Abstract
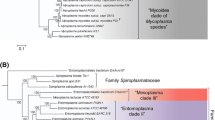
The genus Mycoplasma, including species earlier classified in the genera Eperythrozoon and Haemobartonella, contains ~ 120 species and constitutes an extensively polyphyletic assemblage of bacteria within the phylum Tenericutes. Due to their small genome sizes and lack of unique characteristics, the relationships among the mycoplasmas/Tenericutes are not reliably discerned. Using genome sequences for 140 Tenericutes, their evolutionary relationships were examined using multiple independent approaches. Phylogenomic trees were constructed for 63 conserved proteins, 45 ribosomal proteins, three main subunits of RNA polymerase and 16S rRNA gene sequences. In all of these trees, Tenericutes species reliably grouped into four main clades designated as the “Acholeplasma”, “Spiroplasma”, “Pneumoniae” and “Hominis” clusters. These clades are also distinguished based on a similarity matrix constructed based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Mycoplasma species were dispersed across 3 of these 4 clades highlighting their extensive polyphyly. In parallel, our comparative genomic analyses have identified > 100 conserved signature indels (CSIs) and 14 conserved signature proteins (CSPs), which are uniquely shared by the members of four identified clades, strongly supporting their monophyly and identifying them in molecular terms. Mycoplasma mycoides, the type species of the genus Mycoplasma, and a small number of other Mycoplasma species, formed a strongly supported clade within the “Spiroplasma” cluster. Nine CSIs and 14 CSPs reliably distinguish this clade from all other Mycoplasmatales species. The remainder of the Mycoplasmatales species are part of the “Pneumoniae” and “Hominis” clusters, which group together in phylogenetic trees. Here we are proposing that the order Mycoplasmatales should be emended to encompass only the Mycoplasma species within the “Spiroplasma” cluster and that a new order, Mycoplasmoidales ord. nov., should be created to encompass the other Mycoplasma species. The “Pneumoniae” and the “Hominis” clusters are proposed as two new families, Mycoplasmoidaceae fam. nov., which includes the genera Eperythrozoon, Ureaplasma, and the newly proposed genera Malacoplasma and Mycoplasmoides, and Metamycoplasmataceae fam. nov. to contain the newly proposed genera Metamycoplasma, Mycoplasmopsis, and Mesomycoplasma. The results presented here allow reliable discernment, both in phylogenetic and molecular terms, of the members of the two proposed families as well as different described genera within these families including members of the genus Eperythrozoon, which is comprised of uncultivable organisms. The taxonomic reclassifications proposed here, which more accurately portray the genetic diversity among the Tenericutes/Mycoplasma species, provide a new framework for understanding the biological and clinical aspects of these important microbes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 October 2018
In Tables 9, 10 and 11 of this paper, a few minor errors were noticed in the information for the type strains of the following new name combinations proposed in our paper.
References
Adeolu M, Alnajar S, Naushad S, Gupta RS (2016) Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5575–5599
Adler S, Ellenbogen V (1934) A note on two blood parasites of cattle, Eperythrozoon and Bartonella. J Comp Path 47:219–221
Ahmod NZ, Gupta RS, Shah HN (2011) Identification of a Bacillus anthracis specific indel in the yeaC gene and development of a rapid pyrosequencing assay for distinguishing B. anthracis from the B. cereus group. J Microbiol Meth 87:278–285
Allam NM, Lemcke RM (1975) Mycoplasmas isolated from the respiratory tract of horses. Epidemiol Infect 74:385–408
Alnajar S, Gupta RS (2017) Phylogenomics and comparative genomic studies delineate six main clades within the family Enterobacteriaceae and support the reclassification of several polyphyletic members of the family. Infect Genet Evol 54:108–127
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Antunes A (2014) The family Haloplasmataceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer, Berlin, pp 179–184
Antunes A, Rainey FA, Wanner G, Taborda M, Patzold J, Nobre MF, da Costa MS, Huber R (2008) A new lineage of halophilic, wall-less, contractile bacteria from a brine-filled deep of the Red Sea. J Bacteriol 190:3580–3587
Askaa G, Ernø H (1976) Elevation of Mycoplasma agalactiae subsp. bovis to species rank: Mycoplasma bovis (Hale et al.) comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:323–325
Barbour AG, Adeolu M, Gupta RS (2017) Division of the genus Borrelia into two genera (corresponding to Lyme disease and relapsing fever groups) reflects their genetic and phenotypic distinctiveness and will lead to a better understanding of these two groups of microbes (Margos et al. (2016) There is inadequate evidence to support the division of the genus Borrelia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2058–2067
Barile MF, Del Giudice RA, Carski TR, Gibbs CJ, Morris JA (1968) Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma arginini: spec. nov. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 129:489–494
Barile MF, Del Giudice RA, Tully JG (1972) Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma conjunctivae sp. n. from sheep and goats with keratoconjunctivitis. Infect Immun 5:70–76
Beukes CW, Palmer M, Manyaka P, Chan WY, Avontuur JR, van Zyl E, Huntemann M, Clum A, Pillay M, Palaniappan K, Varghese N, Mikhailova N, Stamatis D, Reddy TBK, Daum C, Shapiro N, Markowitz V, Ivanova N, Kyrpides N, Woyke T, Blom J, Whitman WB, Venter SN, Steenkamp ET (2017) Genome data provides high support for generic boundaries in Burkholderia sensu lato. Front Microbiol 8:1154
