Abstract
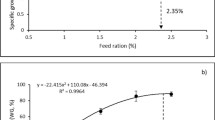
The main focus of recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) is to achieve the highest possible growth rates of the cultured fish at lowest possible cost implications. Growth rates of fish are species- and life stage–specific. Detailed knowledge on the growth rates of the reared species is thus indispensable. Commercial culture of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) in RAS has been growing for the last decades, but knowledge on growth rates is still scarce. The aim of the study was to closely monitor the growth rates of pikeperch in RAS for a total of 98 feeding days. Three common water exchange rates (1000 L kg feed−1, 500 L kg feed−1 and 200 L kg feed−1) were used to simulate different intensities of RAS and evaluate the effect on individual pikeperch from 250 g onwards. Pikeperch were tagged individually and weighted every 2 to 3 weeks. Whole body composition was analysed after 56 and 98 feeding days. The water exchange rate did not show a significant effect on the individual fish. Detailed information on individual pikeperch showed that 75% of pikeperch experienced low or even negative growth during at least one of the time periods. The body composition analysis showed similar results among all treatment groups with slight increases in lipid content at the end of the experiment. Growth of pikeperch in the monitored weight range (191.9–603.1 g) was neither linear nor exponential but indicates a sigmoidal shape. The equation for the average growth of pikeperch within this experiment was y = − 0.012 ± 0.004 x2 + 3.21 ± 0.33 x + 249.76 ± 5.27 with an R2 of 0.53. Based on this equation, pikeperch would experience positive growth in average until day 134 (ranging between day 90 and day 221) of the experiment. The average absolute growth rate among all fish over the whole experimental time period was 1.79 ± 1.00 g day−1, and the average specific growth rate was 0.52 ± 0.26% day−1. Further studies on a wider weight range need to be conducted in order to evaluate the shape of the overall growth curve and determine pikeperch-specific growth models for RAS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer A, Schulz C, Traulsen I, Krieter J (2010) Analysing the growth of turbot (Psetta maxima) in a commercial recirculation system with the use of three different growth models. Aquac Int 19:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-010-9365-0
Brett JR (1979) Environmental factors and growth. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Brett JR (eds) Fish physiology volume VIII, bioenergetics and growth. Academic Press Inc, pp 599–675
Bretz F, Hothorn T, Westfall P (2010) Multiple comparisons using R. Chapman and Hall/CRC. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420010909
Cochran WG (1957) Analysis of covariance: its nature and uses. Biometrics 13:261. https://doi.org/10.2307/2527916
Dalsgaard J, Lund I, Thorarinsdottir R, Drengstig A, Arvonen K, Pedersen PB (2013) Farming different species in RAS in Nordic countries: current status and future perspectives. Aquac Eng 53:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2012.11.008
Davidson J, Good C, Welsh C, Summerfelt ST (2014) Comparing the effects of high vs. low nitrate on the health, performance, and welfare of juvenile rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss within water recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac Eng 59:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2014.01.003
Dumas A, France J, Bureau D (2010) Modelling growth and body composition in fish nutrition: where have we been and where are we going? Aquac Res 41:161–181. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02323.x
Føre M, Alver M, Alfredsen JA, Marafioti G, Senneset G, Birkevold J, Willumsen FV, Lange G, Espmark Å, Terjesen BF (2016) Modelling growth performance and feeding behaviour of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in commercial-size aquaculture net pens: model details and validation through full-scale experiments. Aquaculture 464:268–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.045
Jobling M (ed) (1994) Fish bioenergetics, 1st edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Kangur A, Kangur P (1996) The condition, length and age distribution of pikeperch, Stizostedion lucioperca (L.) in Lake Peipsi. Hydrobiologia 338:179–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00031722
Kaushik SJ, Covès D, Dutto G, Blanc D (2004) Almost total replacement of fish meal by plant protein sources in the diet of a marine teleost, the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquac 230:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00422-8
Laird NM, Ware JH (1982) Random-effects models for longitudinal data. Biometrics 38:963. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529876
