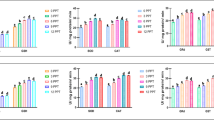
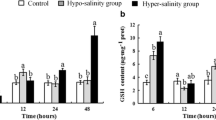
Abstract
Salinity is an important environmental factor that induces oxidative stress in shrimp. This study evaluated the effects of abrupt low-salinity stress (23, 17, and 11) on histological structure, lipid peroxidation, mRNA levels and activities of antioxidant enzymes, and gene expression of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling molecules at different times (6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h) in the gills and hepatopancreas of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Mild or strong increase in the levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) and antioxidant genes and enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) were observed after short-term exposure (6 and 12 h). After 48 and/or 96 h of exposure to low salinity, Nrf2 was significantly downregulated (P < 0.05), which was accompanied by downregulation of the levels of Nrf2-Keap1 pathway-related genes and enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GPX, along with upregulation of Kelch-like-ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Pathological alterations were also observed in the gills and hepatopancreas of M. japonicus after 96 h of exposure to different salinities. The observed changes in antioxidant gene expression are consistent with a requirement for Nrf2 in the induction of antioxidant genes. Furthermore, there was a negative correlation between the mRNA levels of Nrf2 and Keap1, indicating that Keap1 is important for inhibition of the Nrf2 response. Negative relationships were observed between lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities, while positive relationships were observed between activities and gene expression levels of antioxidant enzymes, suggesting the changes in molecular and enzyme activity levels may provide protection against damage from low-salinity stress. In conclusion, our data demonstrated that Nrf2-Keap1 signaling is important for modulating the gene expression levels of antioxidant enzymes. This is the first study to elucidate the effects of low-salinity stress on antioxidant responses in M. japonicus through the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. The results provide insights into the mechanisms by which crustaceans resist salinity stress.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data in this study are available from the author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bebianno MJ, Company R, Serafim A, Camus L, Cosson RP, Fiala-Médoni A (2005) Antioxidant systems and lipid peroxidation in Bathymodiolus azoricus from Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal vent fields. Aquat Toxicol 75:354–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.08.013
Dimitrios, Tsikas (2017) Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem 13-30.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Dodson M, Redmann M, Rajasekaran NS, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J (2015) KEAP1-NRF2 signalling and autophagy in protection against oxidative and reductive proteotoxicity. Biochem J 471:431. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ4710431
Dodson M, Redmann M, Rajasekaran NS, Darley-Usmar V, Zhang J (2015) KEAP1-NRF2 signalling and autophagy in protection against oxidative and reductive proteotoxicity. Biochemical Journal 469:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20150568
FAO (2020) The State of World Fisheries Aquaculture 2020. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.https://doi.org/10.4060/ca9229e
Fei Y, Peng S, Peng S, Shi Z (2011) Effects of low salinity on antioxidant enzymes activities in kidney and muscle of juvenile silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. Acta Ecol Sin 31:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.11.009
Guo YL, Wu P, Jiang WD, Liu Y, Kuang SY, Jiang J, Tang L, Tang WN, Zhang YA, Zhou XQ (2018) The impaired immune function and structural integrity by dietary iron deficiency or excess in gill of fish after infection with Flavobacterium columnare: regulation of NF-kappa B, TOR, JNK, p38MAPK, Nrf2 and MLCK signalling. Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:593–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.01.027
Halliwell B (2012) Free radicals and antioxidants: updating a personal view. Nutr Rev 70:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00476.x
Han D, Chen W, Gu X, Shan R, Zou J, Liu G, Shahid M, Gao J, Han B (2017) Cytoprotective effect of chlorogenic acid against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8:14680–14692. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14747
Huang Y, Li Q, Yuan Y, Zhang Z, Jiang B, Yang S, Jian J (2022) Silencing of Nrf2 in Litopenaeus vannamei, decreased the antioxidant capacity, and increased apoptosis and autophagy. Fish Shellfish Immunol 122:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2022.02.010
Ighodaro O M, Akinloye O A (2017) First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex J Med 287-293.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2017.09.001
Kaspar JW, Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2009) Nrf2: Nrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radical Biol Med 47:1304–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.035
Li CC, Yeh ST, Chen JC (2010) Innate immunity of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei weakened by the combination of a Vibrio alginolyticus injection and low-salinity stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.10.003
Liu Y, Wang WN, Wang AL, Wang JM, Sun RY (2007) Effects of dietary vitamin E supplementation on antioxidant enzyme activities in Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) exposed to acute salinity changes. Aquaculture 265:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.02.010
Liu X, Liu H, Zhai Y, Li Y, Zhu X, Zhang W (2017) Laminarin protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in MRC-5 cells possibly via regulating NRF2. PeerJ 5:36–42. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3642
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2002) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006