Bhandari V, Gupta RS (2014) Molecular signatures for the phylum (class) Thermotogae and a proposal for its division into three orders (Thermotogales, Kosmotogales ord. nov. and Petrotogales ord. nov.) containing four families (Thermotogaceae, Fervidobacteriaceae fam. nov., Kosmotogaceae fam. nov. and Petrotogaceae fam. nov.) and a new genus Pseudothermotoga gen. nov. with five new combinations. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 105:143–168
Blackwood KS, Turenne CY, Harmsen D, Kabani AM (2004) Reassessment of sequence-based targets for identification of Bacillus species. J Clin Microbiol 42:1626–1630
Borrel A, Dujardin-Beaumetz E, Jeantet Jouan C (1910) Le microbe de la péripneumonie. Ann Inst Pasteur 24:168–179
Bradbury JM, Forrest M (1984) Mycoplasma cloacale, a new species isolated from a turkey. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34:389–392
Bradbury JM, Forrest M, Williams A (1983) Mycoplasma lipofaciens, a new species of avian origin. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:329–335
Bradbury JM, Jordan FTW, Shimizu T, Stipkovits L, Varga Z (1988) Mycoplasma anseris sp. nov. found in geese. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:74–76
Bradbury JM, Abdul-Wahab OMS, Yavari CA, Dupiellet JP, Bové JM (1993) Mycoplasma imitans sp. nov. is related to Mycoplasma gallisepticum and found in birds. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:721–728
Brown DR (2010) Phylum XVI. Tenericutes Murray 1984a, 356VP (Effective Publication: Murray 1985b, 33). In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 4. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes. Springer, New York, pp 567–568
Brown DR, Farley JM, Zacher LA, Carlton JM, Clippinger TL, Tully JG, Brown MB (2001a) Mycoplasma alligatoris sp. nov., from American alligators. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:419–424
Brown DR, Talkington DF, Thacker WL, Brown MB, Dillehay DL, Tully JG (2001b) Mycoplasma microti sp. nov., isolated from the respiratory tract of prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:409–412
Brown DR, Klein PA, McLaughlin GS, Schumacher IM, Jacobson ER, Adams HP, Tully JG (2001c) Mycoplasma agassizii sp. nov., isolated from the upper respiratory tract of the desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) and the gopher tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:413–418
Brown DR, Merritt JL, Jacobson ER, Klein PA, Tully JG, Brown MB (2004) Mycoplasma testudineum sp. nov., from a desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) with upper respiratory tract disease. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1527–1529
Brown DR, Demcovitz DL, Plourdé DR, Potter SM, Hunt ME, Jones RD, Rotstein DS (2006) Mycoplasma iguanae sp. nov., from a green iguana (Iguana iguana) with vertebral disease. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:761–764
Brown DR, Bradbury JM, Johansson K-E (2010a) Family I. Acholeplasmataceae Edward and Freundt 1970, 1AL. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology.The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 687–696
Brown DR, Bradbury JM, Whitcomb RF (2010b) Family I. Entoplasmataceae Tully, Bové, Laigart and Whitcomb 1993, 380VP. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 645–653
Brown DR, May M, Bradbury JM, Balish MF, Calcutt MJ, Glass JI, Tasker S, Messick JB, Johansson K-E, Newmark H (2010c) Genus I. Mycoplasma Nowak 1929, 1349 nom. cons. Jud. Comm. Opin. 22, 1958, 166AL. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 575–613
Brown DR, May M, Bradbury JM, Johansson K-E (2010d). Class I. Mollicutes Edward and Freundt 1967, 267AL. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol. 4. Springer, New York, pp 568–573
Brown DR, May M, Bradbury JM, Johansson K-E, Newmark H (2010e). Family I. Mycoplasmataceae Freundt 1955, 71AL emend. Tully, Bové, Laigart and Whitcomb 1993, 382. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 575–639
Campbell C, Adeolu M, Gupta RS (2015) Genome-based taxonomic framework for the class Negativicutes: division of the class Negativicutes into the orders Selenomonadales emend., Acidaminococcales ord. nov. and Veillonellales ord. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3203–3215
Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25:1972–1973
Carmichael LE, St George TD, Sullivan ND, Horsfall N (1972) Isolation, propagation, and characterization studies of an ovine Mycoplasma responsible for proliferative interstitial pneumonia. Cornell Vet 62:654–679
Chandra G, Chater KF (2014) Developmental biology of Streptomyces from the perspective of 100 actinobacterial genome sequences. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:345–379
Clark R (1942) Eperythrozoon felis (sp. nov.) in a cat. J Afr Vet Med Assoc 13:15–16
Cole BC, Golightly L, Ward JR (1967) Characterization of mycoplasma strains from cats. J Bacteriol 94:1451–1458
DaMassa AJ, Tully JG, Rose DL, Pitcher D, Leach RH, Cottew GS (1994) Mycoplasma auris sp. nov., Mycoplasma cottewii sp. nov., and Mycoplasma yeatsii sp. nov., new sterol-requiring mollicutes from the external ear canals of goats. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:479–484
Del Giudice RA, Carski TR, Barile MF, Lemcke RM, Tully JG (1971) Proposal for classifying human strain navel and related simian mycoplasmas as Mycoplasma primatum sp. n. J Bacteriol 108:439–445
Del Giudice RA, Purcell RH, Carski TR, Chanock RM (1974) Mycoplasma lipophilum sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:147–153
