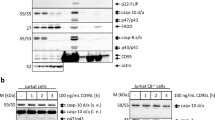
Abstract
Death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) is a platform for the activation of initiator caspase in extrinsic apoptosis. Assembly of DISC is accomplished by two different types of homotypic interaction: one is between death domains (DDs) of a death receptor and FADD, and the other is between death effecter domains (DEDs) of FADD, procaspase-8/-10 and cFLIP. Recent biochemical investigations on the stoichiometry of DISC have revealed that single-DED-containing FADD exists in DISC in a substantially lower abundance than the sum of tandem-DEDs-containing components that are procaspase-8 and cFLIP. In addition, the homology models of the tandem DEDs in procaspase-8 and cFLIP show that two different interaction faces, H1–H4 face and H2–H5 face, are exposed for possible inter-molecular DED–DED interactions. These recent findings led to a proposal of the DED chain model for the interactions between FADD, procaspase-8 and cFLIP in DISC. This emerging view provides new insights on the topology of DED–DED network in DISC and furthermore on how procaspase-8 and cFLIP cluster for dimerization and proteolytic activation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park HH, Lo YC, Lin SC, Wang L, Yang JK, Wu H (2007) The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling of apoptosis and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 25:561–586
Huang B, Eberstadt M, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Fesik SW (1996) NMR structure and mutagenesis of the Fas (APO-1/CD95) death domain. Nature 384:638–641
Eberstadt M, Huang B, Chen Z et al (1998) NMR structure and mutagenesis of the FADD (Mort1) death-effector domain. Nature 392:941–945
Chou JJ, Matsuo H, Duan H, Wagner G (1998) Solution structure of the RAIDD CARD and model for CARD/CARD interaction in caspase-2 and caspase-9 recruitment. Cell 94:171–180
Hiller S, Kohl A, Fiorito F et al (2003) NMR structure of the apoptosis- and inflammation-related NALP1 pyrin domain. Structure 11:1199–1205
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I et al (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91:479–489
Adams JM, Cory S (2002) Apoptosomes: engines for caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:715–720
Qin H, Srinivasula SM, Wu G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES, Shi Y (1999) Structural basis of procaspase-9 recruitment by the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1. Nature 399:549–557
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I et al (1995) Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J 14:5579–5588
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505–512
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC et al (1996) FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell 85:817–827
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D (1996) Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell 85:803–815
Yu X, Acehan D, Menetret JF et al (2005) A structure of the human apoptosome at 12.8 A resolution provides insights into this cell death platform. Structure 13:1725–1735
Teng X, Hardwick JM (2010) The apoptosome at high resolution. Cell 141:402–404
Scott FL, Stec B, Pop C et al (2009) The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering. Nature 457:1019–1022
Wang L, Yang JK, Kabaleeswaran V et al (2010) The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure reveals the basis of DISC assembly and disease mutations. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1324–1329
Yang JK, Wang L, Zheng L et al (2005) Crystal structure of MC159 reveals molecular mechanism of DISC assembly and FLIP inhibition. Mol Cell 20:939–949
Bagneris C, Ageichik AV, Cronin N et al (2008) Crystal structure of a vFlip-IKKgamma complex: insights into viral activation of the IKK signalosome. Mol Cell 30:620–631
Dickens LS, Boyd RS, Jukes-Jones R et al (2012) A death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol Cell 47:291–305
Schleich K, Warnken U, Fricker N et al (2012) Stoichiometry of the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex: experimental and modeling evidence for a death effector domain chain model. Mol Cell 47:306–319
Majkut J, Sgobba M, Holohan C et al (2014) Differential affinity of FLIP and procaspase 8 for FADD’s DED binding surfaces regulates DISC assembly. Nat Commun 5:3350
Yu JW, Shi Y (2008) FLIP and the death effector domain family. Oncogene 27:6216–6227
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ (2001) The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104:487–501
Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Tschopp J (2002) The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci 27:19–26
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Wang J, Chun HJ, Wong W, Spencer DM, Lenardo MJ (2001) Caspase-10 is an initiator caspase in death receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13884–13888
Yang JK (2008) FLIP as an anti-cancer therapeutic target. Yonsei Med J 49:19–27
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1999) The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:1541–1548
Kataoka T, Tschopp J (2004) N-terminal fragment of c-FLIP(L) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts with TRAF2 and induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 24:2627–2636
Golks A, Brenner D, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN (2006) The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med 203:1295–1305
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Tinel A et al (2001) Death receptor recruitment of endogenous caspase-10 and apoptosis initiation in the absence of caspase-8. J Biol Chem 276:46639–46646
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand MA, Walczak H (2002) Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J 21:4520–4530
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M et al (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195
Siegel RM, Martin DA, Zheng L et al (1998) Death-effector filaments: novel cytoplasmic structures that recruit caspases and trigger apoptosis. J Cell Biol 141:1243–1253
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2014R1A2A2A01006834).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J.K. Death effecter domain for the assembly of death-inducing signaling complex. Apoptosis 20, 235–239 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1060-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1060-6