Abstract
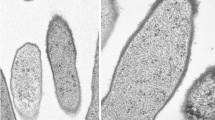
An ovoid to rod-shaped, phototrophic, purple non-sulfur bacterium was isolated from a sediment sample of a hot spring in Tibet, China. Cells of strain YIM 73036T were Gram-stain negative, non-motile and multiplied by binary fission. Strain YIM 73036T grew optimally at pH 7.0–7.5 at 37–45 °C. Growth occurred in 0.5–3.5% (w/v) NaCl. Vitamins were not required for growth. The presence of photosynthesis genes pufL and pufM were shown and photosynthesis pigments were formed. Bacteriochlorophyll α, the bacteriopheophytin and carotenoids were present as photosynthetic pigments. Internal cytoplasmic membranes were of the lamellar type. The organism YIM 73036T was able to grow chemo-organoheterophically, chemo-lithoautotrophically and photo-organoheterotrophically but photo-lithoautotrophic and fermentative growth were not demonstrated. Phylogenetic analysis on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain YIM 73036T is closely related to Rhodobacter blasticus ATCC 33485T (96.65% sequence similarity) and clustered with species of the genus Rhodobacter of the family Rhodobacteraceae. Whole-genome sequence analyses based on the average nucleotide BLAST identity (ANI < 82%) indicated that this isolate belongs to a novel species. The genomic DNA G+C content of organism YIM 73036T was determined to be 66.0 mol%. Strain YIM 73036T contained Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone and C18:1ω7c, C18:1ω7c 11-methyl and C18:0 as the major fatty acids. The major polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine and unidentified phospholipid. Differential phenotypic and chemotaxonomic properties, together with the phylogenetic distinctiveness, demonstrated that strain YIM 73036T is distinguishable from other species of the genus Rhodobacter. On the basis of the data presented, strain YIM 73036T is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Rhodobacter, for which the name Rhodobacter thermarum sp. nov. [type strain YIM 73036T (= KCTC 52712T = CCTCC AB 2016298T)] is proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi SC, Mothersole DJ, Dilbeck P, Niedzwiedzki DM, Zhang H, Qian P, Vasilev C, Grayson KJ, Jackson PJ, Martin EC, Li Y, Holten D, Neil Hunter C (2015) Assembly of functional photosystem omplexes in Rhodobacter sphaeroides incorporating carotenoids from the spirilloxanthin pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1847:189–201
Collins MD, Jones D (1980) Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycans based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. J Appl Bacteriol 48:459–470
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Cui XL, Mao PH, Zeng M, Li WJ, Zhang LP, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2001) Streptimonospora salina gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Nocardiopsaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:357–363
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Girija KR, Sasikala C, Ramana CV, Spröer C, Takaichi S, Thiel V, Imhoff JF (2010) Rhodobacter johrii sp. nov., an endospore producing cryptic species isolated from semi-arid tropical soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2099–2107
Gonzalez C, Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. an amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715
Gordon RE, Barnett DA, Handerhan JE, Pang CH-N (1974) Nocardia coeliaca, Nocardia autotrophica, and the nocardin strain. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:54–63
Gregersen T (1978) Rapid method for distinction of Gram-negative from Gram-positive bacteria. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 5:123–127
Hanada S, Takaichi S, Matsuura K, Nakamura K (2002) Roseiflexus castenholzii gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, filamentous, photosynthetic bacterium that lacks chlorosomes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:187–193
Imhoff JF, Trüper HG, Pfennig N (1984) Rearrangement of the species and genera of the phototrophic “purple nonsulfur bacteria”. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 34(3):340–343
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kovacs N (1956) Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature 178:703
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367
Li WJ, Xu P, Schuman P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China) and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Xhi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung DW, Yiu SM, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam TW, Wang J (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18
Macfaddin JF (1976) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria. Williams & Wilkins Co, Philadelphia