Del Giudice RA, Tully JG, Rose DL, Cole RM (1985) Mycoplasma pirum sp. nov., a terminal structured mollicute from cell cultures. Int J Syst Bacteriol 35:285–291
Del Giudice RA, Rose DL, Tully JG (1995) Mycoplasma adleri sp. nov., an isolate from a goat. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:29–31
Dutilh BE, Snel B, Ettema TJ, Huynen MA (2008) Signature genes as a phylogenomic tool. Mol Biol Evol 25:1659–1667
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002195
Edward DF (1955) A suggested classification and nomenclature for organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. Int Bull Bacteriol Nomencl Taxon 5:85–93
Edward DF, Kanarek AD (1960) Organisms of the pleuropneumonia group of avian origin: their classification into species. Ann New York Acad Sci 79:696–702
Edward DG, Freundt EA (1967) Proposal for Mollicutes as name of the class established for the order Mycoplasmatales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 17:267–268
Erickson BZ, Ross RF, Rose DL, Tully JG, Bové JM (1986) Mycoplasma hyopharyngis, a new species from swine. Int J Syst Bacteriol 36:55–59
Fadiel A, Eichenbaum KD, El Semary N, Epperson B (2007) Mycoplasma genomics: tailoring the genome for minimal life requirements through reductive evolution. Front Biosci 12:2020–2028
Fettweis JM, Serrano MG, Huang B, Brooks P, Glascock AL, Sheth NU, Vaginal Microbiome Consortium, Strauss JF III, Jefferson KK, Buck GA (2014) An emerging mycoplasma associated with trichomoniasis, vaginal infection and disease. PLoS ONE 9:e110943
Firraro G, Brown DR (2011) International committee on systematics of prokaryotes. Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Mollicutes. Minutes of the meetings, 11 and 16 July 2010, Chianciano Terme, Italy. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:695–697
Foley JE, Pedersen NC (2001) ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum’, a low-virulence epierythrocytic parasite of cats. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:815–817
Forrest M, Bradbury JM (1984a) Mycoplasma glycophilum, a new species of avian origin. J Gen Microbiol 130:597–603
Forrest M, Bradbury JM (1984b) Validation of the publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSB. List No. 15. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34:355–357
Forsyth MH, Tully JG, Gorton TS, Hinckley L, Frasca S Jr, Van Kruiningen HJ, Geary SJ (1996) Mycoplasma sturni sp. nov., from the conjunctiva of a European starling (Sturnus vulgaris). Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:716–719
Freundt EA (1953) The occurrence of Micromyces (pleuropneumonia-like organisms) in the female genito-urinary tract. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 32:48–480
Freundt EA (1955) The classification of the pleuropneumonia group of organisms (Borrelomycetales). Int Bull Bacteriol Nomencl Taxon 5:67–78
Freundt EA, Taylor-Robinson D, Purcell RH, Chanock RM, Black FT (1974) Proposal of Mycoplasma buccale nom. nov. and Mycoplasma faucium nom. nov. for Mycoplasma orale “types” 2 and 3, respectively. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:252–255
Gao B, Gupta RS (2005) Conserved indels in protein sequences that are characteristic of the phylum Actinobacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2401–2412
Gao B, Gupta RS (2012) Phylogenetic framework and molecular signatures for the main clades of the phylum Actinobacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:66–112
Gasparich GE (2014) The family Entomoplasmataceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer, Berlin, pp 505–514
Giebel J, Meier J, Binder A, Flossdorf J, Poveda JB, Schmidt R, Kirchhoff H (1991) Mycoplasma phocarhinis sp. nov. and Mycoplasma phocacerebrale sp. nov., two new species from harbor seals (Phoca vitulina L.). Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:39–44
Gourlay RN, Leach RH (1970) A new Mycoplasma species isolated from pneumonic lungs of calves (Mycoplasma dispar sp. nov.). J Med Microbiol 3:111–123
Gourlay RN, Leach RH, Howard CJ (1974) Mycoplasma verecundum, a new species isolated from bovine eyes. J Gen Microbiol 81:475–484
Gourlay RN, Wyld SG, Leach RH (1977) Mycoplasma alvi, a new species from bovine intestinal and urogenital tracts. Int J Syst Bacteriol 27:86–96
Gourlay RN, Wyld SG, Leach RH (1978) Mycoplasma sualvi, a new species from the intestinal and urogenital tracts of pigs. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:289–292
Grosjean H, Breton M, Sirand-Pugnet P, Tardy F, Thiaucourt F, Citti C, Barré A, Yoshizawa S, Fourmy D, de Crécy-Lagard V, Blanchard A (2014) Predicting the minimal translation apparatus: lessons from the reductive evolution of mollicutes. PLoS Genet 10:1004363
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Gundersen DE, Lee IM, Rehner SA, Davis RE, Kingsbury DT (1994) Phylogeny of mycoplasmalike organisms (phytoplasmas): a basis for their classification. J Bacteriol 176:5244–5254
Gupta RS (1998) Protein phylogenies and signature sequences: a reappraisal of evolutionary relationships among archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:1435–1491
Gupta RS (2000) The phylogeny of proteobacteria: relationships to other eubacterial phyla and eukaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:367–402
Gupta RS (2014) Identification of conserved indels that are useful for classification and evolutionary studies. In: Goodfellow M, Sutcliffe I, Chun J (eds) Methods in microbiology. New approaches to prokaryotic systematics. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 153–182
