Abstract
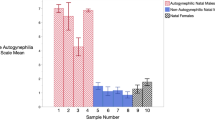
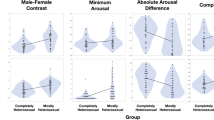
Men’s sexual arousal patterns have been an important window into the nature of their erotic interests. Autogynephilia is a natal male’s paraphilic tendency to be sexually aroused by the thought or image of being a woman. Autogynephilic arousal per se is difficult to assess objectively, because it is inwardly focused. However, assessing sexual arousal patterns of autogynephilic males in response to external stimuli is also potentially useful. For example, there is substantial association between autogynephilia and gynandromorphophilia (GAMP), or sexual attraction to gynandromorphs (GAMs), colloquially “she-males.” GAMP men’s sexual arousal patterns in response to GAM, female, and male stimuli have recently been characterized. In the present study, we extended this understanding by comparing the sexual arousal patterns of autogynephilic male cross-dressers, GAMP men, heterosexual men, and homosexual men. Erotic stimuli included sexually explicit videos of men, women, and GAMs. Autogynephilic men were much more similar in their arousal patterns to heterosexual and GAMP men than to homosexual men. However, similar to GAMP men, autogynephilic men showed increased arousal by GAM stimuli relative to female stimuli compared with heterosexual men.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, J. M. (2003). The man who would be queen: The science of gender-bending and transsexualism. Washington, DC: Joseph Henry Press.
Bailey, J. M. (2009). What is sexual orientation and do women have one? In D. A. Hope (Ed.), Contemporary perspectives on lesbian, gay, and bisexual identities (pp. 43–63). New York, NY: Springer.
Bailey, J. M., & Triea, K. (2007). What many transgender activists don’t want you to know: And why you should know it anyway. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine, 50, 521–534.
Blanchard, R. (1985). Typology of male-to-female transsexualism. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 14, 247–261.
Blanchard, R. (1988). Nonhomosexual gender dysphoria. Journal of Sex Research, 24, 188–193.
Blanchard, R. (1989a). The classification and labeling of nonhomosexual gender dysphorias. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 18, 315–334.
Blanchard, R. (1989b). The concept of autogynephilia and the typology of male gender dysphoria. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 177, 616–623.
Blanchard, R. (1991). Clinical observations and systematic studies of autogynephilia. Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy, 17, 235–251.
Blanchard, R. (1992). Nonmonotonic relation of autogynephilia and heterosexual attraction. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101, 271–276.
Blanchard, R. (1993a). Partial versus complete autogynephilia and gender dysphoria. Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy, 19, 301–307.
Blanchard, R. (1993b). The she-male phenomenon and the concept of partial autogynephilia. Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy, 19, 69–76.
Blanchard, R. (1993c). Varieties of autogynephilia and their relationship to gender dysphoria. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 22, 241–251.
Blanchard, R., Clemmensen, L. H., & Steiner, B. W. (1985). Social desirability response set and systematic distortion in the self-report of adult male gender patients. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 14, 505–516.
Blanchard, R., Clemmensen, L. H., & Steiner, B. W. (1987). Heterosexual and homosexual gender dysphoria. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 16, 139–152.
Blanchard, R., Klassen, P. E., Dickey, R., Kuban, M. E., & Blak, T. (2001). Sensitivity and specificity of the phallometric test for pedophilia in nonadmitting sex offenders. Psychological Assessment, 13, 118–126.
Blanchard, R., Racansky, I. G., & Steiner, B. W. (1986). Phallometric detection of fetishistic arousal in heterosexual male cross-dressers. Journal of Sex Research, 22, 452–462.
Chivers, M. L., Rieger, G., Latty, E., & Bailey, J. M. (2004). A sex difference in the specificity of sexual arousal. Psychological Science, 15, 736–744.
Chivers, M. L., Seto, M. C., & Blanchard, R. (2007). Gender and sexual orientation differences in sexual response to sexual activities versus gender of actors in sexual films. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 1108–1121.
Dreger, A. D. (2008). The controversy surrounding The man who would be queen: A case history of the politics of science, identity, and sex in the Internet age. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 37, 366–421.
Freund, K., & Blanchard, R. (1993). Erotic target location errors in male gender dysphorics, paedophiles, and fetishists. British Journal of Psychiatry, 162, 558–563.
Hsu, K. J., Rosenthal, A. M., & Bailey, J. M. (2015). The psychometric structure of items assessing autogynephilia. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 44, 1301–1312.
Hsu, K. J., Rosenthal, A. M., Miller, D. I., & Bailey, J. M. (2016). Who are gynandromorphophilic men? Characterizing men with sexual interest in transgender women. Psychological Medicine, 46, 819–827.
Janssen, E. (2002). Psychophysiological measures of sexual response. In M. W. Wiederman & B. E. Whitley (Eds.), Handbook for conducting research on human sexuality (pp. 139–171). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Judd, C. M., & Kenny, D. A. (2010). Data analysis in social psychology: Recent and recurring issues. In S. T. Fiske, D. T. Gilbert, & G. Lindzey (Eds.), Handbook of social psychology (5th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 115–139). New York, NY: Wiley.
Lawrence, A. A. (2004). Autogynephilia: A paraphilic model of gender identity disorder. Journal of Gay and Lesbian Psychotherapy, 8, 69–87.
Lawrence, A. A. (2007). Becoming what we love: Autogynephilic transsexualism conceptualized as an expression of romantic love. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine, 50, 506–520.
Lawrence, A. A. (2013). Men trapped in men’s bodies: Narratives of autogynephilic transsexualism. New York, NY: Springer.
Lawrence, A. A., Latty, E. M., Chivers, M. L., & Bailey, J. M. (2005). Measurement of sexual arousal in postoperative male-to-female transsexuals using vaginal photoplethysmography. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 34, 135–145.
Maxwell, S. E., & Delaney, H. D. (2004). Designing experiments and analyzing data: A model comparison perspective (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Rosenthal, A. M., Hsu, K. J., & Bailey, J. M. (in press). Who are gynandromorphophilic men? An Internet survey of men with sexual interest in transgender women. Archives of Sexual Behavior.
Rosenthal, R., & Rosnow, R. L. (1985). Contrast analysis: Focused comparisons in the analysis of variance. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Acknowledgments
We thank Arundati Nagendra for invaluable assistance in maintaining study expenses and materials as well as in recruiting and running participants.
Funding
This study was supported by a research grant from the Provost of Northwestern University (grant number 171-4024200-10031372).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interests related to the study.
Ethical Standards
All research methods and recruitment strategies were approved in accordance with the ethical standards of Northwestern University’s Institutional Review Board for research involving human participants.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, K.J., Rosenthal, A.M., Miller, D.I. et al. Sexual Arousal Patterns of Autogynephilic Male Cross-Dressers. Arch Sex Behav 46, 247–253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-016-0826-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-016-0826-z