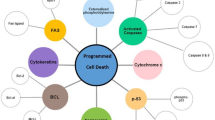
Abstract
XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family known for its important conserved inhibitory effect on caspase activity. Since the introduction of XIAP almost three decades ago, numerous experimental studies have been performed for a wide range of cellular pathways and mechanisms. In this perspective, we summarize key trends of XIAP as an important regulator of cellular signaling. Experimental research indicates that XIAP as a key molecule of cell death not only suppress caspases and apoptosis, but also regulates inflammatory signaling, mitogenic kinase signaling, cell proliferation as well as cell invasion and metastasis. In this review, we provide basic knowledge of the roles of XIAP, explain its role in necroptosis, anoikis, autophagy and neuronal differentiation. XIAP is involved in regulating intracellular ROS production and copper homeostasis which this review focuses on. A different face of XIAP in response to DNA damage and chronic ER stress is also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
References
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wideranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Mehdizadeh K, Ataei F, Hosseinkhani S (2021) Treating MCF7 breast cancer cell with proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib restores apoptotic factors and sensitizes cell to Docetaxel. Med Oncol 38:1–8
Peter ME, Heufelder AE, Hengartner MO (1997) Advances in apoptosis research. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:12736–12737
Mehdizadeh K, Ataei F, Hosseinkhani S (2020) Effects of doxorubicin and docetaxel on susceptibility to apoptosis in high expression level of survivin in HEK and HEK-S cell lines as in vitro models. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 532:139–144
Nuñez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y, Inohara N (1998) Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 17:3237–3245
Bakhshoudeh M, Mehdizadeh K, Hosseinkhani S, Ataei F (2021) Upregulation of apoptotic protease activating factor-1 expression correlates with anti-tumor effect of taxane drug. Med Oncol 38:88–95
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR et al (1998) IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. EMBO J 17:2215–2223
Houshdarpour R, Ataei F, Hosseinkhani S (2021) Efficient stable cell line generation of survivin as an in vitro model for specific functional analysis in apoptosis and drug screening. Mol Biotechnol 63:515–524
Karimzadeh S, Hosseinkhani S, Fathi A, Ataei F, Baharvand H (2018) Insufficient Apaf-1 expression in early stages of neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells might protect them from apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol 97:126–135
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi Y, Nakata K, Reed JC, Takahashi R (2001) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibits caspase-3 and-7 in distinct modes. J Biol Chem 276:27058–27063
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Tu H, Costa M (2020) XIAP’s Profile in human cancer. Biomolecules 10:1493
Wilkinson JC, Wilkinson AS, Galbán S, Csomos RA, Duckett CS (2008) Apoptosis-inducing factor is a target for ubiquitination through interaction with XIAP. Mol Cell Biol 28:237–247
Listen P, Roy N, Tamai K et al (1996) Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature 379:349–353
Birnbaum M, Clem R, Miller L (1994) An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs. J Virol 68:2521–2528
Hinds MG, Norton RS, Vaux DL, Day CL (1999) Solution structure of a baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) repeat. Nat Struct Biol 6:648–651
Yang Y, Fang S, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Ashwell JD (2000) Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 288:874–877
Gyrd-Hansen M, Darding M, Miasari M et al (2008) IAPs contain an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin-binding domain that regulates NF-κB as well as cell survival and oncogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 10:1309–1317
Blankenship JW, Varfolomeev E, Goncharov T et al (2009) Ubiquitin binding modulates IAP antagonist-stimulated proteasomal degradation of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2. Biochem J 417:149–165
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1999) Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J 18:5242–5251
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS, Scott FL (2006) Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep 7:988–994
Scott FL, Denault JB, Riedl SJ, Shin H, Renatus M, Salvesen GS (2005) XIAP inhibits caspase-3 and‐7 using two binding sites: evolutionarily conserved mechanism of IAPs. EMBO J 24:645–655