Gupta RS (2016) Impact of genomics on the understanding of microbial evolution and classification: the importance of Darwin’s views on classification. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40:520–553
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Baker S (2015) Phylogenomic analyses and molecular signatures for the class Halobacteria and its two major clades: a proposal for division of the class Halobacteria into an emended order Halobacteriales and two new orders, Haloferacales ord. nov. and Natrialbales ord. nov., containing the novel families Haloferacaceae fam. nov. and Natrialbaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1050–1069
Gupta RS, Naushad S, Fabros R, Adeolu M (2016) A phylogenomic reappraisal of family-level divisions within the class Halobacteria: proposal to divide the order Halobacteriales into the families Halobacteriaceae, Haloarculaceae fam. nov., and Halococcaceae fam. nov., and the order Haloferacales into the families, Haloferacaceae and Halorubraceae fam nov. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109:565–587
Gupta RS, Nanda A, Khadka B (2017) Novel molecular, structural and evolutionary characteristics of the phosphoketolases from bifidobacteria and Coriobacteriales. PLoS ONE 12:e0172176
Gupta RS, Lo B, Son J (2018) Phylogenomics and comparative genomic studies robustly support division of the genus Mycobacterium into an emended genus Mycobacterium and four novel genera. Front Microbiol 9, 67
Hale HH, Helmboldt CF, Plastridge WN, Stula EF (1962) Bovine mastitis caused by a Mycoplasma species. Cornell Vet. 52:582–591
Hassan FMN, Gupta RS (2018) Novel sequence features of DNA repair genes/proteins from Deinococcus species implicated in protection from oxidatively generated damage. Genes 9:149
Heltander Königsson M, Pettersson B, Johansson K-E (2001) Phylogeny of the seal mycoplasmas Mycoplasma phocae corrig., Mycoplasma phocicerebrale corrig. and Mycoplasma phocirhinis corrig. based on sequence analysis of 16S rDNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1389–1393
Hill AC (1971) Mycoplasma caviae, a new species. J Gen Microbiol 65:109–113
Hill AC (1983a) Mycoplasma collis, a new species isolated from rats and mice. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:847–851
Hill AC (1983b) Mycoplasma cricetuli, a new species from the conjunctivas of Chinese hamsters. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:113–117
Hill AC (1984) Mycoplasma cavipharyngis, a new species isolated from the nasopharynx of guinea-pigs. J Gen Microbiol 130:3183–3188
Hill AC (1985) Mycoplasma testudinis, a new species isolated from a tortoise. Int J Syst Bacteriol 35:489–492
Hill AC (1986) Mycoplasma felifaucium, a new species isolated from the respiratory tract of pumas. J Gen Microbiol 132:1923–1928
Hill AC (1988) Validation of the publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSB: List No. 27. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:449
Hill AC (1989) Validation of the publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSB (List No. 30). Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:371
Hill AC (1991a) Mycoplasma oxoniensis, a new species isolated from Chinese hamster conjunctivas. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:21–25
Hill AC (1991b) Mycoplasma spermatophilum, a new species isolated from human spermatozoa and cervix. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:229–233
Hill AC (1992) Mycoplasma simbae sp. nov., Mycoplasma leopharyngis sp. nov., and Mycoplasma leocaptivus sp. nov., isolated from lions. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:518–523
Hill AC (1993) Mycoplasma indiense sp. nov., isolated from the throats of nonhuman primates. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:36–40
Hugenholtz P, Skarshewski A, Parks DH (2016) Genome-based microbial taxonomy coming of age. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 8:1–11
Jasper DE, Ernø H, Dellinger JD, Christiansen C (1981) Mycoplasma californicum, a new species from cows. Int J Syst Bacteriol 31:339–345
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23:403–405
Johansson K-E, Pettersson B (2002) Taxonomy of Mollicutes. In: Razin S, Herrmann R (eds) Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Springer, Boston, pp 1–29
Jordan FTW, Ernø H, Cottew GS, Hinz KH, Stipkovits L (1982) Characterization and taxonomic description of five mycoplasma serovars (serotypes) of avian origin and their elevation to species rank and further evaluation of the taxonomic status of Mycoplasma synoviae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:108–115
Jores J, Fischer A, Sirand-Pugnet P, Thomann A, Liebler-Tenorio EM, Schnee C, Santana-Cruz I, Heller M, Frey J (2015) Mycoplasma feriruminatoris sp. nov., a fast-growing Mycoplasma species isolated from wild Caprinae. Syst Appl Microbiol 36:533–538
Khadka B, Gupta RS (2017) Identification of a conserved 8 aa insert in the PIP5 K protein in the Saccharomycetaceae family of fungi and the molecular dynamics simulations and structural analysis to investigate its potential functional role. Proteins 85:1454–1467
Kikuth W (1928) Über einen neuen Anämieerreger; Bartonella canis nov. spec. Klin Wochenschr 7:1729–1730
Kim KS, Ko KS, Chang M-W, Hahn TW, Hong SK, Kook YH (2003) Use of rpoB sequences for phylogenetic study of Mycoplasma species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:299–305
Kirchhoff H (1978) Mycoplasma equigenitalium, a new species from the cervix region of mares. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:496–502
