Abstract
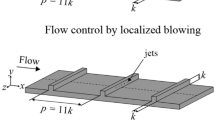
Direct numerical simulation (DNS) is used to investigate the turbulent flat-plate boundary layer with localized micro-blowing. The 32 × 32 array of micro-holes is arranged in a staggered pattern on the solid wall, located in the developed turbulent region. The porosity of the porous wall is 23%, and the blowing fraction is 0.0015. The Reynolds number based on the inflow velocity is set to be 50,000. The structures of the turbulent boundary layer are carefully analyzed to understand the effects of micro-blowing and its drag reduction mechanism. The DNS results show that the drag reduction is efficient, and the local maximum rate of drag reduction achieves 40%. A low-speed “turbulent spot” near the micro-blowing region thickens the boundary layer. Some turbulent properties, such as the mean velocity profile, stream-wise vorticity and stream-wise velocity fluctuation are lifted up. Particularly, the tilting term of vorticity transport is significantly increased. Meanwhile, the visualization of 3-dimensional vortex displays several concave marks on the surface of the near-wall vortices, which is caused by the micro-jets, leading to more broken vortices and isotropic small scales. This impact travels downstream with a small distance due to the accumulation of the micro-jets, while the uplift effect will gradually disappear. In addition, FIK identity reveals that the spatial development term and mean wall-normal convection term play opposite roles in the contribution to the skin friction drag.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderrahaman-Elena, N., García-Mayoral, R.: Analysis of anisotropically permeable surfaces for turbulent drag reduction. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2(11), 114609 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.2.114609
Agostini, L., Leschziner, M.A.: On the influence of outer large-scale structures on near-wall turbulence in channel flow. Phys. Fluids 26(7), 075107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890745
Araya, G., Leonardi, S., Castillo, L.: Steady and time-periodic blowing/suction perturbations in a turbulent channel flow. Physica D 240(1), 59–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2010.08.006
Brooke, J.W., Hanratty, T.J.: Origin of turbulence-producing eddies in a channel flow. Phys. Fluids A 5, 1011–1022 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.858666
Choi, H., Moin, P., Kim, J.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent flow over riblets. J. Fluid Mech. 255, 503–539 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112093002575
Chung, Y.M., Sung, H.J.: Initial relaxation of spatially evolving turbulent channel flow with blowing and suction. AIAA J. 39(11), 2091–2099 (2001). https://doi.org/10.2514/2.1232
Chung, Y.M., Sung, H.J., Krogstad, A.P.: Modulation of near-wall turbulence structure with wall blowing and suction. AIAA J. 40(8), 1529–1535 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2514/2.1849
Du, Y., Karniadakis, G.E.: Suppressing wall turbulence by means of a transverse traveling wave. Science 288(5469), 1230–1234 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.288.5469.1230
Fu, D., Ma, Y., Li, X., et al.: Direct Numerical Simulation of Compressible Turbulence. Science Press, Beijing (2010)
Fukagata, K., Iwamoto, K., Kasagi, N.: Contribution of Reynolds stress distribution to the skin friction in wall-bounded flows. Phys. Fluids 14(11), L73–L76 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1516779
Haddad, M., Labraga, L., Keirsbulck, L.: Effects of blowing through a porous strip in a turbulent channel flow. Exp. Therm. Fluid 31(8), 1021–1032 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2006.10.007
Hwang, D.: Review of research into the concept of the microblowing technique for turbulent skin friction reduction. Prog. Aerosp. 40(8), 559–575 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2005.01.002
Hwang, D.: A proof of concept experiment for reducing skin friction by using a micro-blowing technique. In: 35th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, p. 546 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1997-546
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K.: Direct numerical simulation of spatially developing turbulent boundary layers with uniform blowing or suction. J. Fluid Mech. 681, 154–172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2011.219
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K., Orlu, R., Schlatter, P.: Drag reduction in spatially developing turbulent boundary layers by spatially intermittent blowing at constant mass-flux. J. Turbul. 17, 913 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/14685248.2016.1192285
Kametani, Y., Fukagata, K., Örlü, R., Schlatter, P.: Effect of uniform blowing/suction in a turbulent boundary layer at moderate Reynolds number. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 55, 132–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2015.05.019
Karlsson, R.I., Johansson, T.G.: LDV measurements of higher order moments of velocity fluctuations in a turbulent boundary layer. In: 3rd International Symposium on Applications of Laser Anemometry to Fluid Mechanics (1986)
