Abstract
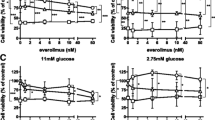
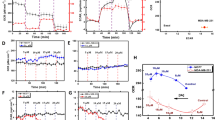
Metformin, an AMPK activator, has been reported to improve pathological response to chemotherapy in diabetic breast cancer patients. To date, its mechanism of action in cancer, especially in cancer stem cells (CSCs) have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we demonstrated that metformin, but not other AMPK activators (e.g. AICAR and A-769662), synergizes 5-fluouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FEC) combination chemotherapy in non-stem breast cancer cells and breast cancer stem cells. We show that this occurs through an AMPK-dependent mechanism in parental breast cancer cell lines. In contrast, the synergistic effects of metformin and FEC occurred in an AMPK-independent mechanism in breast CSCs. Further analyses revealed that metformin accelerated glucose consumption and lactate production more severely in the breast CSCs but the production of intracellular ATP was severely hampered, leading to a severe energy crisis and impairs the ability of CSCs to repair FEC-induced DNA damage. Indeed, addition of extracellular ATP completely abrogated the synergistic effects of metformin on FEC sensitivity in breast CSCs. In conclusion, our results suggest that metformin synergizes FEC sensitivity through distinct mechanism in parental breast cancer cell lines and CSCs, thus providing further evidence for the clinical relevance of metformin for the treatment of cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Kakarala M, Wicha MS (2008) Implications of the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and therapy. J Clin Oncol 26(17):2813–2820. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3931
Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S (2005) Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 5(4):275–284. doi:10.1038/nrc1590
Rosen JM, Jordan CT (2009) The increasing complexity of the cancer stem cell paradigm. Science 324(5935):1670–1673. doi:10.1126/science.1171837
Creighton CJ, Li X, Landis M, Dixon JM, Neumeister VM, Sjolund A et al (2009) Residual breast cancers after conventional therapy display mesenchymal as well as tumor-initiating features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(33):13820–13825. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905718106
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C, Osborne CK, Wu MF et al (2008) Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(9):672–679. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn123
Del Barco S, Vazquez-Martin A, Cufi S, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Bosch-Barrera J, Joven J et al (2011) Metformin: multi-faceted protection against cancer. Oncotarget 2(12):896–917
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K (2009) Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res 69(19):7507–7511. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2994
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Struhl K (2013) Metformin inhibits the inflammatory response associated with cellular transformation and cancer stem cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(3):972–977. doi:10.1073/pnas.1221055110
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K (2011) Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res 71(9):3196–3201. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3471
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B et al (2010) Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3(11):1451–1461. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0157
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC, Shridhar V (2011) Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med 15(1):166–178. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00954.x
Godsland IF (2010) Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in the development and progression of cancer. Clin Sci 118(5):315–332. doi:10.1042/CS20090399
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM et al (2009) Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(20):3297–3302. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.19.6410
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ et al (2003) In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev 17(10):1253–1270. doi:10.1101/gad.1061803
Lim LY, Vidnovic N, Ellisen LW, Leong CO (2009) Mutant p53 mediates survival of breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 101(9):1606–1612. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605335
Leong CO, Vidnovic N, DeYoung MP, Sgroi D, Ellisen LW (2007) The p63/p73 network mediates chemosensitivity to cisplatin in a biologically defined subset of primary breast cancers. J Clin Invest 117(5):1370–1380. doi:10.1172/JCI30866
Greco WR, Bravo G, Parsons JC (1995) The search for synergy: a critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol Rev 47(2):331–385
Keith CT, Borisy AA, Stockwell BR (2005) Multicomponent therapeutics for networked systems. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(1):71–78. doi:10.1038/nrd1609
Prichard MN, Shipman C Jr (1990) A three-dimensional model to analyze drug-drug interactions. Antiviral Res 14(4–5):181–205
Tan BS, Tiong KH, Muruhadas A, Randhawa N, Choo HL, Bradshaw TD et al (2011) CYP2S1 and CYP2W1 Mediate 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole (GW-610, NSC 721648) sensitivity in breast and colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 10(10):1982–1992. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0391
Bradshaw TD, Stone EL, Trapani V, Leong CO, Matthews CS, te Poele R et al (2008) Mechanisms of acquired resistance to 2-(4-Amino-3-methylphenyl)benzothiazole in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 110(1):57–68. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9690-9
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L et al (2008) The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science 320(5882):1496–1501. doi:10.1126/science.1157535
Tan BS, Kang O, Mai CW, Tiong KH, Khoo AS, Pichika MR et al (2013) 6-Shogaol inhibits breast and colon cancer cell proliferation through activation of peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma). Cancer Lett 336(1):127–139. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.014
Low SY, Tan BS, Choo HL, Tiong KH, Khoo AS, Leong CO (2012) Suppression of BCL-2 synergizes cisplatin sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 314(2):166–175. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.09.025
Liu PP, Liao J, Tang ZJ, Wu WJ, Yang J, Zeng ZL et al (2014) Metabolic regulation of cancer cell side population by glucose through activation of the Akt pathway. Cell Death Differ 21(1):124–135. doi:10.1038/cdd.2013.131
Leong CO, Suggitt M, Swaine DJ, Bibby MC, Stevens MF, Bradshaw TD (2004) In vitro, in vivo, and in silico analyses of the antitumor activity of 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazoles. Mol Cancer Ther 3(12):1565–1575
Konca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Gozdz S et al (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 534(1–2):15–20
Lokody I (2013) Gene regulation: chromatin editing reveals enhancer targets. Nat Rev Genet 14(11):749. doi:10.1038/nrg3601