Luchiari AC, De Morais Freire FA, Pirhonen J, Koskela J (2009) Longer wavelengths of light improve the growth, intake and feed efficiency of individually reared juvenile pikeperch Sander lucioperca (L.). Aquac Res 40:880–886. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02160.x
Lugert V, Thaller G, Tetens J, Schulz C, Krieter J (2014) A review on fish growth calculation: multiple functions in fish production and their specific application. Rev Aquac 8:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12071
Nakagawa S, Schielzeth H (2013) A general and simple method for obtaining R2 from generalized linear mixed-effects models. In: O’Hara RB (ed) Methods in ecology and evolution, pp 133–142
Nyina-Wamwiza L, Xu XL, Blanchard G, Kestemont P (2005) Effect of dietary protein, lipid and carbohydrate ratio on growth, feed efficiency and body composition of pikeperch Sander lucioperca fingerlings. Aquac Res 36:486–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2005.01233.x
Schaarschmidt F, Vaas L (2009) Analysis of trials with complex treatment strucutre using multiple contrast tests, HortScience. American Society for Horticultural Science
Schulz C, Knaus U, Wirth M, Rennert B (2005) Effects of varying dietary fatty acid profile on growth performance, fatty acid, body and tissue composition of juvenile pike perch (Sander lucioperca). Aquac Nutr 11:403–413
Schulz C, Günther S, Wirth M, Rennert B (2006) Growth performance and body composition of pike perch (Sander lucioperca) fed varying formulated and natural diets. Aquac Int 14:577–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-006-9056-z
Schulz C, Böhm M, Wirth M, Rennert B (2007) Effect of dietary protein on growth, feed conversion, body composition and survival of pike perch fingerlings (Sander lucioperca). Aquac Nutr 13:373–380
Steinberg K, Zimmermann J, Stiller KT, Meyer S, Schulz C (2017) The effect of carbon dioxide on growth and energy metabolism in pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). Aquaculture 481:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.09.003
Steinberg K, Zimmermann J, Stiller KT, Nwanna L, Meyer S, Schulz C (2018) Elevated nitrate levels affect the energy metabolism of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) in RAS. Aquaculture 497:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.08.017
Thorarensen H, Imsland AKD, Gústavsson A, Gunnarsson S, Árnasond J, Steinarsson A, Bouwmans J, Receveur L, Björnsdóttir R (2018) Potential interactive effects of ammonia and CO2 on growth performance and feed utilization in juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 484:272–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.11.040
Timmons M, Ebeling J (2007) Recirculating aquaculture, 01-007 ed. Cayuga Aqua Ventures, Ithaca
Torno J, Einwächter V, Schroeder JP, Schulz C (2018a) Nitrate has a low impact on performance parameters and health status of on-growing European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) reared in RAS. Aquaculture 489:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.01.043
Torno C, Staats S, de Pascual-Teresa S, Rimbach G, Schulz C (2018b) Effects of resveratrol and genistein on growth, nutrient utilization, and fatty acid composition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 491:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.03.020
Verbeke G (1997) Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. In: Linear mixed models for longitudinal data. Springer, New York, NY, pp 63–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2294-1_3
Weatherley A, 1990. Approaches to understanding fish growth. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119, 662–672. doi:https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8659(1990)119<0662:ATUFG>2.3.CO;2
Zakęś Z, Hopko M, Kowalska A, Partyka K, Stawecki K (2013) Impact of feeding pikeperch Sander lucioperca (L.) feeds of different particle size on the results of the initial on-growing phase in recirculation systems. Arch. Polish Fish 21:3–9. https://doi.org/10.2478/aopf-2013-0001
Acknowledgement
We thank the guest auditorial team for the invitation to submit a paper to this special issue. Special thanks to Dr. Claudia Torno, Anna Fickler, Cornelius Söder and Dr. Johann Torno for the assistance during the experimental period. Special thanks to Dr. Mario Hasler for his detailed statistical advice. We are furthermore grateful for the guidance provided by Michael Schlachter and the help of the whole team at the GMA during sampling.
Funding
This research was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Project number 031A290A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinberg, K., Zimmermann, J., Meyer, S. et al. Individual growth rates of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) depending on water exchange rates in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquacult Int 27, 1025–1035 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00373-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00373-7