Kirchhoff H, Beyene P, Fischer M, Flossdorf J, Heitmann J, Khattab B, Lopatta D, Rosengarten R, Seidel G, Yousef C (1987) Mycoplasma mobile sp. nov., a new species from fish. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:192–197
Kirchhoff H, Schmidt R, Lehmann H, Clark HW, Hill AC (1996) Mycoplasma elephantis sp. nov., a new species from elephants. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:437–441
Kirchhoff H, Mohan K, Schmidt R, Runge MR, Brown DR, Brown MB, Foggin CM, Muvavarirwa P, Lehmann H, Flossdorf J (1997) Mycoplasma crocodyli sp. nov., a new species from crocodiles. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:742–746
Kobayashi H, Runge M, Schmidt R, Kubo M, Yamamoto K, Kirchhoff H (1997) Mycoplasma lagogenitalium sp. nov., from the preputial smegma of Afghan pikas (Ochotona rufescens rufescens). Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1208–1211
Kong F, Gilbert GL (2004) Postgenomic taxonomy of human ureaplasmas - a case study based on multiple gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1815–1821
Krasteva I, Inglis NF, Sacchini F, Nicholas R, Ayling R, Churchward CP, March J, Lainson A, Mclean K, Hughes V, Imrie L, Manson E, Clark J, Pini A, Smith DGE (2014) Proteomic characterisation of two strains of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides of differing pathogenicity. J Proteomics Bioinform 13:2
Kreier JP, Tistic M (1963) Anaplasmosis. XII. The growth and survival in deer and sheep of the parasites present in the blood of calves infected with the Oregon strain of Anaplasma marginale. Am J Vet Res 24:697–702
Langford EV, Leach RH (1973) Characterization of a mycoplasma isolated from infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis: M. bovoculi sp. nov. Can J Microbiol 19:1435–1444
Langford EV, Ruhnke HL, Onoviran O (1976) Mycoplasma canadense, a new bovine species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 26:212–219
Lawson PA, Citron DM, Tyrrell KL, Finegold SM (2016) Reclassification of Clostridium difficile as Clostridioides difficile (Hall and O’Toole 1935) Prevot 1938. Anaerobe 40:95–99
Le SQ, Gascuel O (2008) An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol Biol Evol 25:1307–1320
Leach RH (1967) Comparative studies of mycoplasma of bovine orign. Ann New York Acad Sci 143:305–316
Leach RH (1973) Further studies on classification of bovine strains of Mycoplasmatales, with proposals for new species, Acholeplasma modicum and Mycoplasma alkalescens. J Gen Microbiol 75:135–153
Leclercq S, Dittmer J, Bouchon D, Cordaux R (2014) Phylogenomics of “Candidatus Hepatoplasma crinochetorum,” a lineage of mollicutes associated with noninsect arthropods. Genome Biol Evol 6:407–415
Lemcke RM, Kirchhoff H (1979) Mycoplasma subdolum, a new species isolated from horses. Int J Syst Bacteriol 29:42–50
Lemcke RM, Poland J (1980) Mycoplasma fastidiosum: a new species from horses. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:151–162
Lo SC, Hayes MM, Tully JG, Wang RY-H, Kotani H, Pierce PF, Rose DL, Shih JW-K (1992) Mycoplasma penetrans sp. nov., from the urogenital tract of patients with AIDS. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:357–364
Madden DL, Moats KE, London WT, Matthew EB, Sever JL (1974) Mycoplasma moatsii, a new species isolated from recently imported Grivit monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops). Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:459–464
Maniloff J (2002) Phylogeny and evolution. In: Razin S, Herrmann R (eds) Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Springer, Boston, pp 31–43
Manso-Silván L, Perrier X, Thiaucourt F (2007) Phylogeny of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster based on analysis of five conserved protein-coding sequences and possible implications for the taxonomy of the group. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2247–2258
Manso-Silván L, Vilei EM, Sachse K, Djordjevic SP, Thiaucourt F, Frey J (2009) Mycoplasma leachii sp. nov. as a new species designation for Mycoplasma sp. bovine group 7 of Leach, and reclassification of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides LC as a serovar of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1353–1358
Maré CJ, Switzer WP (1965) New species: Mycoplasma hypopneumoniae; a causative agent of virus pig pneumonia. Vet Med Small Animal Clin 60:841–846
Martini M, Marcone C, Lee I-M, Firrao G (2014) The family Acholeplasmataceae (including Phytoplasmas). In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer, Berlin, pp 469–504
May M, Brown DR (2014) International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes. Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Mollicutes. Minutes of the meetings (closed and open), 1 and 5 June 2014, Blumenau SC, Brazil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3904–3906
May M, Balish MF, Blanchard A (2014) In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer, Berlin, pp 515–550
Mayer M (1921) Über einige bakterienähnliche Parasiten der Erythrozyten bei Menschen und Tieren. Arch Schiffs Tropenhyg 25:150–152
McGarrity GJ, Rose DL, Kwiatkowski V, Dion AS, Phillips DM, Tully JG (1983) Mycoplasma muris, a new species from laboratory mice. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:350–355
Messick JB, Walker PG, Raphael W, Berent L, Shi X (2002) ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemodidelphidis’ sp. nov., ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemolamae’ sp. nov. and Mycoplasma haemocanis comb. nov., haemotrophic parasites from a naturally infected opossum (Didelphis virginiana), alpaca (Lama pacos) and dog (Canis familiaris): phylogenetic and secondary structural relatedness of their 16S rRNA genes to other mycoplasmas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:693–698