O’Brien CS, Howell SJ, Farnie G, Clarke RB (2009) Resistance to endocrine therapy: are breast cancer stem cells the culprits? J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 14(1):45–54. doi:10.1007/s10911-009-9115-y
Rocha GZ, Dias MM, Ropelle ER, Osorio-Costa F, Rossato FA, Vercesi AE et al (2011) Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and antitumoral growth. Clin Cancer Res 17(12):3993–4005. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2243
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J et al (2001) Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 108(8):1167–1174. doi:10.1172/JCI13505
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P et al (2008) The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene 27(25):3576–3586. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1211024
Foretz M, Hebrard S, Leclerc J, Zarrinpashneh E, Soty M, Mithieux G et al (2010) Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state. J Clin Invest 120(7):2355–2369. doi:10.1172/JCI40671
Kalender A, Selvaraj A, Kim SY, Gulati P, Brule S, Viollet B et al (2010) Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag GTPase-dependent manner. Cell Metab 11(5):390–401. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2010.03.014
Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G, Laurent K, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Auberger P et al (2011) Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell-cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res 71(13):4366–4372. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1769
El-Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Averet N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X (2000) Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on the respiratory chain complex I. J Biol Chem 275(1):223–228
Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP (2000) Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J 348(Pt 3):607–614
Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA et al (2005) The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science 310(5754):1642–1646. doi:10.1126/science.1120781
Fu D, Calvo JA, Samson LD (2012) Balancing repair and tolerance of DNA damage caused by alkylating agents. Nat Rev Cancer 12(2):104–120. doi:10.1038/nrc3185
Pearl LH, Schierz AC, Ward SE, Al-Lazikani B, Pearl FM (2015) Therapeutic opportunities within the DNA damage response. Nat Rev Cancer 15(3):166–180. doi:10.1038/nrc3891
Huang J, Liang B, Qiu J, Laurent BC (2005) ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes in DNA double-strand break repair: remodeling, pairing and (re)pairing. Cell Cycle 4(12):1713–1715
van Attikum H, Gasser SM (2005) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling and DNA double-strand break repair. Cell Cycle 4(8):1011–1014
van Attikum H, Fritsch O, Hohn B, Gasser SM (2004) Recruitment of the INO80 complex by H2A phosphorylation links ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling with DNA double-strand break repair. Cell 119(6):777–788. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.033
Dowling RJ, Niraula S, Stambolic V, Goodwin PJ (2012) Metformin in cancer: translational challenges. J Mol Endocrinol 48(3):R31–R43. doi:10.1530/JME-12-0007
Rosilio C, Lounnas N, Nebout M, Imbert V, Hagenbeek T, Spits H et al (2013) The metabolic perturbators metformin, phenformin and AICAR interfere with the growth and survival of murine PTEN-deficient T cell lymphomas and human T-ALL/T-LL cancer cells. Cancer Lett 336(1):114–126. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.015
Bost F, Sahra IB, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF (2012) Metformin and cancer therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 24(1):103–108. doi:10.1097/CCO.0b013e32834d8155
Ben Sahra I, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF, Bost F (2010) Metformin in cancer therapy: a new perspective for an old antidiabetic drug? Mol Cancer Ther 9(5):1092–1099. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1186
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Giuliano S, Larbret F, Ponzio G, Gounon P et al (2010) Targeting cancer cell metabolism: the combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 70(6):2465–2475. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2782
Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE et al (2009) Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle 8(6):909–915
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N (2007) Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67(22):10804–10812. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2310
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M (2006) Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66(21):10269–10273. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1500
Shackelford DB, Shaw RJ (2009) The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):563–575. doi:10.1038/nrc2676
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Meric-Bernstam F (2010) Metformin: a therapeutic opportunity in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(6):1695–1700. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1805
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Menendez JA (2009) The antidiabetic drug metformin suppresses HER2 (erbB-2) oncoprotein overexpression via inhibition of the mTOR effector p70S6K1 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 8(1):88–96
Yuan S, Wang F, Chen G, Zhang H, Feng L, Wang L et al (2013) Effective elimination of cancer stem cells by a novel drug combination strategy. Stem Cells 31(1):23–34. doi:10.1002/stem.1273
Gammon L, Biddle A, Heywood HK, Johannessen AC, Mackenzie IC (2013) Sub-sets of cancer stem cells differ intrinsically in their patterns of oxygen metabolism. PLoS One 8(4):e62493. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062493
Bosco JL, Antonsen S, Sorensen HT, Pedersen L, Lash TL (2011) Metformin and incident breast cancer among diabetic women: a population-based case-control study in Denmark. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 20(1):101–111. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0817
Kim HJ, Kwon H, Lee JW, Lee SB, Park HS, Sohn G et al (2015) Metformin increases survival in hormone receptor-positive, Her2-positive breast cancer patients with diabetes. Breast Cancer Res 17(1):64. doi:10.1186/s13058-015-0574-3
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the funds raised through the Yayasan Sime Darby LPGA Tournament, donors of Cancer Research Initiatives Foundation and the Ministry of Higher Education Grant [UM.C/HIR/MOHE/06 and ERGS/1/2013/SKK01/IMU/02/1].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest pertaining to this study.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
No human participants and/or animals was involved in this study.
Informed consent
No informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Jaslyn Sian-Siu Soo and Char-Hong Ng are joint first authors and shared equal contribution.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soo, J.SS., Ng, CH., Tan, S.H. et al. Metformin synergizes 5-fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FEC) combination therapy through impairing intracellular ATP production and DNA repair in breast cancer stem cells. Apoptosis 20, 1373–1387 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1158-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1158-5