Abstract
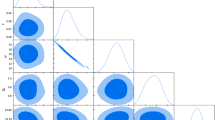
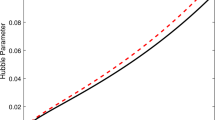
In this work, we constrain the time-varying vacuum energy models in Brans-Dicke theory within the framework of a flat Friedmann-Lamaître-Robertson-Walker space-time by using the latest observational data. In the first step, the analytical solution of field equations are found by considering the two functional forms of cosmological constant, viz. power-series form: \(\Lambda =n_{1} H+n_{2} H^{2}\) and power-law form: \(\Lambda \propto a^{-n}\), where \(n_{1}\), \(n_{2}\) and \(n\) are all constants, and \(H\) and \(a\) are the Hubble parameter and scale factor, respectively. Then, to test the viability of the models, the latest data sample such as Hubble \(H(z)\) data, Type Ia supernovae and baryon acoustic oscillations are used to constrain the model parameters. We apply the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method to find the best-fit values of the space parameters of both the models. The cosmological implications of the models are discussed by using the best-fit values of parameters. It is found that both the models are in good agreement with the datasets and are consistent with the analytical solutions. We use jerk parameter and selection criteria (AIC and BIC) to find the consistency of the proposed models with the observation as compared to \(\Lambda \)CDM model. Both the models explain the late-time acceleration of the Universe.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The manuscript has no associated data. The datasets used in this paper are openly available on https://doi.org/10.17909/T95Q4X.
References
Ade, P.A.R., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 517, A16 (2014)
Ade, P.A.R., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 594, 13 (2016)
Aghanim, N., et al. (Planck Collaboration): Astron. Astrophys. 641, A6 (2020). arXiv:1807.06209
Akaike, H.: IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19, 716 (1974)
Arik, M., Çalik, M.: Mod. Phys. Lett. A 21, 1241 (2006)
Arik, M., Çalik, M., Sheftel, M.B.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 17, 225 (2008)
Astier, P., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 447, 31 (2006)
Banerjee, N., Pavon, D.: Phys. Rev. D 63, 043504 (2001a)
Banerjee, N., Pavon, D.: Class. Quantum Gravity 18, 593 (2001b)
Banerjee, N., Pavon, D.: Phys. Lett. B 647, 447 (2007)
Basilakos, S.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 2347 (2009)
Basilakos, S., Plionis, M., Solà, J.: Phys. Rev. D 80, 083511 (2009)
Bertolami, O.: Nuovo Cimento B 93, 36 (1986)
Bessada, D., Miranda, O.D.: Phys. Rev. D 88, 083530 (2013)
Blake, C., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 418, 1707 (2011)
Blandford, R.D., et al.: ASP Conf. Ser. 339, 27 (2004). arXiv:astro-ph/0408279
Borges, H.A., Carneiro, S.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 37, 1385 (2005)
Brans, C.H., Dicke, R.H.: Phys. Rev. 124, 925 (1961)
Carneiro, S.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 12, 1669 (2003)
Carneiro, S., Pigozzo, C., Borges, H.A.: Phys. Rev. D 74, 023532 (2006)
Carneiro, S., Dantas, M.A., Pigozzo, C., Alcaniz, J.S.: Phys. Rev. D 77, 083504 (2008)
Carvalho, J.C., Lima, J.A.S., Waga, I.: Phys. Rev. D 46, 2404 (1992)
Chen, W., Wu, Y.S.: Phys. Rev. D 41, 695 (1990)
Copeland, E.J., Sami, M., Tsujikawa, S.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 15, 1753 (2006)
Das, S., Corasaniti, P.S., Khoury, J.: Phys. Rev. D 73, 083509 (2006)
Eisenstein, D.J., et al. (SDSS Collab.): Astrophys. J. 633, 560 (2005). arXiv:astro-ph/0501171
Feldman, H.A., et al.: Astrophys. J. 596, L131 (2003)
Foreman-Mackey, D., Hogg, D., Lang, D., Goodman, J.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 125, 306 (2013)
Gaztañaga, E., Cabré, A., Hui, L.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399, 1663 (2009)
Gomez-Gomar, J., Isern, J., Jean, P.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 295, 1 (1998)
Gomez-Valent, A., et al.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 01, 004 (2015a). arXiv:1409.7048
Gomez-Valent, A., et al.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 12, 048 (2015b). arXiv:1509.03298
Grande, J., Sola, J., Stefancic, H.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 8, 11 (2006)
Jayadevan, A.P., et al.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 364, 67 (2019)
