Abstract
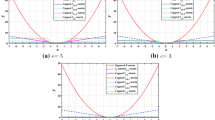
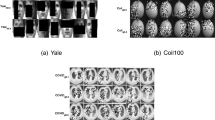
Classical linear discriminant analysis (LDA) is based on squared Frobenious norm and hence is sensitive to outliers and noise. To improve the robustness of LDA, this paper introduces a capped l2,1-norm of a matrix, which employs non-squared l2-norm and “capped” operation, and further proposes a novel capped l2,1-norm linear discriminant analysis, called CLDA. Due to the use of capped l2,1-norm, CLDA can effectively remove extreme outliers and suppress the effect of noise data. In fact, CLDA can also be viewed as a weighted LDA and is solved through a series of generalized eigenvalue problems. The experimental results on an artificial data set, some UCI data sets and two image data sets demonstrate the effectiveness of CLDA.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.php and Coil100 and USPS data sets are available on request from the authors.
References
Fisher RA (1936) The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann Eugen 7 (2):179–188
Fukunaga K (1991) Introduction To Statistical Pattern Recognition, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Ibrahim W, Abadeh MS (2019) Protein fold recognition using deep kernelized extreme learning machine and linear discriminant analysis. Neural Comput Appl 31(8):4201–4214
Gutiérrez-Reguera F, Jurado JM, Montoya-Mayor R et al (2018) Geographical classification of Spanish bottled mineral waters by means of iterative models based on linear discriminant analysis and artificial neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 29(2):459–468
Tao D, Li X, Wu X et al (2007) General tensor discriminant analysis and gabor features for gait recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(10):1700–1715
Wan H, Wang H, Guo G et al (2017) Separability-oriented subclass discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(2):409–422
Khanbebin SN, Mehrdad V (2020) Local improvement approach and linear discriminant analysis-based local binary pattern for face recognition. Neural Comput Appl:1–17
Chen LF, Liao HYM, Ko MT et al (2000) A new LDA-based face recognition system which can solve the small sample size problem. Pattern Recogn 33(10):1713–1726
Yu H, Yang J (2001) A direct LDA algorithm for high-dimensional data<a̱with application to face recognition. Pattern Recogn 34(10):2067–2070
Swets DL, Weng JJ (1996) Using discriminant eigenfeatures for image retrieval. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 18(8):831–836
Lai Z, Mo D, Wong WK et al (2018) Robust discriminant regression for feature extraction. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(8):2472–2484
Randles RH, Broffitt JD, Ramberg JS et al (1978) Generalized linear and quadratic discriminant functions using robust estimates. Publ Am Stat Assoc 73(363):564–568
Friedman JH (1989) Regularized discriminant analysis. J Amer Stat Assoc 84(405):165–175
Hubert M, Van Driessen K (2004) Fast and robust discriminant analysis. Computat Stat Data Anal 45(2):301–320
Yu S, Cao Z, Jiang X (2017) Robust linear discriminant analysis with a Laplacian assumption on projection distribution. IEEE Int Conf Acoustics Speech Signal Process (ICASSP):2567–2571
Kim SJ, Magnani A, Boyd S (2005) Robust fisher discriminant analysis. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst:659–666
Sugiyama M (2007) Dimensionality reduction of multimodal labeled data by local fisher discriminant analysis. J Mach Learn Res 8(1):1027–1061
Wang Z, Ruan Q, An G (2015) Projection-optimal local fisher discriminant analysis for feature extraction. Neural Comput Appl 26(3):589–601
Zhang Z, Chow TWS (2012) Robust linearly optimized discriminant analysis. Neurocomputing 79(3):140–157
Okwonu FZ, Othman AR (2013) Comparative performance of classical fisher linear discriminant analysis and robust fisher linear discriminant analysis. Matematika 29:213–220
Zhong F, Zhang J (2013) Linear discriminant analysis based on L1-norm maximization. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(8):3018–3027
Wang H, Lu X, Hu Z et al (2014) Fisher discriminant analysis with L1-norm. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(6):828–842
Liu Y, Gao Q, Miao S et al (2017) A non-greedy algorithm for L1-norm LDA. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(2):684–695
Ye Q, Yang J, Liu F et al (2018) L1-norm distance linear discriminant analysis based on an effective iterative algorithm. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Vid Technol 28(1):114–129
Chen X, Yang J, Jin Z (2014) An improved linear discriminant analysis with L1-norm for robust feature extraction. 22nd IEEE Int Conf Pattern Recognit:1585–1590
