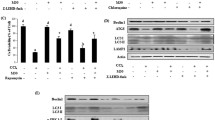
Abstract
A variety of data suggesting apoptotic cell death as a key feature of liver injury stimulated researchers to investigate the therapeutic potential of anti-apoptotic strategies in experimental models. However, the overestimated role of apoptotic cell death in liver injury has tempered the clinical translation of the protection afforded by anti-apoptotic regimes in experimental models. Thus, the hope for apoptosis modulation as potential treatment strategy for injured liver in humans could not be confirmed. Herein, we evaluated the degree of apoptosis in different hepatic stress models which are relevant for the human pathophysiology. Using morphological criteria of apoptosis, caspase-3 activation as well as TUNEL assay in combination with a positive control of apoptosis in liver injury, we quantified apoptotic cell death discriminating between parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells and confirmed these results by cleaved caspase-3 and PARP-1 protein expression. Discussing our findings and relating them to the existing literature on the potential role of apoptotic cell death, we strongly recommend reconsidering anti-apoptotic strategies to ameliorate liver injury efficiently.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuchmann M, Galle PR (2001) Apoptosis in liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:785–790
Yoon JH, Gores GJ (2002) Death receptor-mediated apoptosis and the liver. J Hepatol 37:400–410
Gujral JS, Knight TR, Farhood A, Bajt ML, Jaeschke H (2002) Mode of cell death after acetaminophen overdose in mice: apoptosis or oncotic necrosis? Toxicol Sci 67:322–328
Maier S, Traeger T, Entleutner M, Westerholt A, Kleist B, Huser N, Holzmann B, Stier A, Pfeffer K, Heidecke CD (2004) Cecal ligation and puncture versus colon ascendens stent peritonitis: two distinct animal models for polymicrobial sepsis. Shock 21:505–511
Georgiev P, Jochum W, Heinrich S, Jang JH, Nocito A, Dahm F, Clavien PA (2008) Characterization of time-related changes after experimental bile duct ligation. Br J Surg 95:646–656
Tarcin O, Basaranoglu M, Tahan V, Tahan G, Sucullu I, Yilmaz N, Sood G, Snyder N, Hilman G, Celikel C, Tozun N (2011) Time course of collagen peak in bile duct-ligated rats. BMC Gastroenterol 11:45
Constandinou C, Henderson N, Iredale JP (2005) Modeling liver fibrosis in rodents. Methods Mol Med 117:237–250
Fausto N (2000) Liver regeneration. J Hepatol 32:19–31
Eipel C, Hirschmann M, Abshagen K, Menger MD, Vollmar B (2007) Local interaction of apoptotic hepatocytes and Kupffer cells in a rat model of systemic endotoxemia. Hepatol Res 37:863–871
El-Gibaly AM, Scheuer C, Menger MD, Vollmar B (2004) Improvement of rat liver graft quality by pifithrin-alpha-mediated inhibition of hepatocyte necrapoptosis. Hepatology 39:1553–1562
Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y, Davidson NE, Poirier GG (1993) Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 53:3976–3985
Brauns SC, Dealtry G, Milne P, Naudé R, Van de Venter M (2005) Caspase-3 activation and induction of PARP cleavage by cyclic dipeptide cyclo(Phe-Pro) in HT-29 cells. Anticancer Res 25:4197–4202
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ, Babu PP (2010) PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal 8:31
Schmidt ES, Schmidt FW (1988) Glutamate dehydrogenase: biochemical and clinical aspects of an interesting enzyme. Clin Chim Acta 173:43–55
Eichhorst ST (2005) Modulation of apoptosis as a target for liver disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9:83–99
Gujral JS, Bucci TJ, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2001) Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion in rats: apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology 33:397–405
Redaelli CA, Tian YH, Schaffner T, Ledermann M, Baer HU, Dufour JF (2002) Extended preservation of rat liver graft by induction of heme oxygenase-1. Hepatology 35:1082–1092
Jaeschke H, Lemasters JJ (2003) Apoptosis versus oncotic necrosis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gastroenterology 125:1246–1257
Gujral JS, Liu J, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2004) Reduced oncotic necrosis in fas receptor-deficient c57bl/6j-lpr mice after bile duct ligation. Hepatology 40:998–1007
Huet PM, Nagaoka MR, Desbiens G, Tarrab E, Brault A, Bralet MP, Bilodeau M (2004) Sinusoidal endothelial cell and hepatocyte death following cold ischemia-warm reperfusion of the rat liver. Hepatology 39:1110–1119
