths for both solitary and periodic waves. Two-soliton solutions for the KdV equation are studied using the Hirota direct method. Increasing value of \(\gamma \) reduces amplitude of the soliton without affecting the width and increasing value of \(\kappa \) reduces width of the soliton. Phase shift for two-soliton is also shown and found that for different values of \(\kappa \), the phase shift increases on increasing value of \(\gamma \). The findings of our result aid in understanding the dynamics of nonlinear waves and two-soliton solutions in Venus’ lower ionosphere.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdikian, A., Saha, A., Alimirzaei, S.: Bifurcation analysis of ion-acoustic waves in a adiabatic trapped electron and warm ion plasma. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 14(1), 1051–1058 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2020.1798062
Afify, M., Elkamash, I., Shihab, M., et al.: Evolution of ion-acoustic soliton waves in Venus’ ionosphere permeated by the solar wind. Adv. Space Res. 67(12), 4110–4120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.02.037
Cairns, R.A., Mamun, A.A., Bingham, R., et al.: Ion-acoustic solitons in a magnetized plasma with nonthermal electrons. Phys. Scr. T 63, 80–86 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/1996/t63/012
Chapagai, D.P., Tamang, J., Saha, A.: Bifurcation analysis for small-amplitude nonlinear and supernonlinear ion-acoustic waves in a superthermal plasma. Z. Naturforsch. A 75(3), 183–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2019-0210
Chotoo, K., Schwadron, N.A., Mason, G.M., et al.: The suprathermal seed population for corotating interaction region ions at 1 au deduced from composition and spectra of \(H^{+}\), \(He^{++}\), and \(He^{+}\)observed on wind. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 105(A10), 23107–23122 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1029/1998ja000015
Christon, S.: A comparison of the Mercury and Earth magnetospheres: electron measurements and substorm time scales. Icarus 71(3), 448–471 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0019-1035(87)90040-6
Colin, L.: The pioneer Venus program. J. Geophys. Res. 85(A13), 7575 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1029/ja085ia13p07575
Collier, M.R., Hamilton, D.C.: The relationship between kappa and temperature in energetic ion spectra at Jupiter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22(3), 303–306 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1029/94gl02997
Decker, R., Krimigis, S.: Voyager observations of low-energy ions during solar cycle 23. Adv. Space Res. 32(4), 597–602 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0273-1177(03)00356-9
Drazin, P.G.: Johnson R.S.: Solitons. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Dubinin, E., Luhmann, J.G., Slavin, J.A.: Solar Wind and Terrestrial Planets (2020). https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190647926.013.184
Dunne, J.A.: Mariner 10 Venus encounter. Science 183(4131), 1289–1291 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.183.4131.1289
El-Shafeay, N., El-Taibany, W., Moslem, W., et al.: Super rogue waves at venusian ionosphere and mantle. Adv. Space Res. 72(6), 2427–2441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2023.05.025
Elmandoh, A., Fayad, A.A., Tolba, R.E., Soliton, M.W.M.: blow up, and shock-like ion-acoustic waves in magnetized plasma at Venus? Ionosphere. Indian J. Phys. 1(9) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-023-02608-z
Fayad, A.A., Elkamash, I.S., Fichtner, H., Lazar, M., El-Labany, S.K., Moslem, W.M.: On the propagation of electrostatic wave modes in the inhomogeneous ionospheric plasma of Venus. Phys. Plasmas 28(8) (2021b). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0050039
Fayad, A.A., Moslem, W.M., El-Labany, S.K.: Effect of streaming velocity, magnetic field, and higher-order correction on the nature of ion acoustic solitons in the Venusian ionosphere. Phys. Scr. 96(4), 045602 (2021a). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abdbf4
Futaana, Y., Wieser, G.S., Barabash, S., et al.: Solar wind interaction and impact on the Venus atmosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 212(3–4), 1453–1509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0362-8
Gloeckler, G.: The solar wind ion composition spectrometer. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. (1992)
Gringauz, K.: A comparison of the magnetospheres of Mars, Venus and the Earth. Adv. Space Res. 1(1), 5–24 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1177(81)90084-3
Han, J.N., Yang, X.X., Tian, D.X., et al.: Head-on collision of ion-acoustic solitary waves in a weakly relativistic electron?positron?ion plasma. Phys. Lett. A 372(27–28), 4817–4821 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2008.05.018