Meyling A, Friis NF (1972) Serological identification of a new porcine mycoplasma species, Mycoplasma flocculare. Acta Vet Scand 13:287–289
Möller Palau-Ribes F, Enderlein D, Hagen N, Herbst W, Hafez HM, Lierz M (2016) Description and prevalence of Mycoplasma ciconiae sp. nov. isolated from white stork nestlings (Ciconia ciconia). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3477–3484
Murray RGE (1984) The higher taxa, or, a place for everything? In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 31–34
Mushegian AR, Koonin EV (1996) A minimal gene set for cellular life derived by comparison of complete bacterial genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10268–10273
Naushad HS, Lee B, Gupta RS (2014) Conserved signature indels and signature proteins as novel tools for understanding microbial phylogeny and systematics: identification of molecular signatures that are specific for the phytopathogenic genera Dickeya, Pectobacterium and Brenneria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:366–383
Neimark H, Johansson K-E, Rikihisa Y, Tully JG (2001) Proposal to transfer some members of the genera Haemobartonella and Eperythrozoon to the genus Mycoplasma with descriptions of ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemofelis’, ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomuris’, ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemosuis’ and ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma wenyonii’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:891–899
Neimark H, Johansson K-E, Rikihisa Y, Tully JG (2002) Revision of haemotrophic Mycoplasma species names. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:683
Neimark H, Hoff B, Ganter M (2004) Mycoplasma ovis comb. nov. (formerly Eperythrozoon ovis), an epierythrocytic agent of haemolytic anaemia in sheep and goats. Int J Syst Evol Micorbiol 54:365–371
Neimark H, Peters W, Robinson BL, Stewart LB (2005) Phylogenetic analysis and description of Eperythrozoon coccoides, proposal to transfer to the genus Mycoplasma as Mycoplasma coccoides comb. nov. and Request for an Opinion. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1385–1391
Neitz WO, Alexander RA, du Toit OJ (1934) Eperythrozoon ovis (sp. nov.) infection in sheep. Onderstepoort J Vet Sci 3:263–274
Nowak J (1929) Morphologie, nature et cycle évolutif du microbe de la péripneumonie des bovidés. Ann Inst Pasteur 43:1330–1352
Olson NO, Kerr KM, Campbell A (1964) Control of infectious synovitis 13. The antigen study of three strains. Avian Dis 8:209–214
Oshima K, Nishida H (2007) Phylogenetic relationships among mycoplasmas based on the whole genomic information. J Mol Evol 65:249–258
Panangala VS, Stringfellow JS, Dybvig K, Woodard A, Sun F, Rose DL, Gresham MM (1993) Mycoplasma corogypsi sp. nov., a new species from the footpad abscess of a black vulture. Coragyps atratus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:585–590
Parker CT, Tindall BJ, Garrity GM (2016) International code of nomenclature of Prokaryotes. Prokaryotic code 2008 revision). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000778
Parte AC (2014) LPSN-list of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. Nucl Acids Res 42:D613–D616
Peters IR, Helps CR, McAuliffe L, Neimark H, Lappin MR, Gruffydd-Jones TJ, Day MJ, Hoelzle LE, Willi B, Meli M, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Tasker S (2008) RNase P RNA gene (rnpB) phylogeny of hemoplasmas and other Mycoplasma species. J Clin Microbiol 46:1873–1877
Pettersson B, Tully JG, Bolske G, Johansson KE et al (2000) EUpdated phylogenetic description of the Mycoplasma hominis cluster (Weisburg et al. 1989) based on 16S rDNA sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:291–301
Pitcher DG, Windsor D, Windsor H, Bradbury JM, Yavari C, Jensen JS, Ling C, Webster D (2005) Mycoplasma amphoriforme sp. nov., isolated from a patient with chronic bronchopneumonia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2589–2594
Pollack JD, Williams MV, Banzon J, Jones MA, Harvey L, Tully JG (1996) Comparative metabolism of Mesoplasma, Entomoplasma, Mycoplasma, and Acholeplasma. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:885–890
Poveda JB, Giebel J, Flossdorf J, Meier J, Kirchhoff H (1994) Mycoplasma buteonis sp. nov., Mycoplasma falconis sp. nov., and Mycoplasma gypis sp. nov., three species from birds of prey. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:94–98
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2-approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 5:e9490
Razin S (1992) Mycoplasma taxonomy and ecology. In: Maniloff J, McElhaney RN, Finch LR, Baseman JB (eds) Mycoplasmas: molecular biology and pathogenesis. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., pp 3–22
Razin S, Herrmann R (2002) Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York
Razin S, Yogev D, Naot Y (1998) Molecular biology and pathogenicity of mycoplasmas. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:1094–1156
Regassa LB (2014) The Family Spiroplasmataceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer, Berlin, pp 551–567
Roberts DH (1964) The isolation of an influenza A virus and a mycoplasma associated with duck sinusitis. Vet Rec 76:470–473
Rokas A, Holland PW (2000) Rare genomic changes as a tool for phylogenetics. Trends Ecol Evol 15:454–459
Rose DL, Tully JG, Langford EV (1978) Mycoplasma citelli, a new species from ground squirrels. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:567–572