Johri, V.P., Kalyani, D.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 26, 1217 (1994)
Karchi, A.P.K., Shojaie, H.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 25, 1650045 (2016)
Karimkhani, E., Khoadam-Mohammadi, A.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 364, 177 (2019)
Khokhlov, A., Mueller, E., Hoeflich, P.: Astron. Astrophys. 270, 223 (1993)
Kim, H.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 364, 813 (2005)
Komatsu, E., et al.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 180, 330 (2009)
Komatsu, E., et al.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 192, 11 (2011)
Kumar, P., Singh, C.P.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 362, 52 (2017)
Li, J.-X., Wu, F.-Q., Li, Y.-C., Gong, Y., Chen, X.-L.: Res. Astron. Astrophys. 15(12), 2151 (2015)
Liddle, A.R.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 377, L74 (2007)
Lima, J.A.S.: Phys. Rev. D 54, 2571 (1996)
Lima, J.A.S., Basilakos, S., Solà, J.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 431, 923 (2013)
Mota, D.F., Barrow, J.D.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 349, 291 (2004)
Oliveira, F.A., Costa, F.E.M., Lima, J.A.S.: Class. Quantum Gravity 31(04), 045004 (2014)
Overduin, J.M., Cooperstock, S.: Phys. Rev. D 58, 043506 (1998)
Ozer, M., Taha, O.: Phys. Lett. B 171, 363 (1986)
Ozer, M., Taha, O.: Nucl. Phys. B 287, 776 (1987)
Peebles, P.L.E., Ratra, B.: Astrophys. J. 325, L17 (1988)
Perico, E.L.D., et al.: Phys. Rev. D 88, 063531 (2013)
Perlmutter, S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 517, 565 (1999)
Pimental, L.O.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 112, 175 (1985)
Ram, S., Singh, C.P.: Nuovo Cimento B 114, 245 (1999)
Rapetti, D., Allen, S.W., Amin, M.A., Blandford, R.D.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 375, 1510 (2007)
Riess, A.G., et al.: Astrophys. J. 607, 665 (2004)
Sanchez, A.G., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 425, 415 (2011)
Schützhold, R.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 081302 (2002)
Schwarz, G.: Ann. Stat. 6, 461 (1978)
Scolnic, D.M., et al.: Astrophys. J. 859, 101 (2018)
Sen, S., Sen, A.A.: Phys. Rev. D 63, 124006 (2001)
Sen, A.A., Sen, S., Sethi, S.: Phys. Rev. D 63, 107501 (2001)
Shapiro, I.L., Solá, J.: Phys. Lett. B 475, 236 (2000)
Sharif, M., Syed Asit Ali Shah: Mod. Phys. Lett. A 34, 1950083 (2019)
Sheykhi, A.: Phys. Rev. D 81, 023525 (2010)
Singh, C.P.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 338, 411 (2012)
Singh, C.P., Kaur, S.: Phys. Rev. D 100, 084057 (2019)
Singh, C.P., Kaur, S.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 365, 2 (2020)
Singh, C.P., Kumar, P.: Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 3297 (2017)
Singh, C.P., Solà Peracaula, J.: Eur. Phys. J. C 81, 960 (2021)
Solà, J., Gomez-Valent, A., de Cruz Perez, J.: Astrophys. J. 836, 43 (2017)
Spergel, D.N., et al.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 170, 377 (2007)
Srivastava, M., Singh, C.P.: Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 15, 1850124 (2018)
Stern, D., Jimenez, R., Verde, L., Kaminokowski, M., Stanford, S.A.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 02, 08 (2010)
Szydlowski, M., Stachowski, A.: J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 066, 10 (2015)
Uhera, K., Kim, C.W.: Phys. Rev. D 26, 2575 (1982)
Weinberg, S.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 61, 1 (1989)
Xu, L., et al.: Mod. Phys. Lett. A 25, 1441 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewer for thoughtful remarks and suggestions. One of the authors, VK is thankful to Delhi Technological University, New Delhi for providing Research Fellowship to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.P. Singh has written the main manuscript text, conceptualization, investigation, methodology and observation part. Vinita Khatri has prepared the figures and observation part. Both the authors have reviewed the manuscript and agreed for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khatri, V., Singh, C.P. Constraining the time-varying vacuum energy models in Brans-Dicke theory. Astrophys Space Sci 368, 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-023-04173-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-023-04173-7