Abstract
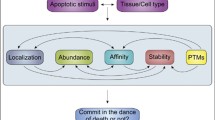
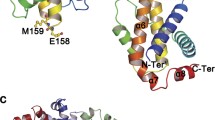
A critical process in apoptosis is the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane (MOM). This process is known to be regulated by the multi-domain Bcl-2 family proteins. For example, the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak are responsible for forming pores at MOM. The anti-apoptotic proteins (including Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL), on the other hand, can inhibit this pore-forming process. Interestingly, although these two subgroups of proteins perform opposite apoptotic functions, their structures are very similar. This raises two highly interesting questions: (1) Why do these structurally similar proteins play opposite roles in apoptosis? (2) What are the roles of different functional domains of a Bcl-2 family protein in determining its apoptotic property? In this study, we generated a series of deletion mutants and substitution chimera, and used a combination of molecular biology, bio-informatics and living cell imaging techniques to answer these questions. Our major findings are: (1) All of the Bcl-2 family proteins appear to possess an intrinsic pro-apoptotic property. (2) The N-termini of these proteins play an active role in suppressing their pro-apoptotic function. (3) The apoptotic potency is positively correlated with membrane affinity of the alpha 5/6 helix domains. (4) Charge distribution flanking the alpha 5/6 helices is also important for the apoptotic potency. These findings explain why different members of Bcl-2 family proteins with similar domain composition can function oppositely in the apoptotic process.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bak:
-
Bcl-2-antagonist killer
- Bax:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- Bcl-2:
-
B cell lymphoma-2
- Bcl-xL:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- BH domain:
-
Bcl-2 homology domain
- Caspase:
-
Cysteine aspartase
- CCD:
-
Charge-coupled device
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
- EYFP:
-
Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- Hr:
-
Hour
- Mcl-1:
-
Myeloid cell leukaemia sequence 1
- MEM:
-
Minimum essential medium
- MOM:
-
Mitochondrial outer membrane
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- pDNA:
-
Plasmid DNA
- TM:
-
Transmembrane
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet light
- VDAC:
-
Voltage-dependent anion channel
References
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96(2):245–254
Meier P, Finch A, Evan G (2000) Apoptosis in development. Nature 407(6805):796–801
Martin SJ, Cotter TG (1991) Ultraviolet B irradiation of human leukaemia HL-60 cells in vitro induces apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol 59(4):1001–1016
Nagata S (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88(3):355–365
Schmidt S, Rainer J, Ploner C, Presul E, Riml S, Kofler R (2004) Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and glucocorticoid resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cell Death Differ 11(Suppl 1):S45–S55
Singh TR, Shankar S, Chen X, Asim M, Srivastava RK (2003) Synergistic interactions of chemotherapeutic drugs and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2 ligand on apoptosis and on regression of breast carcinoma in vivo. Cancer Res 63(17):5390–5400
Li J, Yuan J (2008) Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 27(48):6194–6206
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13(15):1899–1911
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281(5381):1322–1326
Reed JC (1998) Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 17(25):3225–3236
Siddiqui WA, Ahad A, Ahsan H (2015) The mystery of BCL2 family: Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: an update. Arch Toxicol 89(3):289–317
Adams JM, Cory S (2001) Life-or-death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 26(1):61–66
Borner C (2003) The Bcl-2 protein family: sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol 39(11):615–647
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2000) Bcl-2 family: life-or-death switch. FEBS Lett 466(1):6–10