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin D, Collins M, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Naziri D, Hamidi M, Hassanzadeh S, Tarhriz V, Zanjani BM, Nazemyieh H, Hejazi MA, Hejazi MS (2014) Analysis of carotenoid production by Halorubrum sp. TBZ126; an extremely halophilic archeon from Urmia Lake. Adv Pharm Bull 4(1):61
Pfennig N, Truper HG (1992) The family Chromatiaceae. In: Balows A, Tru¨per HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 3200–3221
Raj PS, Ramaprasad EV, Vaseef S, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (2013) Rhodobacter viridis sp. nov., a phototrophic bacterium isolated from mud of a stream. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:181–186
Ramana VV, Sasikala Ch, Ramaprasad EVV, Ramana ChV (2010) Description of Ectothiorhodospira salini sp. nov. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:313–319
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl 20:16
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. Am Soc Microbiol, Washington, pp 607–654
Srinivas TN, Kumar PA, Sasikala C, Ramana CV, Imhoff JF (2007) Rhodobacter vinayakumarii sp. nov., a marine phototrophic alphaproteobacterium from tidal waters, and emended description of the genus Rhodobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1984–1987
Srinivas TNR, Kumar PA, Sasikala C, Spröer C, Ramana CV (2008) Rhodobacter ovatus sp. nov., a phototrophic alphaproteobacterium isolated from a polluted pond. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1379–1383
Subhash Y, Lee SS (2016) Rhodobacter sediminis sp. nov., isolated from lagoon sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2965–2970
Suresh G, Sailaja B, Ashif A, Dave Bharti P, Sasikala Ch, Ramana Ch (2017) Description of Rhodobacter azollae sp. nov. and Rhodobacter lacus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3289–3295
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tank M, Thiel V, Imhoff JF (2009) Phylogenetic relationship of phototrophic purple sulfur bacteria according to pufL and pufM genes. Int Microbiol 12:175–185
Tarhriz V, Thiel V, Nematzadeh G, Hejazi MA, Imhoff JF, Hejazi MS (2013) Tabrizicola aquatica gen. nov. sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium isolated from Qurugo¨l Lake nearby Tabriz city, Iran. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:1205–1215
Venkata RV, Sasikala C, Ramana C (2008) Rhodobacter maris sp. nov., a phototrophic alphaproteobacterium isolated from amarine habitat of India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1719–1722
Venkata RV, Anil KP, Srinivas TN, Sasikala C, Ramana C (2009) Rhodobacter aestuarii sp. nov., a phototrophic alphaproteobacterium isolated from an estuarine environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1133–1136
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Chen GZ, Chen HH, Xu H, Jiang CL (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Oxalobacteraceae isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017a) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA and whole genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim JM, Kwon SJ, Chun J (2017b) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Zhang H, Harrington LB, Lu Y, Prado M, Saer R, Rempel D, Blankenship RB, Gross ML (2016) Native mass spectrometry characterizes the photosynthetic reaction center complex from the purple bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 28:87–95
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Yu-Guang Zhou (CGMCC, China) and Professor Jung-Sook Lee (KCTC, Korea) for their kindly providing the reference type strains. This work was supported by the Key Project of International Cooperation of Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST, China) (No. 2013DFA31980), Science and Technology Infrastructure work project (No. 2015FY110100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470139) and Basic Scientific Research Service Fee Project in Colleges and Universities (No. 17lgjc19). W-J Li was also supported by Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges & Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014). We also acknowledge Molecular Medicine Research Center, Biomedicine Institute, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (Tabriz, Iran) for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IUK, NH, MX and WJL conducted this study. IUK, NH, MSH, VT and MX performed the experiments. XYZ and WJL supervised the experiments. IUK, NH, MML, and WDX wrote the manuscript. All of the authors assisted in writing the manuscript, discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no direct or indirect conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, I.U., Habib, N., Xiao, M. et al. Rhodobacter thermarum sp. nov., a novel phototrophic bacterium isolated from sediment of a hot spring. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 867–875 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-01219-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-01219-7