Abstract
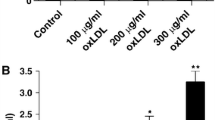
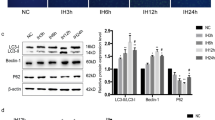
This study was aimed to evaluate lysosomes–mitochondria cross-signaling in angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and whether atorvastatin played a protective role via lysosomal-mitochondrial axis. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry, Hoechst 33342 and AO/EB assay. The temporal relationship of lysosomal and mitochondrial permeabilization was established. Activity of Cathepsin D (CTSD) was suppressed by pharmacological and genetic approaches. Proteins production were measured by western blotting. Our study showed that Ang II could induce the apoptosis of HUVECs in a dose-depended and time-depended manner. Exposure to 1 μM Ang II for 24 h resulted in mitochondrial depolarization, cytochrome c release, and increased ROS production. Lysosomal permeabilization and CTSD redistribution into the cytoplasm occurred several hours prior to mitochondrial dysfunction. These effects were all suppressed by atorvastatin. Either pharmacological or genetic inhibition of CTSD preserved mitochondrial function and decreased apoptosis in HUVECs. Most importantly, we found that the protective effect of atorvastatin was significantly greater than pharmacological or genetic inhibition of CTSD. Finally, overexpression of CTSD without exposure to Ang II had no effect on mitochondrial function and apoptosis. Our data strongly suggested that Ang II induced apoptosis through the lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in HUVECs. Furthermore, atorvastatin played an important role in the regulation of lysosomes and mitochondria stability, resulting in an antagonistic role against Ang II on HUVECs.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whaley-Connell A, Johnson MS, Sowers JR (2010) Aldosterone: role in the cardiometabolic syndrome and resistant hypertension. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52(5):401–409
Aroor AR, Demarco VG, Jia G, Sun Z, Nistala R, Meininger GA, Sowers JR (2013) The role of tissue Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone system in the development of endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness. Front Endocrinol 4:161
Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM (2004) From bedside to bench to bedside: role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in remodeling of resistance arteries in hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287(2):H435–H446
Touyz RM (2003) The role of angiotensin II in regulating vascular structural and functional changes in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 5(2):155–164
Sata M, Fukuda D (2010) Crucial role of renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Med Invest 57(1–2):12–25
Pan MH, Hsieh MC, Kuo JM, Lai CS, Wu H, Sang S, Ho CT (2008) 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells via ROS production, caspase activation, and GADD 153 expression. Mol Nutr Food Res 52(5):527–537
Bouchier-Hayes L, Lartigue L, Newmeyer DD (2005) Mitochondria: pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin Investig 115(10):2640–2647
Lane N (2006) Mitochondrial disease: powerhouse of disease. Nature 440(7084):600–602
Yang HY, Bian YF, Zhang HP, Gao F, Xiao CS, Liang B, Li J, Zhang NN, Yang ZM (2012) Angiotensin-(1-7) treatment ameliorates angiotensin II-induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 39(12):1004–1010
Ahsan A, Han G, Pan J, Liu S, Padhiar AA, Chu P, Sun Z, Zhang Z, Sun B, Wu J, Irshad A, Lin Y, Peng J, Tang Z (2015) Phosphocreatine protects endothelial cells from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by modulating the PI3 K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Apoptosis 20(12):1563–1576
Surico D, Farruggio S, Marotta P, Raina G, Mary D, Surico N, Vacca G, Grossini E (2015) Human chorionic gonadotropin protects vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress by apoptosis inhibition, cell survival signalling activation and mitochondrial function protection. Cell Physiol Biochem 36(6):2108–2120
Leist M, Jaattela M (2001) Four deaths and a funeral: from caspases to alternative mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(8):589–598
Guicciardi ME, Leist M, Gores GJ (2004) Lysosomes in cell death. Oncogene 23(16):2881–2890
Davignon J (2004) Beneficial cardiovascular pleiotropic effects of statins. Circulation 109(23 Suppl 1):III39–III43
Carnicka S, Adameova A, Nemcekova M, Matejikova J, Pancza D, Ravingerova T (2011) Distinct effects of acute pretreatment with lipophilic and hydrophilic statins on myocardial stunning, arrhythmias and lethal injury in the rat heart subjected to ischemia/reperfusion. Physiol Res 60(5):825–830
Guimaraes DA, Rizzi E, Ceron CS, Pinheiro LC, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE (2013) Atorvastatin and sildenafil lower blood pressure and improve endothelial dysfunction, but only atorvastatin increases vascular stores of nitric oxide in hypertension. Redox Biol 1:578–585
Zhou MS, Tian R, Jaimes EA, Raij L (2014) Combination therapy of amlodipine and atorvastatin has more beneficial vascular effects than monotherapy in salt-sensitive hypertension. Am J Hypertens 27(6):873–880
Chen S, Liu B, Kong D, Li S, Li C, Wang H, Sun Y (2015) Atorvastatin calcium inhibits phenotypic modulation of PDGF-BB-induced VSMCs via down-regulation the Akt signaling pathway. PLoS One 10(4):e0122577
Yang G, Wang S, Zhong L, Dong X, Zhang W, Jiang L, Geng C, Sun X, Liu X, Chen M, Ma Y (2012) 6-Gingerol induces apoptosis through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in human hepatoma G2 cells. Phytother Res 26(11):1667–1673
