Abstract
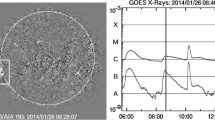
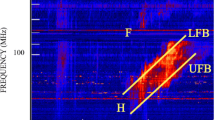
It is now well established that Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) may produce shocks in near Sun and interplanetary medium. A Type-II radio burst is characterized by shock and associated emission with very slow frequency drift rate (∼0.1 MHz/sec). A CME driven shock and their velocity, acceleration/deceleration signature can be observed by a Type-II solar radio burst which drifts with the shock speed and is split in bands of plasma radio emission. These emissions can be seen in radio spectrographs as split bands both in fundamental and harmonic frequencies close to a ratio of 1:2. In this paper, we present an analysis of a CME associated with a band splitting Type-II radio burst observed using multi-instruments in multi-wavelengths. We observed the CME event that occurred in 02 May 2013 (05:24 UT) and is associated with an M1.1 class solar flare from the active region NOAA 11731 located at N10W23 on the solar disk. We use the widely accepted Newkirk coronal density model to estimate the height in the solar atmosphere to compare our results. We conclude that the speed of CME is high enough to produce a Type-II solar radio burst. The analysis of this paper also involved an estimation of the coronal ambient magnetic field and its comparison with the empirical active region magnetic field model (Dulk and McLean in Sol. Phys. 57:279, 1978). This shows the good results. Observations provide sufficient evidence that the unusual patch signature in Type-II solar radio burst is due to the CME–CME interaction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., et al.: Sol. Phys. 162, 357 (1995)
Cho, K.-S., Lee, J., Gary, D.E., Moon, Y.-J., Park, Y.D.: Astrophys. J. 665, 799–804 (2007)
Dagnew, Fithanegest Kassa, Gopalswamy, N., Tessema, S.B., Umuhire, A.C., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, Pretti, Xie, Hong: Solar and Stellar Astrophysics (2020)
Domingo, V., Fleck, B., Poland, A.I.: Space Sci. Rev. 72, 81 (1995)
Dulk, G.A., McLean, D.J.: Sol. Phys. 57, 279 (1978)
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P., Usoskin, I.G.: Properties of ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during Solar Cycle 23, Space Sci. Rev. p. 171 (2012)
Gopalswamy, N.: In: Rucker, H.O., Kurth, W.S., Louarn, P., Fischer, G. (eds.) Coronal Mass Ejections and Solar Radio Emissions, Planetary, Solar and Heliospheric Radio Emissions (PRE VII), p. 325. Austrian Acad. Sci. Press, Vienna (2011)
Gopalswamy, N., et al.: Coronal mass ejections, type II radio bursts, and solar energetic particle events in the SOHO era. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3033–3047 (2008)
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Monstein, C.: Astrophys. J. 863, L39 (2018)
Leblanc, Y., Dulk, George A., Bougeret, Jean-Louis, et al.: Sol. Phys. 183, 165 (1998)
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., et al.: Sol. Phys. 275, 17 (2012)
Newkirk, G. Jr.: Astrophys. J. 133, 983 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1086/147104
Newkirk, G.A.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 5, 213 (1967)
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: Sol. Phys. 275, 3 (2012)
Raymond, J.C., et al.: SOHO and radio observations of a CME shock wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1439–1442 (2000)
Satio, K., et al.: A non-spherical axisymmetric model of the solar K corona of the minimum type. Ann. Tokyo Astron. Obs. Ser. 2, 12–53 (1970)
Smerd, S.F., Sheridan, K.V., Stewart, R.T.: In: Newkirk, G.A. (ed.) Coronal Disturbances. IAU Symp., vol. 57, p. 389. Reidel, Dordrecht (1974)
Smerd, S.F., Sheridan, K.V., Stewart, R.T.: Astrophys. Lett. 16, 23 (1975)
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Kontar, E.P., Krucker, S., Vršnak, B.: Astrophys. J. 712, 1410 (2010)
Vasanth, V., Umapathy, S., Vršnak, B., et al.: Investigation of the coronal magnetic field using a type II solar radio burst. Sol. Phys. 289, 251–261 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0318-4
Vršnak, B., Aurass, H., Magdalenic, J., Gopalswamy, N.: Astron. Astrophys. 377, 321 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20011067
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge NASA’s open data policy for SOHO, STEREO, SDO and WIND data. We acknowledge the NOAA/NGDC for making the GOES soft X-ray and Dst data available to be included in the CME catalog of LASCO/SOHO available at NASA’s CDAW data warehouse.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lata Soni, S., Ebenezer, E. & lal Yadav, M. Multi-wavelength analysis of CME-driven shock and Type II solar radio burst band-splitting. Astrophys Space Sci 366, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-021-03933-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-021-03933-7