Abstract
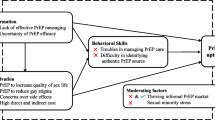
Antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is highly effective in preventing HIV. Despite its promise, PrEP use is low, especially among young Black men who have sex with men (YBMSM). The prevalence of HIV in Mississippi (MS) is among the highest in the United States, with the bulk of new infections occurring amongst YBMSM living in Jackson, MS. We recruited 20 PrEP-eligible YBMSM and 10 clinic staff from MS health clinics between October 2021 and April 2022. Data were collected remotely using in-depth interviews and a brief survey, which lasted approximately 45–60 min. Interview content included PrEP knowledge/experiences, HIV risk perception, and PrEP use barriers and facilitators. Qualitative data were coded then organized using NVivo. Using thematic analysis methodology, data were assessed for current barriers to PrEP use. An array of barriers were identified by participants. Barriers included structural factors (cost of PrEP, lack of discreet clinics, time commitment, competing interests); social factors (unaware of HIV risk, stigma and homophobia, fear that partners would find out about PrEP use, not knowing anyone on PrEP); behavioral factors (sexual risk factors, denial, less priority for prevention vs treatment); and clinical factors (misunderstood side effects, fear PrEP won’t work). Significant barriers to PrEP use among YBMSM stem from structural, social, behavioral, and clinical factors. These results will inform intervention efforts tailored to mitigate barriers and improve PrEP uptake among YBMSM in the southern United States.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
N/A.
References
Adeagbo, O., Harrison, S., Qiao, S., & Li, X. (2021). Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) uptake among black men who have sex with men (BMSM) in the Southern U.S. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9715.
AIDSVu. (2022). Local data: Mississippi https://aidsvu.org/local-data/united-states/south/mississippi/
Arnold, T., Brinkley-Rubinstein, L., Chan, P. A., Perez-Brumer, A., Bologna, E. S., Beauchamps, L., Johnson, K., Mena, L., & Nunn, A. (2017). Social, structural, behavioral and clinical factors influencing retention in Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) care in Mississippi. PLoS ONE, 12(2), e0172354. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172354
Braun, V., Clarke, V., Hayfield, N., & Terry, G. (2019). Thematic analysis. In P. Liamputtong (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in health social sciences (pp. 843–860). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_103
Bush, S., Magnuson, D., Rawlings, K. M., Hawkins, T., McCallister, S., & Mera Giler, R. (2016). ASM/ICAAC: Racial characteristics of FTC/TDF for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the US. In Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Boston, MA. http://www.natap.org/2016/HIV/062216_02.htm
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2018). HIV prevention pill not reaching most Americans who could benefit – especially people of color https://www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/newsroom/2018/croi-2018-prep-press-release.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). HIV in the United States by region: HIV diagnoses. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/statistics/overview/diagnoses.html
Chan, G. A., Johnson, K. L., Mosca, N. G., Dobbs, T. E., Dombrowski, J. C., Bennett, A. B., Buskin, S. E., & Golden, M. R. (2017). Emerging regional and racial disparities in the lifetime risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection among men who have sex with men: A comparative life table analysis in King County, WA and Mississippi. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 44(4), 227–232. https://doi.org/10.1097/olq.0000000000000589
Chase, E., Mena, L., Johnson, K. L., Prather, M., & Khosropour, C. M. (2023). Patterns of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use in a population accessing PrEP in Jackson, Mississippi. AIDS and Behavior, 27, 1082–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-022-03845-9
Edeza, A., Karina Santamaria, E., Valente, P. K., Gomez, A., Ogunbajo, A., & Biello, K. (2021). Experienced barriers to adherence to pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention among MSM: A systematic review and meta-ethnography of qualitative studies. AIDS Care, 33(6), 697–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2020.1778628
Elopre, L., Ott, C., Lambert, C. C., Amico, K. R., Sullivan, P. S., Marrazzo, J., Mugavero, M. J., & Turan, J. M. (2021). Missed prevention opportunities: Why young, black MSM with recent HIV diagnosis did not access HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis services. AIDS and Behavior, 25(5), 1464–1473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-020-02985-0