Heerikhuisen, J., Pogorelov, N.V., Zank, G.P., et al.: Pick-up ions in the outer heliosheath: a possible mechanism for the interstellar boundary explorer ribbon. Astrophys. J. 708(2), L126–L130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/2041-8205/708/2/l126
Hirota, R.: The Direct Method in Soliton Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004). https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511543043
Kerzhanovich, V.V., Mararov, Y.F., Marov, M.Y., et al.: Venera 11 and venera 12: preliminary evaluations of wind velocity and turbulence in the atmosphere of Venus. Moon Planets 23(3), 261–270 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00902043
Krimigis, S.M., Carbary, J.F., Keath, E.P., et al.: Characteristics of hot plasma in the Jovian magnetosphere: results from the Voyager spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 86(A10), 8227–8257 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1029/ja086ia10p08227
Liu, H.F., Yang, L., Tang, C.J., et al.: Alfvenic turbulence driven temperature anisotropies of thermal non-equilibrium ions. Europhys. Lett. 123(6), 65004 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/123/65004
Livadiotis, G., McComas, D.J.: Invariant kappa distribution in space plasmas out of equilibrium. Astrophys. J. 741(2), 88 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637x/741/2/88
Livadiotis, G., McComas, D.J.: Understanding kappa distributions: a toolbox for space science and astrophysics. Space Sci. Rev. 175(1–4), 183–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-013-9982-9
Lonngren, K.E.: Soliton experiments in plasmas. Plasma Phys. 25(9), 943–982 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1088/0032-1028/25/9/001
Lundin, R.: Ion acceleration and outflow from Mars and Venus: an overview. In: Space Sciences Series of ISSI, pp. 309–334. Springer (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3290-6
Maksimovic, M., Pierrard, V., Riley, P.: Ulysses electron distributions fitted with kappa functions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24(9), 1151–1154 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1029/97gl00992
Mann, G., Classen, H.T., Keppler, E., et al.: On electron acceleration at cir related shock waves. Astron. Astrophys. 391(2), 749–756 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20020866
Marov, M.Y., Grinspoon, D.H.: The Planet Venus. Press, London (1998)
Mauk, B.H.: Energetic ion characteristics and neutral gas interactions in Jupiter’s magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 109(A9) (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003ja010270
Moslem, W., Rezk, S., Abdelsalam, U., et al.: Shocklike soliton because of an impinge of protons and electrons solar particles with Venus ionosphere. Adv. Space Res. 61(8), 2190–2197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.01.023
Nakamura, Y.: Experiments on ion-acoustic solitons in plasmas invited review article. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 10(3), 180–195 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1109/tps.1982.4316165
Pierrard, V., Lemaire, J.: Fitting the AE-8 energy spectra with two Maxwellian functions. Radiat. Meas. 26(3), 333–337 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(96)00057-1
Russell, C., Scarf, F.: Evidence for lightning on Venus. Adv. Space Res. 10(5), 125–136 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1177(90)90173-w
Russell, C., Leinweber, H., Hart, R., et al.: Venus express observations of ULF and ELF waves in the Venus ionosphere: wave properties and sources. Icarus 226(2), 1527–1537 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2013.08.019
Saha, A., Banerjee, S.: Dynamical Systems and Nonlinear Waves in Plasmas. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2021). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003042549
Saha, A., Chatterjee, P.: Propagation and interaction of dust acoustic multi-soliton in dusty plasmas with q-nonextensive electrons and ions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 353(1), 169–177 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-2028-2
Saha, A., Tamang, J.: Effect of q-nonextensive hot electrons on bifurcations of nonlinear and supernonlinear ion-acoustic periodic waves. Adv. Space Res. 63(5), 1596–1606 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.11.010
Saini, N.S., Kaur, M., Singla, S.: Ion-acoustic nonlinear structures in a nonmaxwellian plasma in the presence of an electron beam. J. Astrophys. Astron. 43(2) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-022-09851-6
Salem, S., Moslem, W., Lazar, M., et al.: Ionospheric losses of Venus in the solar wind. Adv. Space Res. 65(1), 129–137 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.09.032
Sayed, F.S.H., Moslem, W.M., Tolba, R.E., et al.: Three-dimensional propagation of ion-acoustic waves in the plasma environment of the venusian ionosphere. Phys. Scr. 95(11), 115603 (2020b). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abbfcd
