Abstract
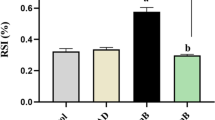
Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) is one of the main causes for corneal endothelial blindness, which is characterized by the progressive decline of corneal endothelial cells. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) was reported to be involved in cell death and apoptosis of several diseases. However, the role of PARP1 in the progression of FECD remains elusive. In the present study, we reported that UVA irradiation caused the corneal endothelial damage and corneal edema in mice, which was accompanied with the elevated activity of PARP1 and PAR. The PARP1 inhibitor PJ34 resolved the corneal edema and protected corneal endothelium from UVA-induced oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell apoptosis. Mechanistically, PARP1 inhibition exerted its anti-apoptotic effects through downregulation of the phosphorylation levels of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK and subsequently the increase of MKP-1. Our results suggest that PARP1 inhibition protects corneal endothelium from UVA-induced oxidative damage, which provides a potential alternative strategy for the therapy of FECD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- FECD:
-
Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy
- CECs:
-
Corneal endothelial cells
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- PARP:
-
Poly ADP-ribose polymerase
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis inducing factor
- MKP-1:
-
MAPK phosphatase-1
References
Ong Tone S, Kocaba V, Böhm M, Wylegala A, White TL, Jurkunas UV (2021) Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: the vicious cycle of Fuchs pathogenesis. Prog Retin Eye Res 80:100863
Jurkunas UV, Bitar MS, Funaki T, Azizi B (2010) Evidence of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Am J Pathol 177(5):2278–2289
Shoham A, Hadziahmetovic M, Dunaief JL, Mydlarski MB, Schipper HM (2008) Oxidative stress in diseases of the human cornea. Free Radic Biol Med 45(8):1047–1055
Borderie VM, Baudrimont M, Vallée A, Ereau TL, Gray F, Laroche L (2000) Corneal endothelial cell apoptosis in patients with Fuchs’ dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41(9):2501–2505
Li QJ, Ashraf MF, Shen DF, Green WR, Stark WJ, Chan CC, O’Brien TP (2001) The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of Fuchs endothelial dystrophy of the cornea. Arch Ophthalmol 119(11):1597–1604
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9(1):49–89
Alemasova EE, Lavrik OI (2019) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP1: reaction mechanism and regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 47(8):3811–3827
Luo X, Kraus WL (2012) On PAR with PARP: cellular stress signaling through poly(ADP-ribose) and PARP-1. Genes Dev 26(5):417–432
Hou WH, Chen SH, Yu X (2019) Poly-ADP ribosylation in DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Mutat Res 780:82–91
Lee Y, Kang HC, Lee BD, Lee YI, Kim YP, Shin JH (2014) Poly (ADP-ribose) in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep 47(8):424–432
Fatokun AA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2014) Parthanatos: mitochondrial-linked mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Br J Pharmacol 171(8):2000–2016
Liu C, Vyas A, Kassab MA, Singh AK, Yu X (2017) The role of poly ADP-ribosylation in the first wave of DNA damage response. Nucleic Acids Res 45(14):8129–8141
Schuhwerk H, Atteya R, Siniuk K, Wang ZQ (2017) PARPing for balance in the homeostasis of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 63:81–91
Abdelkarim GE, Gertz K, Harms C, Katchanov J, Dirnagl U, Szabó C, Endres M (2001) Protective effects of PJ34, a novel, potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in in vitro and in vivo models of stroke. Int J Mol Med 7(3):255–260
Jagtap P, Szabó C (2005) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and the therapeutic effects of its inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(5):421–440
Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, Kyle S, Meuth M, Curtin NJ, Helleday T (2005) Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 434(7035):913–917
Andrabi SA, Kim NS, Yu SW, Wang H, Koh DW, Sasaki M, Klaus JA, Otsuka T, Zhang Z, Koehler RC, Hurn PD, Poirier GG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer is a death signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(48):18308–18313
Liu C, Miyajima T, Melangath G, Miyai T, Vasanth S, Deshpande N, Kumar V, Ong Tone S, Gupta R, Zhu S, Vojnovic D, Chen Y, Rogan EG, Mondal B, Zahid M (2020) Jurkunas UV (2006) Ultraviolet A light induces DNA damage and estrogen-DNA adducts in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy causing females to be more affected. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(1):573–583
Krishnakumar R, Kraus WL (2010) The PARP side of the nucleus: molecular actions, physiological outcomes, and clinical targets. Mol Cell 39(1):8–24
Liu C, Vojnovic D, Kochevar IE, Jurkunas UV (2016) UV-A irradiation activates Nrf2-regulated antioxidant defense and induces p53/caspase3-dependent apoptosis in corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(4):2319–2327
Poyan Mehr A, Tran MT, Ralto KM, Leaf DE, Washco V, Messmer J, Lerner A, Kher A, Kim SH, Khoury CC, Herzig SJ, Trovato ME, Simon-Tillaux N, Lynch MR, Thadhani RI, Clish CB, Khabbaz KR, Rhee EP, Waikar SS, Berg AH, Parikh SM (2018) De novo NAD(+) biosynthetic impairment in acute kidney injury in humans. Nat Med 24(9):1351–1359