Ezennia, O., Geter, A., & Smith, D. K. (2019). The PrEP care continuum and black men who have sex with men: A scoping review of published data on awareness, uptake, adherence, and retention in PrEP care. AIDS and Behavior, 23(10), 2654–2673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-019-02641-2
Fauci, A. S., Redfield, R. R., Sigounas, G., Weahkee, M. D., & Giroir, B. P. (2019). Ending the HIV epidemic: A plan for the United States. Journal of the American Medical Association, 321(9), 844–845. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.1343
Fields, S. D., & Tung, E. (2021). Patient-focused selection of PrEP medication for individuals at risk of HIV: A narrative review. Infectious Diseases and Therapy, 10(1), 165–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40121-020-00384-5
Grant, R. M., Lama, J. R., Anderson, P. L., McMahan, V., Liu, A. Y., Vargas, L., Goicochea, P., Casapia, M., Guanira-Carranza, J. V., Ramirez-Cardich, M. E., Montoya-Herrera, O., Fernandez, T., Veloso, V. G., Buchbinder, S. P., Chariyalertsak, S., Schechter, M., Bekker, L. G., Mayer, K. H., Kallas, E. G., & Glidden, D. V. (2010). Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. New England Journal of Medicine, 363(27), 2587–2599. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1011205
Greene, G. J., Swann, G., Fought, A. J., Carballo-Diéguez, A., Hope, T. J., Kiser, P. F., Mustanski, B., & D’Aquila, R. T. (2017). Preferences for long-acting pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), daily oral PrEP, or condoms for HIV prevention among U.S. men who have sex with men. AIDS and Behavior, 21(5), 1336–1349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-016-1565-9
Hannaford, A., Lipshie-Williams, M., Starrels, J. L., Arnsten, J. H., Rizzuto, J., Cohen, P., Jacobs, D., & Patel, V. V. (2018). The use of online posts to identify barriers to and facilitators of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among men who have sex with men: A comparison to a systematic review of the peer-reviewed literature. AIDS and Behavior, 22(4), 1080–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-017-2011-3
Harris, P. A., Taylor, R., Thielke, R., Payne, J., Gonzalez, N., & Conde, J. G. (2009). Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 42(2), 377–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
He, J., Wang, Y., Du, Z., Liao, J., He, N., & Hao, Y. (2020). Peer education for HIV prevention among high-risk groups: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infectious Diseases, 20(1), 338. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05003-9
Hrostowski, S., & Pelts, M. (2018). The promises and challenges of preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in Mississippi. Journal of HIV & Retro Virus. https://doi.org/10.21767/2471-9676.100038
IBM. (2021). IBM SPSS Statistics (Version 28) [Software]. IBM Corporation.
Marcus, J. L., Volk, J. E., Pinder, J., Liu, A. Y., Bacon, O., Hare, C. B., & Cohen, S. E. (2016). Successful implementation of HIV preexposure prophylaxis: Lessons learned from three clinical settings. Current HIV/AIDS Reports, 13(2), 116–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-016-0308-x
Matacotta, J. J., Rosales-Perez, F. J., & Carrillo, C. M. (2020). HIV preexposure prophylaxis and treatment as prevention—beliefs and access barriers in men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women: A systematic review. Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Reviews, 7(3), 265–274. https://doi.org/10.17294/2330-0698.1737
Ogbuagu, O., Ruane, P. J., Podzamczer, D., Salazar, L. C., Henry, K., Asmuth, D. M., Wohl, D., Gilson, R., Shao, Y., Ebrahimi, R., Cox, S., Kintu, A., Carter, C., Das, M., Baeten, J. M., Brainard, D. M., Whitlock, G., Brunetta, J. M., Kronborg, G., & Spinner, C. D. (2021). Long-term safety and efficacy of emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide vs emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for HIV-1 pre-exposure prophylaxis: Week 96 results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet HIV, 8(7), e397–e407. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2352-3018(21)00071-0
Pichon, L. C., Teti, M., McGoy, S., Murry, V. M., & Juarez, P. D. (2022). Engaging Black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the South in identifying strategies to increase PrEP uptake. BMC Health Services Research, 22(1), 1491. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-08914-2
QSR International Pty Ltd. (2020). NVivo (Version 12). https://www.qsrinternational.com/nvivo-qualitative-data-analysis-software/home?_ga=2.147882994.43489428.1663089518-1458777242.1663089518
Quinn, K. G., Christenson, E., Spector, A., Amirkhanian, Y., & Kelly, J. A. (2020). The influence of peers on PrEP perceptions and use among young black gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men: A qualitative examination. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 49(6), 2129–2143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-019-01593-x
Rawlings, M. K., & Parham-Hopson, D. (2021). HIV in the South. In B. Ojikutu & V. Stone (Eds.), HIV in US communities of color (pp. 135–146). Springer.