Sun C, Cai M, Gunasekera AH et al (1999) NMR structure and mutagenesis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein XIAP. Nature 401:818–822
Fraser AG, James C, Evan GI, Hengartner MO (1999) Caenorhabditis elegans inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) homologue BIR-1 plays a conserved role in cytokinesis. Curr Biol 9:292–302
Uren AG, Beilharz T, O’Connell MJ et al (1999) Role for yeast inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)-like proteins in cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:10170–10175
Fuchs Y, Steller H (2011) Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 147:742–758
Vasudevan D, Ryoo HD (2015) Regulation of cell death by IAPs and their antagonists. Crr Top Dev Biol 114:185–208
White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young L, Farrell K, Steller H (1994) Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Sci 264:677–683
Grether ME, Abrams JM, Agapite J, White K, Steller H (1995) The head involution defective gene of Drosophila melanogaster functions in programmed cell death. Genes Dev 9:1694–1708
Chen P, Nordstrom W, Gish B, Abrams JM (1996) grim, a novel cell death gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev 10:1773–1782
Goyal L, McCall K, Agapite J, Hartwieg E, Steller H (2000) Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J 19:589–597
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c–dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102:33–42
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M et al (2000) Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102:43–53
Hegde R, Srinivasula SM, Zhang Z et al (2002) Identification of Omi/HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J Biol Chem 277:432–438
Schile AJ, García-Fernández M, Steller H (2008) Regulation of apoptosis by XIAP ubiquitin-ligase activity. Genes Dev 22:2256–2266
Qin S, Yang C, Zhang B et al (2016) XIAP inhibits mature Smac-induced apoptosis by degrading it through ubiquitination in NSCLC. Int J Oncol 49:1289–1296
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi Y, Takahashi R (2001) Ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein promotes proteasomal degradation of caspase-3 and enhances its anti-apoptotic effect in Fas-induced cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A9 8:8662–8667
Shin H, Okada K, Wilkinson JC et al (2003) Identification of ubiquitination sites on the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Biochem J 373:965–971
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124:619–626
Taddei M, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Chiarugi P (2012) Anoikis: an emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J Pathol 226:380–393
Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ (2009) Life and death by death receptors. FASEB 23:1625–1637
Chiarugi P, Giannoni E (2008) Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1352–1364
Marconi A, Atzei P, Panza C et al (2004) FLICE/caspase-8 activation triggers anoikis induced by β1-integrin blockade in human keratinocytes. J Cell Sci 117:5815–5823
Aoudjit F, Vuori K (2001) Matrix attachment regulates Fas-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells: a role for c-flip and implications for anoikis. J Cell Biol 152:633–644
García-Fernández M, Kissel H, Brown S et al (2010) Sept4/ARTS is required for stem cell apoptosis and tumor suppression. Genes Dev 24:2282–2293
Gottfried Y, Rotem A, Lotan R, Steller H, Larisch S (2004) The mitochondrial ARTS protein promotes apoptosis through targeting XIAP. EMBO J 23:1627–1635
Liu Z, Li H, Wu X et al (2006) Detachment-induced upregulation of XIAP and cIAP2 delays anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 25:7680–7690
Stehlik C, De Martin R, Kumabashiri I, Schmid JA, Binder BR, Lipp J (1998) Nuclear factor (NF)-κB–regulated X-chromosome–linked iap gene expression protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor α–induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 188:211–216
Biswas DK, Martin KJ, McAlister C et al (2003) Apoptosis caused by chemotherapeutic inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation. Cancer Res 63:290–295
Yamakita Y, Totsukawa G, Yamashiro S et al (1999) Dissociation of FAK/p130CAS/c-Src complex during mitosis: role of mitosis-specific serine phosphorylation of FAK. Cancer Res 144:315–324
Ikeda H, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M et al (1998) Apoptosis is a major mode of cell death caused by ischaemia and ischaemia/reperfusion injury to the rat intestinal epithelium. Gut 42:530–537
Levine B, Klionsky DJ (2004) Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 6:463–477
Klionsky DJ (2007) Autophagy: from phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:931–937
Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Thompson CB (2005) Autophagy in metazoans: cell survival in the land of plenty. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:439–448
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V, White E (2007) Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:961–967
Mah LY, Ryan KM (2012) Autophagy and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4:a008821
Huang X, Wu Z, Mei Y, Wu M (2013) XIAP inhibits autophagy via XIAP-Mdm2‐p53 signalling. EMBO J 32:2204–2216
Itahana K, Mao H, Jin A et al (2007) Targeted inactivation of Mdm2 RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in the mouse reveals mechanistic insights into p53 regulation. Cancer Cell 12:355–366
Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Malik SA, Kroemer G (2010) Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:181–185
Tasdemir E, Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L et al (2008) Regulation of autophagy by cytoplasmic p53. Nat Cell Biol 10:676–687
Gao X, Zhang L, Wei Y et al (2019) Prognostic value of XIAP level in patients with various cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer 10:1528
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P (2015) Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 517:311–320
Wang X, Yousefi S, Simon H-U (2018) Necroptosis and neutrophil-associated disorders. Cell Death Dis 9:1–9
Damgaard RB, Nachbur U, Yabal M et al (2012) The ubiquitin ligase XIAP recruits LUBAC for NOD2 signaling in inflammation and innate immunity. Mol cell 46:746–758
Lawlor KE, Khan N, Mildenhall A et al (2015) RIPK3 promotes cell death and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the absence of MLKL. Nat Commun 6:1–19
Yabal M, Müller N, Adler H et al (2014) XIAP restricts TNF-and RIP3-dependent cell death and inflammasome activation. Cell Rep 7:1796–1808
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Berghe TV, Kroemer G (2010) Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:700–714
Silke J, Rickard JA, Gerlic M (2015) The diverse role of RIP kinases in necroptosis and inflammation. Nat Immunol 16:689–697
Murphy JM, Czabotar PE, Hildebrand JM et al (2013) The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a molecular switch mechanism. Immunity 39:443–453
Gyrd-Hansen M, Meier P (2010) IAPs: from caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-κB, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10:561–574
Wicki S, Gurzeler U, Wong WW-L, Jost PJ, Bachmann D, Kaufmann T (2016) Loss of XIAP facilitates switch to TNF α-induced necroptosis in mouse neutrophils. Cell Death Dis 7:e2422–e2422
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM, Green DR (2017) Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:127–136
Tenev T, Bianchi K, Darding M et al (2011) The Ripoptosome, a signaling platform that assembles in response to genotoxic stress and loss of IAPs. Mol cell 43:432–448
Moulin M, Anderton H, Voss AK et al (2012) IAPs limit activation of RIP kinases by TNF receptor 1 during development. EMBO J 31:1679–1691
He S, Liang Y, Shao F, Wang X (2011) Toll-like receptors activate programmed necrosis in macrophages through a receptor-interacting kinase-3–mediated pathway. Proceedings of the Natl Acad Sci 108:20054–20059
Fadó R, Moubarak RS, Miñano-Molina AJ et al (2013) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein negatively regulates neuronal differentiation through interaction with cRAF and Trk. Sci rep 3:1–11
Yamaguchi K, Nagai Si, Ninomiya-Tsuji J et al (1999) XIAP, a cellular member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family, links the receptors to Tables 1–TAK1 in the BMP signaling pathway. EMBO J 18:179–187
Olayioye M, Kaufmann H, Pakusch M, Vaux D, Lindeman G, Visvader J (2005) XIAP-deficiency leads to delayed lobuloalveolar development in the mammary gland. Cell Death Differ 12:87–90
Dogan T, Harms GS, Hekman M et al (2008) X-linked and cellular IAPs modulate the stability of C-RAF kinase and cell motility. Nat cell biol 10:1447–1455
Heiman MG, Shaham S (2010) Twigs into branches: how a filopodium becomes a dendrite. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:86–91
Moubarak RS, Solé C, Pascual M et al (2010) The death receptor antagonist FLIP-L interacts with Trk and is necessary for neurite outgrowth induced by neurotrophins. J Neurosci 30:6094–6105
Liu J, Zhang D, Luo W et al (2011) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) mediates cancer cell motility via Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (RhoGDI)-dependent regulation of the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 286:15630–15640
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A (2002) ROS, stress-activated kinases and stress signaling in cancer. EMBO Rep 3:420–425
Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:205–214