Kelekar A, Thompson CB (1998) Bcl-2-family proteins: the role of the BH3 domain in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 8(8):324–330
Nguyen M, Millar DG, Yong VW, Korsmeyer SJ, Shore GC (1993) Targeting of Bcl-2 to the mitochondrial outer membrane by a COOH-terminal signal anchor sequence. J Biol Chem 268(34):25265–25268
van Delft MF, Huang DC (2006) How the Bcl-2 family of proteins interact to regulate apoptosis. Cell Res 16(2):203–213
Zhou L, Chang DC (2008) Dynamics and structure of the Bax-Bak complex responsible for releasing mitochondrial proteins during apoptosis. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 13):2186–2196
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292(5517):727–730
Zong WX, Lindsten T, Ross AJ, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB (2001) BH3-only proteins that bind pro-survival Bcl-2 family members fail to induce apoptosis in the absence of Bax and Bak. Genes Dev 15(12):1481–1486
Deng Y, Lin Y, Wu X (2002) TRAIL-induced apoptosis requires Bax-dependent mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO. Genes Dev 16(1):33–45
Finucane DM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Waterhouse NJ, Cotter TG, Green DR (1999) Bax-induced caspase activation and apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable by Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem 274(4):2225–2233
Gross A, Yin XM, Wang K, Wei MC, Jockel J, Milliman C, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Caspase cleaved BID targets mitochondria and is required for cytochrome c release, while BCL-XL prevents this release but not tumor necrosis factor-R1/Fas death. J Biol Chem 274(2):1156–1163
Cheng EH, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA, Mak TW, Lindsten T, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) BCL-2, BCL-X(L) sequester BH3 domain-only molecules preventing BAX- and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol Cell 8(3):705–711
Ruffolo SC, Shore GC (2003) BCL-2 selectively interacts with the BID-induced open conformer of BAK, inhibiting BAK auto-oligomerization. J Biol Chem 278(27):25039–25045
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, Wei A, Naik E, Fletcher JI, Adams JM, Huang DC (2005) Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 19(11):1294–1305
Lin B, Kolluri SK, Lin F, Liu W, Han YH, Cao X, Dawson MI, Reed JC, Zhang XK (2004) Conversion of Bcl-2 from protector to killer by interaction with nuclear orphan receptor Nur77/TR3. Cell 116(4):527–540
Chen G, Deng X (2015) Targeting Bcl2 in cancer. Oncoscience 2(10):813–814
Cheng EH, Kirsch DG, Clem RJ, Ravi R, Kastan MB, Bedi A, Ueno K, Hardwick JM (1997) Conversion of Bcl-2 to a Bax-like death effector by caspases. Science 278(5345):1966–1968
Clohessy JG, Zhuang J, Brady HJ (2004) Characterisation of Mcl-1 cleavage during apoptosis of haematopoietic cells. Br J Haematol 125(5):655–665
Fujita N, Nagahashi A, Nagashima K, Rokudai S, Tsuruo T (1998) Acceleration of apoptotic cell death after the cleavage of Bcl-XL protein by caspase-3-like proteases. Oncogene 17(10):1295–1304
Jonas EA, Hickman JA, Chachar M, Polster BM, Brandt TA, Fannjiang Y, Ivanovska I, Basanez G, Kinnally KW, Zimmerberg J, Hardwick JM, Kaczmarek LK (2004) Proapoptotic N-truncated BCL-xL protein activates endogenous mitochondrial channels in living synaptic terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(37):13590–13595
Basanez G, Zhang J, Chau BN, Maksaev GI, Frolov VA, Brandt TA, Burch J, Hardwick JM, Zimmerberg J (2001) Pro-apoptotic cleavage products of Bcl-xL form cytochrome c-conducting pores in pure lipid membranes. J Biol Chem 276(33):31083–31091
Alirol E, James D, Huber D, Marchetto A, Vergani L, Martinou JC, Scorrano L (2006) The mitochondrial fission protein hFis1 requires the endoplasmic reticulum gateway to induce apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 17(11):4593–4605
Xiao K, Wang Y, Chang Z, Lao Y, Chang DC (2014) p32, a novel binding partner of Mcl-1, positively regulates mitochondrial Ca(2 +) uptake and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451(2):322–328