Ma J, Li M, Kumar KP, Li J, He Q, Zhang Y, Owais A, Yin H, Tao W, Jing S (2018) Protective effects of cichoric acid on H2O2-induced oxidative injury in hepatocytes and larval zebrafish models. Biomed Pharmacother 104:679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.081
Malandrakis EE, Exadactylos A, Dadali O, Golomazou E, Klaoudatos S, Panagiotaki P (2014) Molecular cloning of four glutathione peroxidase (GPx) homologs and expression analysis during stress exposure of the marine teleost Sparus aurata. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 168:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2013.11.005
Martínez-Alvarez R, Hidalgo MC, Domezain A, Morales AE, Sanz A (2002) Physiological changes of sturgeon Acipenser naccarii caused by increasing environmental salinity. J Exp Biol 205:3699. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.205.23.3699
Nam Y, Cho Y, Choi B, Kim K, Kim S, Dong K (2010) Alteration of antioxidant enzymes at the mRNA level during short-term starvation of rockbream Oplegnathus fasciatus. Fish Sci 71:1385–1387. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01107.x
Pan L-Q, Zhang L-J, Liu H-Y (2007) Effects of salinity and pH on ion-transport enzyme activities, survival and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei postlarvae. Aquaculture 273:711–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.07.218
Ren X, Xu Y, Yu Z, Mu C, Li J (2020) The role of Nrf2 in mitigating cadmium-induced oxidative stress of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Environ Pollut 269:116112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116112
Sadi G, Bozan D, Yildiz HB (2014) Redox regulation of antioxidant enzymes: post-translational modulation of catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity by resveratrol in diabetic rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 393:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2051-1
Sarkar S, Mukherjee S, Chattopadhyay A, Bhattacharya S (2014) Low dose of arsenic trioxide triggers oxidative stress in zebrafish brain: expression of antioxidant genes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.012
Silvestre F (2020) Signaling pathways of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms exposed to xenobiotics. J Exp Zool Part A Ecol Integr Physiol 333:436–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.2356
Storey KB (1996) Oxidative stress: animal adaptations in nature. Brazilian J Med Biol Res = Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas 29:1715
Sykiotis GP, Bohmann D (2008) Keap1/Nrf2 signaling regulates oxidative stress tolerance and lifespan in Drosophila. Dev Cell 14:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.12.002
Tong KI, Kobayashi A, Katsuoka F, Yamamoto M (2006) Two-site substrate recognition model for the Keap1-Nrf2 system: a hinge and latch mechanism. Biol Chem 277:36544–31320. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2006.164
Tsoi KH, Ma KY, Wu TH, Fennessy ST, Chu KH, Chan TY (2014) Verification of the cryptic species Penaeus pulchricaudatus in the commercially important kuruma shrimp P. japonicus (Decapoda: Penaeidae) using molecular taxonomy. Invertebr Syst 28:476–490. https://doi.org/10.1071/is14001
Wang M, Zhu Z (2019) Nrf2 is involved in osmoregulation, antioxidation and immunopotentiation in Coilia nasus under salinity stress. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 33:1453–1463. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2019.1673671
Winston GW, Giulio R (1991) Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 19:137–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445X(91)90033-6
Xie SW, Tian LX, Jin Y, Yang HJ, Liang GY, Liu YJ (2014) Effect of glycine supplementation on growth performance, body composition and salinity stress of juvenile Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei fed low fishmeal diet. Aquaculture 418–419:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.10.023
Yun W, Yd A, Jha C, Jw A, Cz A, Sja B, Hla C, Zhe ZB (2021) Characterization and functional study of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in black tiger shrimp ( Penaeus monodon ). Fish Shellfish Immunol 119:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2021.10.016
Zeng L, Zheng J-L, Wang Y-H, Xu M-Y, Zhu A-Y (2016) The role of Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in inorganic mercury induced oxidative stress in the liver of large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.002
Zeng L, Ai CX, Wang YH, Zhang JS, Wu CW (2017) Abrupt salinity stress induces oxidative stress via the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish Physiol Biochem 43:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0334-z
Acknowledgements
The authors would thank all the colleagues in the lab for helpful discussion and technical advice.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D plan “blue granary science and technology innovation” key Special Project in 2020 (2020YFD0900205), the 2020 Zhanjiang Science and Technology development Special Fund Competitive Distribution Project-Breeding of new Penaeus japonicus varieties with fast growing (2020A702), and the 2019 Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Special Fund (“Special Project + Task List”) Competitive Distribution Project (2019A04008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Haixin Ou contributed to the preparation of material, completion of experiments, data collection, data analysis, writing, and revising of the manuscript. Jianyong Liu contributed to the data collection, data analysis, and revising of the manuscript. The first draft was written by Haixin Ou and reviewed by all authors. The final manuscript was read and approved by all authors for publishing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the Regulations of the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangdong Ocean University. Animal protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Guangdong Ocean University (Zhanjiang, China).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Brian Austin
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, H., Liu, J. Role of Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in the antioxidant defense response induced by low salinity in the kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus). Aquacult Int 30, 2793–2811 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-022-00941-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-022-00941-4