Fickert P, Trauner M, Fuchsbichler A, Zollner G, Wagner M, Marschall HU, Zatloukal K, Denk H (2005) Oncosis represents the main type of cell death in mouse models of cholestasis. J Hepatol 42:378–385
Malhi H, Gores GJ, Lemasters JJ (2006) Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver: a tale of two deaths? Hepatology 43:S31–S44
Sigal M, Siebert N, Zechner D, Menschikow E, Abshagen K, Vollmar B, Eipel C (2010) Darbepoetin-alpha inhibits the perpetuation of necro-inflammation and delays the progression of cholestatic fibrosis in mice. Lab Invest 90:1447–1456
Woolbright BL, Jaeschke H (2012) Novel insight into mechanisms of cholestatic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 18:4985–4993
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Schuchmann M, Fleischer B, Galle PR (2006) The role of apoptosis versus oncotic necrosis in liver injury: facts or faith? J Hepatol 44:984–993
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 4:321–328
Watanabe M, Hitomi M, van der Wee K, Rothenberg F, Fisher SA, Zucker R, Svoboda KK, Goldsmith EC, Heiskanen KM, Nieminen AL (2002) The pros and cons of apoptosis assays for use in the study of cells, tissues, and organs. Microsc Microanal 8:375–391
Montalvo-Jave EE, Escalante-Tattersfield T, Ortega-Salgado JA, Pina E, Geller DA (2008) Factors in the pathophysiology of the liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 147:153–159
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Tapuria N, Fuller B, Davidson B, Seifalian A (2010) Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: processes in inflammatory networks—a review. Liver Transpl 16:1016–1032
Bahde R, Spiegel HU (2010) Hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury from bench to bedside. Br J Surg 97:1461–1475
Weigand K, Brost S, Steinebrunner N, Buchler M, Schemmer P, Muller M (2012) Ischemia/reperfusion injury in liver surgery and transplantation: pathophysiology. HPB Surg Article ID176723
Ikeda T, Yanaga K, Kishikawa K, Kakizoe S, Shimada M, Sugimachi K (1992) Ischemic injury in liver transplantation: difference in injury sites between warm and cold ischemia in rats. Hepatology 16:454–461
Gao W, Bentley RC, Madden JF, Clavien PA (1998) Apoptosis of sinusoidal endothelial cells is a critical mechanism of preservation injury in rat liver transplantation. Hepatology 27:1652–1660
Rudiger HA, Graf R, Clavien PA (2003) Liver ischemia: apoptosis as a central mechanism of injury. J Invest Surg 16:149–159
Festi D, Montagnani M, Azzaroli F, Lodato F, Mazzella G, Roda A, Di Biase AR, Roda E, Simoni P, Colecchia A (2007) Clinical efficacy and effectiveness of ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver diseases. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2:155–177
Jonker JW, Stedman CA, Liddle C, Downes M (2009) Hepatobiliary abc transporters: physiology, regulation and implications for disease. Front Biosci 14:4904–4920
Copaci I, Micu L, Iliescu L, Voiculescu M (2005) New therapeutical indications of ursodeoxycholic acid. Rom J Gastroenterol 14:259–266
Roma MG, Toledo FD, Boaglio AC, Basiglio CL, Crocenzi FA, Sanchez Pozzi EJ (2011) Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: Linking action mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Clin Sci (Lond) 121:523–544
Amaral JD, Viana RJ, Ramalho RM, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2009) Bile acids: regulation of apoptosis by ursodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res 50:1721–1734
Perez MJ, Briz O (2009) Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol 15:1677–1689
Roma MG, Crocenzi FA, Sanchez Pozzi EA (2008) Hepatocellular transport in acquired cholestasis: new insights into functional, regulatory and therapeutic aspects. Clin Sci (Lond) 114:567–588
Paumgartner G (2010) Pharmacotherapy of cholestatic liver diseases. J Dig Dis 11:119–125
Qiao L, Yacoub A, Studer E, Gupta S, Pei XY, Grant S, Hylemon PB, Dent P (2002) Inhibition of the mapk and PI3K pathways enhances udca-induced apoptosis in primary rodent hepatocytes. Hepatology 35:779–789
Schoemaker MH, Conde de la Rosa L, Buist-Homan M, Vrenken TE, Havinga R, Poelstra K, Haisma HJ, Jansen PL, Moshage H (2004) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid protects rat hepatocytes from bile acid-induced apoptosis via activation of survival pathways. Hepatology 39:1563–1573
Rodrigues CM, Ma X, Linehan-Stieers C, Fan G, Kren BT, Steer CJ (1999) Ursodeoxycholic acid prevents cytochrome c release in apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial membrane depolarization and channel formation. Cell Death Differ 6:842–854