Rosendal S (1973) Mycoplasma cynos, a new canine Mycoplasma species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 23:49–54
Rosendal S (1974) Mycoplasma molare, a new canine Mycoplasma species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:125–130
Rosendal S (1975) Canine mycoplasmas: serological studies of type and reference strains, with a proposal for the new species, Mycoplasma opalescens. APMIS 83:463–470
Ross RF, Karmon JA (1970) Heterogeneity among strains of Mycoplasma granularum and identification of Mycoplasma hyosynoviae, sp. n. J Bacteriol 103:707–713
Ruhnke HL, Madoff S (1992) Mycoplasma phocidae sp. nov., isolated from harbor seals (Phoca vitulina L.). Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:211–214
Sabin AB (1941) The filtrable microorganisms of the pleuropneumonia group. Bacteriol Rev 5:331–335
Salih MM, Friis NF, Arseculeratne SN, Freundt EA, Christiansen C (1983) Mycoplasma mustelae, a new species from mink. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:476–479
Schilling V (1928) Eperythrozoon coccoides, eine neue durch Splenektomie aktivierbare Dauerinfektion der weissen Maus. Klin Wschr 7:1853–1855
Schoeffler AJ, May AP, Berger JM (2010) A domain insertion in Escherichia coli GyrB adopts a novel fold that plays a critical role in gyrase function. Nucl Acids Res 38:7830–7844
Sha BE, Zariffard MR, Wang QJ, Chen HY, Bremer J, Cohen MH, Spear GT (2005) Female genital-tract HIV load correlates inversely with Lactobacillus species but positively with bacterial vaginosis and Mycoplasma hominis. J Infect Dis 191:25–32
Shepard MC, Lunceford CD, Ford DK, Purcell RH, Taylor-Robinson D, Razin S, Black FT (1974) Ureaplasma urealyticum gen. nov., sp. nov.: proposed nomenclature for the human T (T-strain) mycoplasmas. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:160–171
Shimizu T, Ernø H, Nagatomo H (1978) Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma columbinum and Mycoplasma columborale, two new species from pigeons. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:538–546
Singh B, Gupta RS (2009) Conserved inserts in the Hsp60 (GroEL) and Hsp70 (DnaK) proteins are essential for cellular growth. Mol Genet Genomics 281:361–373
Sirand-Pugnet P, Citti C, Barré A, Blanchard A (2007) Evolution of mollicutes: down a bumpy road with twists and turns. Res Microbiol 158:754–766
Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA (1980) Approved lists of bacterial names. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:225–420
Somerson NL, Taylor-Robinson D, Chanock RM (1963) Hemolysin production as an aid in the identification and quantitation of Eaton agent (Mycoplasma pneumoniae). Am J Hyg 77:122–128
Spergser J, Langer S, Muck S, Macher K, Szostak M, Rosengarten R, Busse HJ (2011) Mycoplasma mucosicanis sp. nov., isolated from the mucosa of dogs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:716–721
Splitter EJ (1950) Eperythrozoon suis n. sp. and Eperythrozoon parvum n. sp., two new blood parasites of swine. Science 111:513–514
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313
Suárez-Pérez A, Ramírez AS, Rosales RS, Calabuig P, Poveda C, Rosselló-Móra R, Nicholas RA, Poveda JB (2012) Mycoplasma neophronis sp. nov., isolated from the upper respiratory tract of Canarian Egyptian vultures (Neophron percnopterus majorensis). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1321–1325
Switzer WP (1955) Studies on infectious atrophic rhinitis. IV. Characterization of a pleuropneumonia-like organism isolated from the nasal cavities of swine. Am J Vet Res 16:540–544
Tagawa M, Matsumoto K, Inokuma H (2008) Molecular detection of Mycoplasma wenyonii and ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos’ in cattle in Hokkaido, Japan. Vet Microbiol 132:177–180
Taylor-Robinson D, Canchola J, Fox H, Chanock RM (1964) A newly identified oral mycoplasma (M. orale) and its relationship to other human mycoplasmas. Am J Hyg 80:135–148
Thompson CC, Vieira NM, Vicente AC, Thompson FL (2011) Towards a genome based taxonomy of Mycoplasmas. Infect Genet Evol 11:1798–1804
Tindall BJ (1999) Misunderstanding the bacteriological code. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1313–1316
Tindall BJ (2014) The Request for an Opinion that the current use of the genus name Mycoplasma be maintained and Mycoplasma coccoides be considered a legitimate name is denied. Opinion 92. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3586–3587
Toth KF, Harrison N, Sears BB (1994) Phylogenetic relationships among members of the class Mollicutes deduced from rps3 gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:119–124
Trüper HG, de’Clari L (1998) Taxonomic note: erratum and correction of further specific epithets formed as substantives (nouns) ‘in apposition’. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:615
Tully JG, Barile MF, Del Giudice RA, Carski TR, Armstrong D, Razin S (1970) Proposal for classifying strain PG-24 and related canine mycoplasmas as Mycoplasma edwardii sp. n. J Bacteriol 101:346–349
Tully JG, Barile MF, Edward DG, Theodore TS, Ernø H (1974) Characterization of some caprine mycoplasmas, with proposals for new species, Mycoplasma capricolum and Mycoplasma putrefaciens. J Gen Microbiol 85:102–120
Tully JG, Taylor-Robinson DAVI, Rose DL, Cole RM, Bove JM (1983) Mycoplasma genitalium, a new species from the human urogenital tract. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:387–396