Reif, S., Wilson, E., & McAllaster, C. (2018). Perceptions and impact of HIV stigma among high risk populations in the US Deep South. Journal of HIV and AIDS, 4(2). https://doi.org/10.16966/2380-5536.154
Rosenberg, E. S., Grey, J. A., Sanchez, T. H., & Sullivan, P. S. (2016). Rates of prevalent HIV infection, prevalent diagnoses, and new diagnoses among men who have sex with men in US states, metropolitan statistical areas, and counties, 2012–2013. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance, 2(1), e22. https://doi.org/10.2196/publichealth.5684
Rouffiac, A.-E., Whiteley, L., Brown, L., Mena, L., Craker, L., Healy, M., & Haubrick, K. (2020). A mobile intervention to improve uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis for southern black men who have sex with men: Protocol for intervention development and pilot randomized controlled trial. JMIR Research Protocols, 9(2), e15781–e15781. https://doi.org/10.2196/15781
Russ, S., Zhang, C., & Liu, Y. (2021). Pre-exposure prophylaxis care continuum, barriers, and facilitators among black men who have sex with men in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS and Behavior, 25(7), 2278–2288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-020-03156-x
State of Mississippi Department of Health. (2015). 2015 STD/HIV epidemiologic profile. https://msdh.ms.gov/msdhsite/_static/resources/7543.pdf
Sullivan, P. S., Salazar, L., Buchbinder, S., & Sanchez, T. H. (2009). Estimating the proportion of HIV transmissions from main sex partners among men who have sex with men in five US cities. AIDS, 23(9), 1153–1162. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832baa34
United States Food and Drug Administration. (2021). FDA approves first injectable treatment for HIV pre-exposure prevention https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-injectable-treatment-hiv-pre-exposure-prevention
Whiteley, L., Rouffiac, A.-E., Brown, L., Mena, L., Craker, L., Healy, M., & Haubrick, K. (2019). A mobile intervention to improve uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for Southern Black MSM: A protocol for intervention development and randomized controlled trial (Preprint). doi:https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.15781
Whiteley, L., Craker, L., Sun, S., Tarantino, N., Hershkowitz, D., Moskowitz, J., Arnold, T., Haubrick, K., Olsen, E., Mena, L., & Brown, L. K. (2021). Factors associated with PrEP adherence among MSM living in Jackson, Mississippi. Journal of HIV/AIDS & Social Services, 20(3), 246–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/15381501.2021.1956666
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Mental Health: K23MH124539-01A1 and T32MH078788. Author time was also supported by the Providence/Boston Center for AIDS Research P30AI042853. Dr. Elwy is partially supported by Institutional Development Award Number U54GM115677 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health, which funds Advance Clinical and Translational Research (Advance-CTR). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Rogers receives research funding from Gilead Sciences #IN-US-276-5463. Authors have disclosed all conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the University of Mississippi Institutional Review Board reviewed and approved this project, and its conduct was consistent with applicable federal law (Approval Number FWA00003630).
Informed Consent
All participants completed written informed consent prior to participating.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arnold, T., Giorlando, K.K., Barnett, A.P. et al. Social, Structural, Behavioral, and Clinical Barriers Influencing Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Use Among Young Black Men Who Have Sex with Men in the South: A Qualitative Update to a 2016 Study. Arch Sex Behav 53, 785–797 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-023-02721-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-023-02721-4