White TL, Deshpande N, Kumar V, Gauthier AG, Jurkunas UV (2021) Cell cycle re-entry and arrest in G2/M phase induces senescence and fibrosis in fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Free Radic Biol Med 164:34–43
Katikireddy KR, White TL, Miyajima T, Vasanth S, Raoof D, Chen Y, Price MO, Price FW, Jurkunas UV (2018) NQO1 downregulation potentiates menadione-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition during rosette formation in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Free Radic Biol Med 116:19–30
Halilovic A, Schmedt T, Benischke AS, Hamill C, Chen Y, Santos JH, Jurkunas UV (2016) Menadione-induced DNA damage leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and fragmentation during rosette formation in fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:1072–1083
Haydari MN, Perron MC, Laprise S, Roy O, Cameron JD, Proulx S, Brunette I (2012) A short-term in vivo experimental model for Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 10:6343–6354
Liu C, Miyajima T, Melangath G, Miyai T, Vasanth S, Deshpande N, Kumar V, Ong Tone S, Gupta R, Zhu S, Vojnovic D, Chen Y, Rogan EG, Mondal B, Zahid M, Jurkunas UV (2020) Ultraviolet A light induces DNA damage and estrogen-DNA adducts in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy causing females to be more affected. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:573–583
Ridley AJ, Whiteside JR, McMillan TJ, Allinson SL (2009) Cellular and sub-cellular responses to UVA in relation to carcinogenesis. Int J Radiat Biol 85:177–195
Vile GF, Tyrrell RM (1995) UVA radiation-induced oxidative damage to lipids and proteins in vitro and in human skin fibroblasts is dependent on iron and singlet oxygen. Free Radic Biol Med 18:721–730
Santos JH, Hunakova L, Chen Y, Bortner C, Van Houten B (2003) Cell sorting experiments link persistent mitochondrial DNA damage with loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem 278:1728–1734
Yakes FM, Van Houten B (1997) Mitochondrial DNA damage is more extensive and persists longer than nuclear DNA damage in human cells following oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:514–519
Langelier MF, Pascal JM (2013) PARP-1 mechanism for coupling DNA damage detection to poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23:134–143
Bartha E, Solti I, Kereskai L, Lantos J, Plozer E, Magyar K, Szabados E, Kálai T, Hideg K, Halmosi R, Sumegi B, Toth K (2009) PARP inhibition delays transition of hypertensive cardiopathy to heart failure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res 83:501–510
Mester L, Szabo A, Atlasz T, Szabadfi K, Reglodi D, Kiss P, Racz B, Tamas A, Gallyas F Jr, Sumegi B, Hocsak E, Gabriel R, Kovacs K (2009) Protection against chronic hypoperfusion-induced retinal neurodegeneration by PARP inhibition via activation of PI-3-kinase Akt pathway and suppression of JNK and p38 MAP kinases. Neurotox Res 16:68–76
Moubarak RS, Yuste VJ, Artus C, Bouharrour A, Greer PA, Menissier-de Murcia J, Susin SA (2007) Sequential activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, calpains, and Bax is essential in apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated programmed necrosis. Mol Cell Biol 13:4844–4862
Xu Y, Huang S, Liu ZG, Han J (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signaling to mitochondria in necrotic cell death requires RIP1/TRAF2-mediated JNK1 activation. J Biol Chem 13:8788–8795
Mathieu J, Flexor M, Lanotte M, Besançon F (2008) A PARP-1/JNK1 cascade participates in the synergistic apoptotic effect of TNFalpha and all-trans retinoic acid in APL cells. Oncogene 27:3361–3370
Zhang C, Du L, Sun P, Shen L, Zhu J, Pang K, Wu X (2017) Construction of tissue-engineered full-thickness cornea substitute using limbal epithelial cell-like and corneal endothelial cell-like cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials 124:180–194
Miki T, Lehmann T, Cai H, Stolz DB, Strom SC (2005) Stem cell characteristics of amniotic epithelial cells. Stem Cells 23:1549–1559
Inagaki E, Hatou S, Higa K, Yoshida S, Shibata S, Okano H, Tsubota K, Shimmura S (2017) Skin-derived precursors as a source of progenitors for corneal endothelial regeneration. Stem Cells Transl Med 6:788–798
Ljubimov AV, Saghizadeh M (2015) Progress in corneal wound healing. Prog Retin Eye Res 49:17–45
Acknowledgements
We thank Ph.D Qun Wang gave our work scientific suggestions.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770904 and 81900834) and by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019ZD37 and ZR2019PH110). Weiyun Shi and Qingjun Zhou were partially supported by the Taishan Scholar Program (20161059) and by the Academic Promotion Programme of Shandong First Medical University (2019PT002, 2019RC008, and 2019ZL001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW conceived and designed the experiments; CXD, QJZ and HYD conducted the statistical analysis; DLZ, YJG and BCM performed data collection; ZYL and WYS reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that no competing financial interests or conflict of interest exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Dong, C., Zhou, Q. et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor PJ34 protects against UVA-induced oxidative damage in corneal endothelium. Apoptosis 26, 600–611 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-021-01690-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-021-01690-0