Tully JG, Bové JM, Laigret F, Whitcomb RF (1993) Revised taxonomy of the class Mollicutes: proposed elevation of a monophyletic cluster of arthropod-associated mollicutes to ordinal rank (Entomplasmatales ord. nov.), with provision for familiar rank to separate species with nonhelical morphology (Entomoplasmataceae fam. nov.) from helical species (Spiroplasmataceae), and emended descriptions of the order Mycoplasmatales, family Mycoplasmataceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:378–385
Tyzzer EE, Weiman D (1939) Haemobartonella n.g. (Bartonella olim pro parte), H. microti n. sp. of the field vole. Microtus pennsylvanicus. Am J Hyg 40:157–241
Uilenberg G, Thiaucourt F, Jongejan F (2004) On molecular taxonomy: what is in a name? Exp Appl Aracol 32:301–312
Uilenberg G, Thiaucourt F, Jongejan F (2006) Mycoplasma and Eperythrozoon (Mycoplasmataceae). Comments on a recent paper. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:13–14
Volokhov DV, Neverov AA, George J, Kong H, Liu SX, Anderson C, Davidson MK, Chizhikov V (2007) Genetic analysis of housekeeping genes of members of the genus Acholeplasma: phylogeny and complementary molecular markers to the 16S rRNA gene. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:699–710
Volokhov DV, Simonyan V, Davidson MK, Chizhikov VE (2012) RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB) gene and the 16S-23S rRNA intergenic transcribed spacer region (ITS) as complementary molecular markers in addition to the 16S rRNA gene for phylogenetic analysis and identification of the species of the family Mycoplasmataceae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 62:515–528
Waite DW, Vanwonterghem I, Rinke C, Parks DH, Zhang Y, Takai K, Sievert SM, Simon J, Campbell BJ, Hanson TE, WoykeT Klotz MG, Hugenholtz P (2017) Comparative genomic analysis of the class Epsilonproteobacteria and proposed reclassification to Epsilonbacteraeota (phyl. nov.). Front Microbiol 8:682
Waites KB, Talkington DF (2004) Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:697–728
Wang Z, Wu M (2013) A phylum-level bacterial phylogenetic marker database. Mol Biol Evol 30:1258–1262
Weisburg WG, Tully JG, Rose DL, Petzel JP, Oyaizu H, Yang D, Mandelco L, Sechrest J, Lawrence TG, Van Etten J (1989) A phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas: basis for their classification. J Bacteriol 171:6455–6467
Westberg J, Persson A, Holmberg A, Goesmann A, Lundeberg J, Johansson K-E, Pettersson B, Uhlén M (2004) The genome sequence of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides SC type strain PG1T, the causative agent of contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP). Genome Res 14:221–227
Whitcomb RF, Tully JG, Bové JM, Bradbury JM, Christiansen G, Kahane I, Kirkpatrick BC, Laigret F, Leach RH, Neimark HC, Pollack JD, Razin S, Sears BB, Taylor-Robinson D (1995) Revised minimum standards for description of new species of the class Mollicutes (division Tenericutes). Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:605–612
Whitman WB (2015) Genome sequences as the type material for taxonomic descriptions of prokaryotes 1. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:217–222
Williamson DL, Gasparich GE, Regassa LB, Saillard C, Renaudin J, Bové JM, Whitcomb RF (2010) Family II. Spiroplasmataceae Skripal 1983, 408VP. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward NL, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 654–686
Wolf M, Müller T, Dandekar T, Pollack JD (2004) Phylogeny of Firmicutes with special reference to Mycoplasma (Mollicutes) as inferred from phosphoglycerate kinase amino acid sequence data. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:871–875
Wong SY, Paschos A, Gupta RS, Schellhorn HE (2014) Insertion/deletion-based approach for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in freshwater environments. Environ Sci Technol 48:11462–11470
Wroblewski W (1931) Morphologie et cycle évolutif des microbes de la péripneumonie des bovidés et de l’agalaxie contagieuse des chèvres et des moutons. Ann Inst Pasteur 47:94–115
Yamamoto R, Bigland CH, Ortmayer HB (1965) Characteristics of Mycoplasma meleagridis sp. n., isolated from turkeys. J Bacteriol 90:47–49
Yarza P, Richter M, Peplies J, Euzéby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO, Rosselló-Móra R (2008) The All-Species Living Tree project: a 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:241–250
Yarza P, Ludwig W, Euzéby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Glöckner FO, Rosselló-Móra R (2010) Update of the all-species living tree project based on 16S and 23S rRNA sequence analyses. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:291–299
Yilmaz P, Parfrey LW, Yarza P, Gerken J, Pruesse E, Quast C, Schweer T, Peplies J, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO (2014) The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucl Acids Res 42:D643–D648
Acknowledgements
We thank Judy Tran, Talha Tahir, Jeen Son and Joseph Manalo for assistance in the identification and formatting of some of the described CSIs and CSPs. We also thank the editor Dr. Iain Sutcliffe for many helpful suggestions concerning the work presented here. This work was supported by Research Grant No. 249924 from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada awarded to Radhey S. Gupta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R.S., Sawnani, S., Adeolu, M. et al. Phylogenetic framework for the phylum Tenericutes based on genome sequence data: proposal for the creation of a new order Mycoplasmoidales ord. nov., containing two new families Mycoplasmoidaceae fam. nov. and Metamycoplasmataceae fam. nov. harbouring Eperythrozoon, Ureaplasma and five novel genera. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 111, 1583–1630 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1047-3