Resch U, Schichl YM, Sattler S, de Martin R (2008) XIAP regulates intracellular ROS by enhancing antioxidant gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 375:156–161
Gabbita SP, Robinson KA, Stewart CA, Floyd RA, Hensley K (2000) Redox regulatory mechanisms of cellular signal transduction. Arch Biochem Biophys 376:1–13
Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf2 signaling in coordinated activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1199–1207
Ueda S, Masutani H, Nakamura H, Tanaka T, Ueno M, Yodoi J (2002) Redox control of cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:405–414
Kamata H, Honda S-i, Maeda S, Chang L, Hirata H, Karin M (2005) Reactive oxygen species promote TNFα-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell 120:649–661
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2003) Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:233–260
Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB (1991) The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem 266:11632–11639
Lu M, Lin S-C, Huang Y et al (2007) XIAP induces NF-κB activation via the BIR1/Table 1 interaction and BIR1 dimerization. Mol cell 26:689–702
Lewis S, Holcik M (2005) IRES in distress: translational regulation of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins XIAP and HIAP2 during cell stress. Cell Death Differ 12:547–553
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y, Gelinas C (2003) To be, or not to be: NF-κ B is the answer–role of Rel/NF-κ B in the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 22:8961–8982
Puig S, Thiele DJ (2002) Molecular mechanisms of copper uptake and distribution. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6:171–180
Tao TY, Liu F, Klomp L, Wijmenga C, Gitlin JD (2003) The copper toxicosis gene product Murr1 directly interacts with the Wilson disease protein. J Biol Chem 278:41593–41596
Burstein E, Ganesh L, Dick RD et al (2004) A novel role for XIAP in copper homeostasis through regulation of MURR1. EMBO J 23:244–254
Fanciulli M, Bruno T, Padova MD et al (2000) Identification of a novel partner of RNA polymerase II subunit 11, Che-1, which interacts with and affects the growth suppression function of Rb. FASEB J 14:904–912
Bruno T, De Angelis R, De Nicola F et al (2002) Che-1 affects cell growth by interfering with the recruitment of HDAC1 by Rb. Cancer Cell 2:387–399
Bruno T, Iezzi S, De Nicola F et al (2008) Che-1 activates XIAP expression in response to DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 15:515–520
Bruno T, De Nicola F, Iezzi S et al (2006) Che-1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR and Chk2 kinases activates p53 transcription and the G2/M checkpoint. Cancer Cell 10:473–486
Bruno T (2007) Che-1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR and CHK2 kinases activates p53 transcription and the g2/m checkpoint. AACR 67:1079
Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334:1081–1086
Tabas I, Ron D (2011) Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat cell biol 13:184–190
Hiramatsu N, Messah C, Han J, LaVail MM, Kaufman RJ, Lin JH (2014) Translational and posttranslational regulation of XIAP by eIF2α and ATF4 promotes ER stress–induced cell death during the unfolded protein response. Mol biol cell 25:1411–1420
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X et al (1998) CHOP is implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 12:982–995
Reimertz C, Kögel D, Rami A, Chittenden T, Prehn JH (2003) Gene expression during ER stress–induced apoptosis in neurons: induction of the BH3-only protein Bbc3/PUMA and activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. J cell biol 162:587–597
Warnakulasuriyarachchi D, Cerquozzi S, Cheung HH, Holcík M (2004) Translational induction of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein HIAP2 during endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates cell death and is mediated via an inducible internal ribosome entry site element. J Biol Chem 279:17148–17157
Muaddi H, Majumder M, Peidis P et al (2010) Phosphorylation of eIF2α at serine 51 is an important determinant of cell survival and adaptation to glucose deficiency. Mol biol cell 21:3220–3231
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research council of Tarbiat Modares University.
Funding
This article was funded by the research council of Tarbiat Modares University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH wrote the first draft of the manuscript. FA edited and finalized the manuscript. MH and FA generated all figures and all structures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanifeh, M., Ataei, F. XIAP as a multifaceted molecule in Cellular Signaling. Apoptosis 27, 441–453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01734-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01734-z