Keirsbulck, L., Labraga, L., Haddad, M.: Influence of blowing on the anisotropy of the Reynolds stress tensor in a turbulent channel flow. Exp. Fluid 40(4), 654 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-005-0105-6
Kim, K., Sung, H.J.: Effects of unsteady blowing through a spanwise slot on a turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mec. 557, 423–450 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112006009906
Komminaho, J., Skote, M.: Reynolds stress budgets in Couette and boundary layer flows. Flow Turbul. Combust. 68, 167–192 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020404706293
Kornilov, V.I.: Current state and prospects of researches on the control of turbulent boundary layer by air blowing. Prog. Aerosp. 76, 1–23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2015.05.001
Kornilov, V.I., Boiko, A.V.: Efficiency of air microblowing through microperforated wall for flat plate drag reduction. AIAA J. 50(3), 724–732 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J051426
Kornilov, V.I., Boiko, A.V.: Flat-plate drag reduction with streamwise noncontinuous microblowing. AIAA J. 52(1), 93–103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J052477
Krogstad, P.Å., Kourakine, A.: Some effects of localized injection on the turbulence structure in a boundary layer. Phys. Fluids 12(11), 2990–2999 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1314338
Lardeau, S., Leschziner, M.A.: The streamwise drag-reduction response of a boundary layer subjected to a sudden imposition of transverse oscillatory wall motion. Phys. Fluids 25(7), 075109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4816290
Liu, C., Araya, G., Leonardi, S.: The role of vorticity in the turbulent/thermal transport of a channel flow with local blowing. Comput. Fluids 158, 133–149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2016.12.020
Park, J., Choi, H.: Effects of uniform blowing or suction from a spanwise slot on a turbulent boundary layer flow. Phys. Fluids 11(10), 3095–3105 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.870167
Pirozzoli, S., Grasso, F., Gatski, T.B.: Direct numerical simulation and analysis of a spatially evolving supersonic turbulent boundary layer at M= 2.25. Phys. Fluids 16(3), 530–545 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1637604
Poinsot, T.J.A., Lelef, S.K.: Boundary conditions for direct simulations of compressible viscous flows. J. Comput. Phys. 101(1), 104–129 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(92)90046-2
Reichardt, H.: Complete representation of the turbulent velocity distribution in smooth pipe. Z. Angew Math. 31, 208–219 (1951)
Schlatter, P., Orlu, R., Li, Q., Brethouwer, G., Fransson, J.H., Johansson, A.V., Alfredsson, P.H., Henningson, D.S.: Turbulent boundary layers up to Reθ=2500 studied through simulation and experiment. Phys. Fluids 21, 051702 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3139294
Schlatter, P., Örlü, R.: Assessment of direct numerical simulation data of turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 659, 116–126 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112010003113
Schlatter, P., Örlü, R.: Turbulent boundary layers at moderate Reynolds numbers: inflow length and tripping effects. J. Fluid Mech. 710, 5–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2012.324
Smits, A.J., Matheson, N., Joubert, P.N.: Low-Reynolds-number turbulent boundary layers in zero and favourable pressure gradients. J. Ship Res. 27, 147–157 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(83)90034-3
Stroh, A., Frohnapfel, B., Schlatter, P., Hasegawa, Y.: A comparison of opposition control in turbulent boundary layer and turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 27(7), 075101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4923234
Sumitani, Y., Kasagi, N.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent transport with uniform wall injection and suction. AIAA J. 33(7), 1220–1228 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.12363
Tillman, T.G., Hwang, D.P.: Drag reduction on a large-scale nacelle using a microblowing technique. In: 37th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, AIAA Paper 1999–0130. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1999-130 (1999)
Wu, X., Moin, P.: Transitional and turbulent boundary layer with heat transfer. Phys. Fluids. 22, 085105 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3475816
Ying, Z., Xin-Liang, L., De-Xun, F., Yan-Wen, M.: Coherent structures in transition of a flat-plate boundary layer at Ma= 0.7. Chin. Phys. Lett. 24(1), 147 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/24/1/040
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European-China Joint Projects ‘Drag Reduction via Turbulent Boundary Layer Flow Control (DRAGY)’ (No. 690623). The National Supercomputing Center in Guangzhou provides the computing resources for the simulations in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, L., Zheng, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of Localized Micro-blowing on a Spatially Developing Flat Turbulent Boundary Layer. Flow Turbulence Combust 107, 51–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-020-00221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-020-00221-2