Abstract
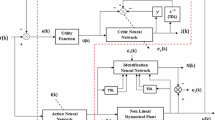
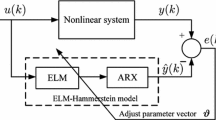
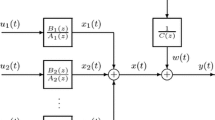
In this paper, we propose a method to increase the model accuracy with linear and nonlinear sub-models. The linear sub-model applies the least square error (LSE) algorithm and the nonlinear sub-model uses neural networks (NN). The two sub-models are updated hierarchically using the Lyapunov function. The proposed method has two advantages: 1) The neural networks is a multi-parametric model. Using the proposed model, the weights of NN model can be summarized into the coefficients or parameters of auto-regressive eXogenous/auto-regressive moving average (ARX/ARMA) model structure, making it easier to establish control laws, 2) learning rate is updated to ensure the convergence of errors at each training epoch. One can improve the accuracy of model and the whole control system. We have demonstrated by the experimental studies that the proposed technique gives better results when compared to the existing studies.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algreer M, Armstrong M, Giaouris D (2012) Active online system identification of switch mode DC DC power converter based on efficient recursive DCD-IIR adaptive filter. IEEE Trans Power Elect 27(11):4425–4435
Barreto G A, Souza L G M (2016) Novel approaches for parameter estimation of local linear models for dynamical system identification. Appl Intell 44(1):149–165
Benaouda D, Murtagh F, Starckc J L, Renaudd O (2006) Wavelet-based nonlinear multiscale decomposition model for electricity load forecasting. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 70:139– 154
Cardona D A B, Nedjah N, Mourellea L M (2017) Online phoneme recognition using multi-layer perceptron networks combined with recurrent non-linear autoregressive neural networks with exogenous inputs. Neurocomputing 265:78–90
Chatterjee S, Nigam S, Singh J B, Upadhyaya L N (2012) Software fault prediction using nonlinear autoregressive with exogenous inputs (narx) network. Appl Intell 37(1):121–129
Chen J, Fang J, Liu W, Tang T, Yang C (2018) clmf: A fine-grained and portable alternating least squares algorithm for parallel matrix factorization. Future Generation Computer Systems
Cheng Y, Wang L, Hu J (2012) Identification of Quasi-ARX neurofuzzy model with an SVR and GA approach. IEICE Trans Fundamentals E.95-A(5):876–883
Feng C B, Zheng W X (1991) Robust identification of stochastic linear systems with correlated noise. IEE Procedings-D 138(5):484–492
Fogel E (1981) A fundamental approach to the convergence analysis of least squares algorithms. IEEE Trans Auto Control AC-26(3):646–655
Hu J, Kumamaru K, Hirasawa K (2001) A Quasi-ARMAX approach to modelling of non-linear systems. Int J Control 74(18):1754–1766
Jami’in M, Sutrisno I, Hu J (2015) Maximum power tracking control for a wind energy conversion system based on a Quasi-ARX neural network model. IEEJ Trans Elect Electron Eng 10(4):368–375
Jami’in MA, Sutrisno I, Hu J (2012) Lyapunov learning algorithm for quasi-ARX neural network to identification of nonlinear dynamical system. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (Seoul), pp 3141–3146
Jami’in MA, Sutrisno I, Hu J, Mariun NB, Marhaban MH (2016) Quasi-arx neural network based adaptive predictive control for nonlinear systems. IEEJ Trans Elect Electron Eng 11(1):83–90
Jami’in MA, Yuyun JE (2017) Hierarchical algorithms of quasi-linear arx neural networks for identification of nonlinear systems. Eng Lett 25(3):321–328
Jiang J, Doraiswami R (1987) Convergence analysis of least-squares identification algorithm for unstable systems. IEE Proceedings 134(5):301–308
Jonas S, Zhang Q, Ljung L, Benveniste A, Delyon B, Glorennec P Y, Hjalmarsson H, Juditsky A (1995) Nonlinear black-box modeling in system identification: a unified overview. Automatica 31(12):1691–1724
Kamal E, Aitouche A, Ghorbani R, Bayart M (2012) Robust fuzzy fault-tolerant control of wind energy conversion systems subject to sensor faults. IEEE Trans Sust Energy 3(2):231–241
Liu X, Wang J, Zheng W (2011) Convergence analysis of refined instrumental variable method for continuous-time system identification. IET Control Theory Appl 5(7):868–877
Ljung L (1977) On positive real transfer functions and the convergence of some recursive schemes. IEEE Trans Automatic Control AC-22(4):539–551
McElveen J K, Lee K R, Bennett J E (1992) Identification of multivariable linear systems from input/output measurements. IEEE Trans Ind Electr 39(3):189–193
Muhando E, Senjyu T, Yona A, Kinjo H, Funabashi T (2007) Disturbance rejection by dual pitch control and self-tuning regulator for wind turbine generator parametric uncertainty compensation. IET Control Theory Appl 1:1431–1440
Nassiri-Toussi K, Ren W (1994) On the convergence of least squares estimates in white noise. IEEE Trans Automatic Control 39(2):364–368
Peng H, Wu J, Inoussa G, Deng Q, Nakano K (2009) Nonlinear system modeling and predictive control using the rbf nets-based quasi-linear arx model. Control Eng Pract 17:59– 66
Purwanto EC, Logeswaran R (2012) An enhanced hybrid method for time series prediction using linear and neural network models. Appl Intell 37(4):511–519
Rao A K, fang Huang Y, Dasgupta S (1990) ARMA parameter estimation using a novel recursive estimation algorithm with selective updating. IEEE Trans Acoustic Speech, Signal Process 38(3):447–457
Soliman M, Malik O, Westwick D (2011) Multiple model multiple-input multiple-output predictive control for variable speed variable pitch wind energy conversion systems. IET Renew Power Gener 5(2):124–136
Toivonen H T, Tötterman S, Åkesson B (2007) Identification of state-dependent parameter models with support vector regression. Int J Control 80(9):1454–1470
Wang H, Song G (2014) Innovative narx recurrent neural network model for ultra-thin shape memory alloy wire. Neurocomputing 134:289–295
Wang L, Cheng Y, Hu J (2010) A quasi-ARX neural network with switching mechanism to adaptive control of nonlinear systems. SICE Journal of Control Measurement, and System Integration 3(4):246–252
Yang Y, Wu Q J (2016) Multilayer extreme learning machine with subnetwork nodes for representation learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(11):2570–2583
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jami’in, M.A., Anam, K., Rulaningtyas, R. et al. Hierarchical linear and nonlinear adaptive learning model for system identification and prediction. Appl Intell 50, 1699–1710 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01615-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01615-0