Li CN, Zheng ZR, Liu MZ et al (2017) Robust recursive absolute value inequalities discriminant analysis with sparseness. Neural Netw 93:205–218
Li CN, Shao YH, Yin W (2020) Etc. Robust and sparse linear discriminant analysis via an alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(3):915–926
Zhang D, Sun Y, Ye Q et al (2020) Recursive discriminative subspace learning with L1-norm distance constraint. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(5):2138–2151
Zheng W, Lin Z, Wang H (2014) L1-norm kernel discriminant analysis via Bayes error bound optimization for robust feature extraction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(4):793–805
Li CN, Shao YH, Wang Z et al (2019) Robust Bhattacharyya bound linear discriminant analysis through an adaptive algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 183:104858
Oh JH, Kwak N (2013) Generalization of linear discriminant analysis using Lp-norm. Pattern Recogn Lett 34(6):679–685
Ye Q, Fu L, Zhang Z et al (2018) Lp-and Ls-norm distance based robust linear discriminant analysis. Neural Netw 105:393–404
Li CN, Shao YH, Wang Z et al (2019) Robust bilateral Lp-norm two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis. Inf Sci 500:274–297
Li CN, Shao YH, Deng NY (2015) Robust L1-norm two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis. Neural Netw 65:92–104
Chen SB, Chen DR, Luo B (2015) L1-norm based two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis (In Chinese). J Electron Inf Technol 37(6):1372–1377
Li M, Wang J, Wang Q et al (2017) Trace ratio 2DLDA with L1-norm optimization. Neurocomputing 266(29):216–225
Li CN, Shang MQ, Shao YH et al (2019) Sparse L1-norm two dimensional linear discriminant analysis via the generalized elastic net regularization[J]. Neurocomputing 337:80–96
Ding C, Zhou D, He X et al (2006) R1-PCA: rotational invariant L1-norm principal component analysis for robust subspace factorization. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on machine learning (ICML)
Li X, Hu W, Wang H et al (2010) Linear discriminant analysis using rotational invariant l1 norm. Neurocomputing 73(13-15):2571–2579
Nie F, Huang H, Cai X et al (2010) Efficient and robust feature selection via joint ℓ2,1-norms minimization. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst:1813–1821
Yang Z, Ye Q, Chen Q et al (2020) Robust discriminant feature selection via joint \({\mathscr{L}}_{2,1}\)-norm distance minimization and maximization. Knowl-Based Syst:106090
Lan G, Hou C, Nie F et al (2018) Robust feature selection via simultaneous sapped norm and sparse regularizer minimization. Neurocomputing 283:228–240
Ma X, Zhao M, Zhang Z et al (2018) Anchored projection based capped l2,1-norm regression for super-resolution. In: Pacific rim international conference on artificial intelligence. Springer, Cham, pp 10–18
Zhao M, Zhang Z, Zhan C, et al. (2017) Graph based semi-supervised classification via capped l2,1-norm regularized dictionary learning. In: 2017 IEEE 15th international conference on industrial informatics (INDIN). IEEE, pp 1019–1024
Nie F, Wang X, Huang H (2017) Multiclass capped lp-norm SVM for robust classifications. Thirty-first AAAI Conf Artif Intell:2415–2421
Lai Z, Liu N, Shen L et al (2018) Robust locally discriminant analysis via capped norm. IEEE Access 7:4641–4652
Wang Z, Nie F, Zhang C et al (2020) Capped ℓp-norm LDA for outliers robust dimension reduction. IEEE Signal Process Lett 27:1315–1319
Gao H, Nie F, Cai W, et al. (2015) Robust capped norm nonnegative matrix factorization: capped norm NMF. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM international on conference on information and knowledge management, pp 871–880
Zhang F, Yang Z, Chen Y et al (2018) Matrix completion via capped nuclear norm. IET Image Process 12(6):959– 966
Sun Q, Xiang S, Ye J (2013) Robust principal component analysis via capped norms. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 311–319
Sun W, Huang Y, Huang L et al (2761) l2,p-Correlation and robust matching pursuit for sparse approximation. Digital Signal Process 104(10):2020
Li T, Li M, Gao Q et al (2017) F-norm distance metric based robust 2DPCA and face recognition. Neural Netw 94:204– 211
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No.620QN234 and No.120RC449), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.62066012, No.12271131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is not any conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Xiong, X., Ren, P. et al. Capped norm linear discriminant analysis and its applications. Appl Intell 53, 18488–18507 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04395-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04395-2