Xiao K, Chen P, Chang DC (2014) The VTLISFG motif in the BH1 domain plays a significant role in regulating the degradation of Mcl-1. FEBS Open Bio 4:147–152
Kall L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer EL (2007) Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction–the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server issue):W429–W432
Kall L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer EL (2005) An HMM posterior decoder for sequence feature prediction that includes homology information. Bioinformatics 21(Suppl 1):i251–i257
Leber B, Lin J, Andrews DW (2007) Embedded together: the life and death consequences of interaction of the Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis 12(5):897–911
Huang DC, Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The conserved N-terminal BH4 domain of Bcl-2 homologues is essential for inhibition of apoptosis and interaction with CED-4. EMBO J 17(4):1029–1039
Hirotani M, Zhang Y, Fujita N, Naito M, Tsuruo T (1999) NH2-terminal BH4 domain of Bcl-2 is functional for heterodimerization with Bax and inhibition of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274(29):20415–20420
Rong YP, Bultynck G, Aromolaran AS, Zhong F, Parys JB, De Smedt H, Mignery GA, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Distelhorst CW (2009) The BH4 domain of Bcl-2 inhibits ER calcium release and apoptosis by binding the regulatory and coupling domain of the IP3 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(34):14397–14402
Sugioka R, Shimizu S, Funatsu T, Tamagawa H, Sawa Y, Kawakami T, Tsujimoto Y (2003) BH4-domain peptide from Bcl-xL exerts anti-apoptotic activity in vivo. Oncogene 22(52):8432–8440
Denis GV, Yu Q, Ma P, Deeds L, Faller DV, Chen CY (2003) Bcl-2, via its BH4 domain, blocks apoptotic signaling mediated by mitochondrial Ras. J Biol Chem 278(8):5775–5785
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Kodama T, Tsujimoto Y (2000) BH4 domain of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members closes voltage-dependent anion channel and inhibits apoptotic mitochondrial changes and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3100–3105
Krajewski S, Tanaka S, Takayama S, Schibler MJ, Fenton W, Reed JC (1993) Investigation of the subcellular distribution of the bcl-2 oncoprotein: residence in the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and outer mitochondrial membranes. Cancer Res 53(19):4701–4714
Kaufmann T, Schlipf S, Sanz J, Neubert K, Stein R, Borner C (2003) Characterization of the signal that directs Bcl-x(L), but not Bcl-2, to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol 160(1):53–64
Petros AM, Olejniczak ET, Fesik SW (2004) Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644(2–3):83–94
George NM, Evans JJ, Luo X (2007) A three-helix homo-oligomerization domain containing BH3 and BH1 is responsible for the apoptotic activity of Bax. Genes Dev 21(15):1937–1948
Petros AM, Medek A, Nettesheim DG, Kim DH, Yoon HS, Swift K, Matayoshi ED, Oltersdorf T, Fesik SW (2001) Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(6):3012–3017
Muchmore SW, Sattler M, Liang H, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Yoon HS, Nettesheim D, Chang BS, Thompson CB, Wong SL, Ng SL, Fesik SW (1996) X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 381(6580):335–341
Oh KJ, Singh P, Lee K, Foss K, Lee S, Park M, Lee S, Aluvila S, Park M, Singh P, Kim RS, Symersky J, Walters DE (2010) Conformational changes in BAK, a pore-forming proapoptotic Bcl-2 family member, upon membrane insertion and direct evidence for the existence of BH3-BH3 contact interface in BAK homo-oligomers. J Biol Chem 285(37):28924–28937
Nouraini S, Six E, Matsuyama S, Krajewski S, Reed JC (2000) The putative pore-forming domain of Bax regulates mitochondrial localization and interaction with Bcl-X(L). Mol Cell Biol 20(5):1604–1615
Dlugosz PJ, Billen LP, Annis MG, Zhu W, Zhang Z, Lin J, Leber B, Andrews DW (2006) Bcl-2 changes conformation to inhibit Bax oligomerization. EMBO J 25(11):2287–2296
Billen LP, Kokoski CL, Lovell JF, Leber B, Andrews DW (2008) Bcl-XL inhibits membrane permeabilization by competing with Bax. PLoS Biol 6(6):e147
