Abstract
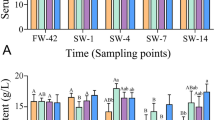
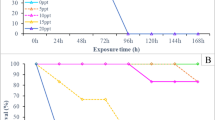
The aim of this research was to evaluate the effect of calcium concentration in water to the osmoregulation and survival of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus lanceolatus) acclimated in freshwater environment. There was no mortality observed in all groups during acclimation to the freshwater up to 3 ‰. Once the fish reached the freshwater (0 ‰), rapid mortality was occurred. Lower salinity induced the lower serum osmolality. Lowest serum osmolality value was observed in the positive control group at 6 h post-transfer (HPT) to freshwater. The values of muscle water content were not significantly different among all groups in all salinities. The highest Na+–K+-ATPase (NKA) activities were observed in the 500 and 1000 mg/L CaCl2 groups at D 10 1 and 6 HPT, respectively, whereas lowest NKA activities were recorded in the positive control and 100 mg/L CaCl2 groups at D 10 6 HPT. This study shows that the hybrid grouper demonstrates excellent tolerance in environment up to 3 ‰.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Jandal NJ, Wilson RW (2011) A comparison of osmoregulatory responses in plasma and tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following acute salinity challenges. Comp Biochem Physiol 159A:175–181
Blanco G, Mercer R (1998) Isozyme diversity of the Na-K-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 275:F633–F650
Bone Q, Moore RM (2008) Biology of fishes, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis Group, New York
Bornancin M, Cuthbert AW, Maetz J (1972) The effects of calcium on branchial sodium fluxes in the sea-water adapted eel, Anguilla anguilla. J Physiol 222:487–496
Carrier JC, Evans DH (1976) The role of environmental calcium in freshwater survival of the marine teleost, Lagodon rhomboides. J Exp Biol 165:529–538
Chapman FA, Garcia LN, Atencio VJ et al (2014) Low-salinity acclimation of juvenile marine goliath grouper Epinephelus itajara. J Appl Aquac 26:179–186
Cheng S-Y, Chen C-S, Chen J-C (2013) Salinity and temperature tolerance of brown-marbled grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:277–286
Ernst O, Zor T (2010) Linearization of the Bradford protein assay. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/1918
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multi functional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Flemming WR, Nichols J, Potts WTW (1974) The effects of low-calcium seawater and actinomycin-d on the sodium metabolism of Fundulus kansae. J Exp Biol 60:267–273
Freire CA, Amando EM, Souza LR et al (2008) Muscle water control in crustaceans and fishes as a function of habitat, osmoregulatory capacity, and degree of euryhalinity. Comp Biochem Physiol 149A:435–446
Hwang P-P, Lee T-H (2007) New insight into fish ion regulation and mitochondrion-rich cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 148A:479–497
Kammerer BD, CechJr JJ, Kultz D (2010) Rapid changes in plasma cortisol, osmolality, and respiration in response to salinity stress in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Comp Biochem Physiol 157A:260–265
Laiz-Carrion R, Guerreiro PM, Fuentes J et al (2005) Branchial osmoregulatory response to salinity in the gilthead sea bream, Sparus auratus. J Exp Zool 303A:563–576
Lucu C, Flik G (1999) Na+–K+-ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange activities in gills of hyperregulating Carcinus maenas. Am J Physiol 276:R490–R499
Martinez-Alvarez RM, Hidalgo MC, Domezain A et al (2002) Physiological changes of sturgeon Acipenser naccarii caused by increasing environmental salinity. J Exp Biol 205:3699–3706
McCormick SD (1993) Method for nonlethal biopsy and measurement of Na+, K+-ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:656–658
McCormick SD, Bradshaw D (2006) Hormonal control of salt and water balance in vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocr 147:3–8
McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christeensen AK (2009) Distinct freshwater and seawater isoform of the Na+/K+-ATPase in gill chloride cells of atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 212:3994–4001
Mitcheson SYD, Craig MT, Bertoncini AA, Carpenter KE, Cheung WWL, Choat JH, Cornosh AS, Fernessey ST, Ferreira BP, Heemstra PC, Liu M, Myer RF, Pollard DA, Rhodes KL, Rocha LA, Russel BC, Samoilys MA, Sanciango J (2013) Fishing grouper toward extinction: a global assessment of threats and extinction risks in a billion dollar fishery. Fish Fisher 14:119–136
Noh GE, Rho S, Chang YJ et al (2013) Gene encoding prolactin in cinnamon clownfish Amphiprion melanopus and its expression upon acclimation to low salinities. Aquat Biosyst 9:1
Nordlie FG (2009) Environmental influences on regulation of blood plasma/serum component in teleost fishes: a review. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 19:481–564
Parra JEG, Baldisserotto B (2008) Effect of water pH and hardness on survival and growth of freshwater teleosts. In: Baldisserotto B, Mancera JM, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish osmoregulation. Science Publishers, British Isle, pp 135–150
Price EE, Donahue MJ, Dickson KL et al (1990) Effects of elevated calcium concentration on Na-K-ATPase activity of two euryhaline species, Cyprinodon variegatus and Mysid psisbahia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 44:121–128
Rimmer MA, McBridge S, Williams KC (2004) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR monograph no. 110. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, Canberra, Australia
Sampaio LE, Bianchini A (2002) Salinity effects on osmoregulation and growth of the euryhaline flounder Paralichthys orbignyanus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 269:187–196
Sardella BA, Kultz D (2009) Osmo- and ionoregulatory responses of green sturgeon (Acipensermedirostris) to salinity acclimation. J Comp Physiol 179B:383–390
Sutarmat T, Yudha HT (2013) Analisis keragaan pertumbuhan benih kerapu hibrida hasil hibridisasi kerapu macan (Epinephelusfuscoguttatus) dengan kerapu kertang (Epinepheluslanceolatus) dan kerapu batik (Epinephelusmicrodon). J Ris Akuakultur 8(3):363–372
Szuster BW, Albasri H (2010) Site selection for grouper mariculture in Indonesia. Int J Fish Aquac 2:87–92
Wurtz WA, Stickney RR (1989) Responses of red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) to calcium and magnesium concentrations in fresh and salt water. Aquaculture 76:21–35
Zhao F, Wang Y, Zhang L et al (2013) Survival, growth, food conversion efficiency and plasma osmolality of juvenile Siganus guttatus (Bloch, 1787): experimental analyses of salinity effects. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:1025–1030
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the head of Center for Brackish water Aquaculture and Fisheries in Jepara for giving the access to conduct this experiment, and Mr. Setiyanto for technical assistance during experiment. We also wish to thank two anonymous reviewers for valuable advice and constructive comments to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arrokhman, S., Wijayanti, N. & Soegianto, A. Survival and osmoregulation of juvenile of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus lanceolatus) during acclimation in calcium-supplemented freshwater. Aquacult Int 25, 693–704 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0069-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0069-y