Zhang Y, Hong JY, Rockwell CE, Copple BL, Jaeschke H, Klaassen CD (2011) Effect of bile duct ligation on bile acid composition in mouse serum and liver. Liver Int 32:58–69
Fickert P, Wagner M, Marschall HU, Fuchsbichler A, Zollner G, Tsybrovskyy O, Zatloukal K, Liu J, Waalkes MP, Cover C, Denk H, Hofmann AF, Jaeschke H, Trauner M (2006) 24-Norursodeoxycholic acid is superior to ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of sclerosing cholangitis in mdr2 (abcb4) knockout mice. Gastroenterology 130:465–481
Ikeda T, Sato C, Noguchi O, Kobayashi F, Tozuka S, Sakamoto S, Marumo F (1996) Improvement of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in primary biliary cirrhosis after ursodeoxycholic acid therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:366–372
Issa R, Williams E, Trim N, Kendall T, Arthur MJ, Reichen J, Benyon RC, Iredale JP (2001) Apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells: involvement in resolution of biliary fibrosis and regulation by soluble growth factors. Gut 48:548–557
Koniaris LG, McKillop IH, Schwartz SI, Zimmers TA (2003) Liver regeneration. J Am Coll Surg 197:634–659
Gertsch P, Stipa F, Ho J, Yuen ST, Luk I, Lauder IJ (1997) Changes in hepatic portal resistance and in liver morphology during regeneration: in vitro study in rats. Eur J Surg 163:297–304
Panis Y, McMullan DM, Emond JC (1997) Progressive necrosis after hepatectomy and the pathophysiology of liver failure after massive resection. Surgery 121:142–149
Abshagen K, Eipel C, Menger MD, Vollmar B (2006) Comprehensive analysis of the regenerating mouse liver: an in vivo fluorescence microscopic and immunohistological study. J Surg Res 134:354–362
Sakamoto T, Liu Z, Murase N, Ezure T, Yokomuro S, Poli V, Demetris AJ (1999) Mitosis and apoptosis in the liver of interleukin-6-deficient mice after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology 29:403–411
Taira K, Hiroyasu S, Shiraishi M, Muto Y, Koji T (2001) Role of the Fas system in liver regeneration after a partial hepatectomy in rats. Eur Surg Res 33:334–341
Gupta S (2000) Hepatic polyploidy and liver growth control. Semin Cancer Biol 10:161–171
Zimmermann A (2004) Regulation of liver regeneration. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19(Suppl 4):iv6–iv10
Fujiyoshi M, Ozaki M (2011) Molecular mechanisms of liver regeneration and protection for treatment of liver dysfunction and diseases. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 18:13–22
Leist M, Gantner F, Bohlinger I, Tiegs G, Germann PG, Wendel A (1995) Tumor necrosis factor-induced hepatocyte apoptosis precedes liver failure in experimental murine shock models. Am J Pathol 146:1220–1234
Tapalaga D, Tiegs G, Angermuller S (2002) Nfkappab and caspase-3 activity in apoptotic hepatocytes of galactosamine-sensitized mice treated with tnfalpha. J Histochem Cytochem 50:1599–1609
Neuman MG (2001) Apoptosis in diseases of the liver. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 38:109–166
Bohlinger I, Leist M, Gantner F, Angermuller S, Tiegs G, Wendel A (1996) DNA fragmentation in mouse organs during endotoxic shock. Am J Pathol 149:1381–1393
Morikawa A, Sugiyama T, Kato Y, Koide N, Jiang GZ, Takahashi K, Tamada Y, Yokochi T (1996) Apoptotic cell death in the response of d-galactosamine-sensitized mice to lipopolysaccharide as an experimental endotoxic shock model. Infect Immun 64:734–738
Baskin-Bey ES, Washburn K, Feng S, Oltersdorf T, Shapiro D, Huyghe M, Burgart L, Garrity-Park M, van Vilsteren FG, Oliver LK, Rosen CB, Gores GJ (2007) Clinical trial of the pan-caspase inhibitor, idn-6556, in human liver preservation injury. Am J Transplant 7:218–225
Eipel C, Hildebrandt A, Scholz B, Schyschka L, Minor T, Kreikemeyer B, Ibrahim SM, Vollmar B (2011) Mutation of mitochondrial atp8 gene improves hepatic energy status in a murine model of acute endotoxemic liver failure. Life Sci 88:343–349
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bonn-Bad Godesberg, Germany (Ei 768/1-2; AB 453/1-1). The authors kindly thank Berit Blendow, Dorothea Frenz, Eva Lorbeer-Rehfeldt and Maren Nerowski (Institute for Experimental Surgery, University of Rostock) for excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bannert, K., Kuhla, A., Abshagen, K. et al. Anti-apoptotic therapeutic approaches in liver diseases: do they really make sense?. Apoptosis 19, 1243–1253 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1004-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1004-1