Mitrofan LM, Castells FB, Pelkonen J, Monkkonen J (2010) Lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in zoledronic acid-induced apoptosis in human follicular lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem 285(3):1967–1979
Byczkowska A, Kunikowska A, Kazmierczak A (2013) Determination of ACC-induced cell-programmed death in roots of Vicia faba ssp. minor seedlings by acridine orange and ethidium bromide staining. Protoplasma 250(1):121–128
Rybaczek D, Musialek MW, Balcerczyk A (2015) caffeine-induced premature chromosome condensation results in the apoptosis-like programmed cell death in root meristems of vicia faba. PLoS One 10(11):e0142307
He Y, Mo Q, Hu Y, Chen W, Luo B, Wu L, Qiao Y, Xu R, Zhou Y, Zuo Z, Deng J, He W, Wei Y (2015) E. adenophorum induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of splenocytes through the mitochondrial pathway and caspase activation in saanen goats. Sci Rep 5:15967
Li Z, Berk M, McIntyre TM, Gores GJ, Feldstein AE (2008) The lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in free fatty acid-induced hepatic lipotoxicity. Hepatology 47(5):1495–1503
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH, Thompson CB (2003) Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 10(6):709–717
Lei T, Guo N, Tan MH, Li YF (2014) Effect of mouse oocyte vitrification on mitochondrial membrane potential and distribution. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 34(1):99–102
Sohn JH, Han KL, Lee SH, Hwang JK (2005) Protective effects of panduratin A against oxidative damage of tert-butylhydroperoxide in human HepG2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 28(6):1083–1086
Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Jiang L, Yang G, Sun X, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X, Chen M (2015) Citreoviridin induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in human liver HepG2 Cells. Toxins 7(8):3030–3044
Boya P, Kroemer G (2008) Lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cell death. Oncogene 27(50):6434–6451
Green DR (2005) Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell 121(5):671–674
De Duve C, Wattiaux R (1966) Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol 28:435–492
Terman A, Gustafsson B, Brunk UT (2006) The lysosomal-mitochondrial axis theory of postmitotic aging and cell death. Chem Biol Interact 163(1–2):29–37
Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T (2002) Autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. Cell Struct Funct 27(6):421–429
Mishima Y, Terui Y, Mishima Y, Taniyama A, Kuniyoshi R, Takizawa T, Kimura S, Ozawa K, Hatake K (2008) Autophagy and autophagic cell death are next targets for elimination of the resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Sci 99(11):2200–2208
Roberg K, Ollinger K (1998) Oxidative stress causes relocation of the lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D with ensuing apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Am J Pathol 152(5):1151–1156
Kagedal K, Johansson U, Ollinger K (2001) The lysosomal protease cathepsin D mediates apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. FASEB J 15(9):1592–1594
Brunk UT, Neuzil J, Eaton JW (2001) Lysosomal involvement in apoptosis. Redox report: communications in free radical research 6(2):91–97
Gigli R, Pereira GJ, Antunes F, Bechara A, Garcia DM, Spindola DG, Jasiulionis MG, Caires AC, Smaili SS, Bincoletto C (2016) The biphosphinic paladacycle complex induces melanoma cell death through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis modulation and impaired autophagy. Eur J Med Chem 107:245–254
Turk V, Turk B, Guncar G, Turk D, Kos J (2002) Lysosomal cathepsins: structure, role in antigen processing and presentation, and cancer. Adv Enzyme Regul 42:285–303
Graham DJ, Staffa JA, Shatin D, Andrade SE, Schech SD, La Grenade L, Gurwitz JH, Chan KA, Goodman MJ, Platt R (2004) Incidence of hospitalized rhabdomyolysis in patients treated with lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA 292(21):2585–2590
Sathasivam S (2012) Statin induced myotoxicity. E J Int Med 23(4):317–324
Mabuchi H, Higashikata T, Kawashiri M, Katsuda S, Mizuno M, Nohara A, Inazu A, Koizumi J, Kobayashi J (2005) Reduction of serum ubiquinol-10 and ubiquinone-10 levels by atorvastatin in hypercholesterolemic patients. J Atheroscler Thrombosis 12(2):111–119
Vaughan RA, Garcia-Smith R, Bisoffi M, Conn CA, Trujillo KA (2013) Ubiquinol rescues simvastatin-suppression of mitochondrial content, function and metabolism: implications for statin-induced rhabdomyolysis. Eur J Pharmacol 711(1–3):1–9
Ghavami S, Yeganeh B, Stelmack GL, Kashani HH, Sharma P, Cunnington R, Rattan S, Bathe K, Klonisch T, Dixon IM, Freed DH, Halayko AJ (2012) Apoptosis, autophagy and ER stress in mevalonate cascade inhibition-induced cell death of human atrial fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis 3:e330
Mullen PJ, Zahno A, Lindinger P, Maseneni S, Felser A, Krahenbuhl S, Brecht K (2011) Susceptibility to simvastatin-induced toxicity is partly determined by mitochondrial respiration and phosphorylation state of Akt. Biochim Biophys Acta 12:2079–2087
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 81470417] and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province [Grant No. 2013021090].
Author Contributions
Ye Chang, Zhao Li and Yingxian Sun conceived and designed the experiments; Ye Chang, Yuan Li, Ning Ye, Xiaofan Guo and Guozhe Sun performed the experiments; Ye Chang analyzed the data; Ye Chang wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., Li, Y., Ye, N. et al. Atorvastatin inhibits the apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by angiotensin II via the lysosomal-mitochondrial axis. Apoptosis 21, 977–996 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1271-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1271-0