Annis MG, Soucie EL, Dlugosz PJ, Cruz-Aguado JA, Penn LZ, Leber B, Andrews DW (2005) Bax forms multispanning monomers that oligomerize to permeabilize membranes during apoptosis. EMBO J 24(12):2096–2103
Schinzel A, Kaufmann T, Schuler M, Martinalbo J, Grubb D, Borner C (2004) Conformational control of Bax localization and apoptotic activity by Pro168. J Cell Biol 164(7):1021–1032
Griffiths GJ, Dubrez L, Morgan CP, Jones NA, Whitehouse J, Corfe BM, Dive C, Hickman JA (1999) Cell damage-induced conformational changes of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak in vivo precede the onset of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 144(5):903–914
Barclay LA, Wales TE, Garner TP, Wachter F, Lee S, Guerra RM, Stewart ML, Braun CR, Bird GH, Gavathiotis E, Engen JR, Walensky LD (2015) Inhibition of pro-apoptotic BAX by a noncanonical interaction mechanism. Mol Cell 57(5):873–886
Monaco G, Decrock E, Akl H, Ponsaerts R, Vervliet T, Luyten T, De Maeyer M, Missiaen L, Distelhorst CW, De Smedt H, Parys JB, Leybaert L, Bultynck G (2012) Selective regulation of IP3-receptor-mediated Ca2 + signaling and apoptosis by the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 versus Bcl-Xl. Cell Death Differ 19(2):295–309
Monaco G, Decrock E, Arbel N, van Vliet AR, La Rovere RM, De Smedt H, Parys JB, Agostinis P, Leybaert L, Shoshan-Barmatz V, Bultynck G (2015) The BH4 domain of anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL, but not that of the related Bcl-2, limits the voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1)-mediated transfer of pro-apoptotic Ca2+ signals to mitochondria. J Biol Chem 290(14):9150–9161
Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod JJ, Mazzei G, Maundrell K, Gambale F, Sadoul R, Martinou JC (1997) Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science 277(5324):370–372
Schendel SL, Xie Z, Montal MO, Matsuyama S, Montal M, Reed JC (1997) Channel formation by antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(10):5113–5118
Minn AJ, Velez P, Schendel SL, Liang H, Muchmore SW, Fesik SW, Fill M, Thompson CB (1997) Bcl-x(L) forms an ion channel in synthetic lipid membranes. Nature 385(6614):353–357
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Eskes R, Martinou JC (2000) Bax oligomerization is required for channel-forming activity in liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Biochem J 345(Pt 2):271–278
Lalier L, Cartron PF, Juin P, Nedelkina S, Manon S, Bechinger B, Vallette FM (2007) Bax activation and mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis 12(5):887–896
Azad A, Storey A (2013) BAK multimerization for apoptosis, but not bid binding, is inhibited by negatively charged residue in the BAK hydrophobic groove. Mol Cancer 12:65
Cartron PF, Gallenne T, Bougras G, Gautier F, Manero F, Vusio P, Meflah K, Vallette FM, Juin P (2004) The first alpha helix of Bax plays a necessary role in its ligand-induced activation by the BH3-only proteins Bid and PUMA. Mol Cell 16(5):807–818
Szabo I, Soddemann M, Leanza L, Zoratti M, Gulbins E (2011) Single-point mutations of a lysine residue change function of Bax and Bcl-xL expressed in Bax- and Bak-less mouse embryonic fibroblasts: novel insights into the molecular mechanisms of Bax-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 18(3):427–438
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Dr. Y. Tsujimoto for kindly supplying us the pRSET-Bax gene, Dr. Richard J. Youle for providing the YFP-Bak and pEGFP-Bcl-xL genes, Dr. Steven W. Edwards for providing pEGFP-C3-Mcl-1 gene, Dr. Yong Xie for providing Bcl-2 gene, and Dr. L. Scorrano for providing the MEF and MEF-DKO cell lines. This work was supported by grants from the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (HKUST6466/05 M, N_HKUST616/05 and 660207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kang Xiao, Wenrui Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, K., Zhao, W., Zhou, L. et al. Alpha 5/6 helix domains together with N-terminus determine the apoptotic potency of the Bcl-2 family proteins. Apoptosis 21, 1214–1226 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1283-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1283-9