Sayed, F., Turky, A., Koramy, R., et al.: Nonlinear ion-acoustic waves at Venus ionosphere. Adv. Space Res. 66(6), 1276–1285 (2020a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2020.06.023
Scarf, F.L., Taylor, W.W.L., Russell, C.T., et al.: Lightning on Venus: orbiter detection of whistler signals. J. Geophys. Res. 85(A13), 8158 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1029/ja085ia13p08158
Singh, K., Saini, N.S.: Head-on collision of multi-solitons in a magnetized space dusty plasma in the presence of nonextensive polarization force. Waves Random Complex Media 33(4), 955–971 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2021.1893407
Singh, S.V., Rubia, R., Devanandhan, S., et al.: Nonlinear electrostatic waves in the auroral plasma. Phys. Scr. 95(7), 075602 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ab92db
Siscoe, G.L., Slavin, J.A.: Planetary magnetospheres. Rev. Geophys. 17(7), Article ID 1677 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1029/rg017i007p01677
Strangeway, R.: Plasma waves at Venus. Space Sci. Rev. 55(1–4) (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00177139
Strangeway, R.: Plasma waves and electromagnetic radiation at Venus and Mars. Adv. Space Res. 33(11), 1956–1967 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2003.08.040
Strogatz, S., Friedman, M., Mallinckrodt, A.J., et al.: Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: with applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering. Comput. Phys. 8(5), 532–532 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4823332
Suess, S.T., Tsurutani, B.T. (eds.): From the Sun: Auroras, Magnetic Storms, Solar Flares, Cosmic Rays American Geophysical Union (1998). https://doi.org/10.1029/sp050
Summers, D., Thorne, R.M.: The modified plasma dispersion function. Phys. Fluids B: Plasma Phys. 3(8), 1835–1847 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.859653
Svedhem, H., Titov, D., McCoy, D., et al.: Venus express-the first European mission to Venus. Planet. Space Sci. 55(12), 1636–1652 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/.j.pss.2007.01.013
Tamang, J., Sarkar, K., Saha, A.: Solitary wave solution and dynamic transition of dust ion acoustic waves in a collisional nonextensive dusty plasma with ionization effect. Phys. A, Stat. Mech. Appl. 505, 18–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.02.213
Tamang, J., Nkapkop, J.D.D., Ijaz, M.F., et al.: Dynamical properties of ion-acoustic waves in space plasma and its application to image encryption. IEEE Access 9, 18762–18782 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3054250
Taylor, F.W.: Venus before Venus express. Planet. Space Sci. 54(13–14), 1249–1262 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2006.04.031
Titov, D.V., Svedhem, H., Taylor, F.W., et al.: Venus express: highlights of the nominal mission. Solar Syst. Res. 43(3), 185–209 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/s0038094609030010
Tran, M.Q.: Ion acoustic solitons in a plasma: a review of their experimental properties and related theories. Phys. Scr. 20(3–4), 317–327 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/20/3-4/004
Vasyliunas, V.M.: A survey of low-energy electrons in the evening sector of the magnetosphere with OGO 1 and OGO 3. J. Geophys. Res. 73(9), 2839–2884 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1029/ja073i009p02839
Xiao, F., Shen, C., Wang, Y., et al.: Energetic electron distributions fitted with a relativistic kappa-type function at geosynchronous orbit. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113(A5) (2008). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007ja012903
Yadav, V.K.: Plasma waves around Venus and Mars. IETE Techn. Rev. 38(6), 622–661 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2020.1819889
Zhang, T., Delva, M., Baumjohann, W., et al.: Initial Venus express magnetic field observations of the magnetic barrier at solar minimum. Planet. Space Sci. 56(6), 790–795 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2007.10.013
Zouganelis, I., Maksimovic, M., Meyer-Vernet, N., et al.: A transonic collisionless model of the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 606(1), 542–554 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1086/382866
Acknowledgements
Kusum Chettri is thankful to Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology (SMIT) and Sikkim Manipal University (SMU) for providing research fellowship under TMA Pai University Research Fund (Ref. No. SMU/DOR/2023-59).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chettri, K., Tamang, J., Chatterjee, P. et al. Dynamics of nonlinear ion-acoustic waves in Venus’ lower ionosphere. Astrophys Space Sci 369, 44 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-024-04295-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-024-04295-6