Abstract
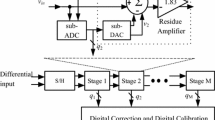
A new technique is introduced for digital background calibration in pipeline analog to digital converters (ADCs). The technique is based on the decision points of the voltage transfer characteristic (VTC) of the pipeline stages, which means the residual VTC is used to estimate the output code of the decision points. By applying the proposed technique, the capacitor mismatch error, the residual amplifier error, and the nonlinearity errors are corrected. To attain proper decision points, the sub-ADC is considered and one of its threshold levels is changed. The mathematical relations of the errors are extracted, and then by applying error coefficients to the final digital outputs, the pipeline ACD is calibrated. This method has a simple digital logic and does not require a particular analog circuit. The proposed technique is applied to the first five stages of a 12-bit 100 MS/s pipeline ADC, and about 0.7 × 106 samples are used. The results show that the presented technique improves the signal-to-noise and distortion ratio (SNDR) and spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) from 34.1 and 35.1 dB to 69.2 and 77.6 dB, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devarajan, S., et al. (2017). A 12-b 10-GS/s interleaved pipeline ADC in 28-nm CMOS technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 52(12), 3204–3218. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2017.2747758
Wu, M. S., & Hong, H. C. (2018). A digital background calibration scheme for pipelined ADCs using multiple-correlation estimation. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2018.8351746
Sahoo, B. D., & Razavi, B. (2013). A 10-b 1-GHz 33-mW CMOS ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(6), 1442–1452. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2013.2252518
Martens, E., Markulic, N., Benites, J. L., & Craninckx, J. (2023). Calibration techniques for optimizing performance of high-speed ADCs. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC). https://doi.org/10.1109/CICC57935.2023.10121250
Datta, B., & Razavi, B. (2009). A 12-bit 200-MHz CMOS ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(9), 2366–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2009.2024809
Ramamurthy, C. Parikh, C. D. & Sen, S. (2021). Deterministic digital calibration of 1.5 bits/stage pipelined ADCs by direct extraction of calibration coefficients. In 34th International Conference on VLSI Design and 20th International Conference on Embedded Systems (VLSID), Guwahati, India, https://doi.org/10.1109/VLSID51830.2021.00010
Yahyaee, S. & Yavari, M. (2022). A histogram-based digital background calibration technique for pipelined A/D converters. In Iranian International Conference on Microelectronics (IICM), Tehran, Iran, https://doi.org/10.1109/IICM57986.2022.10152348
Gholami, P., & Yavari, M. (2018). Digital background calibration with histogram of decision points in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 65(1), 16–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2017.2660765
Mafi, H., Mohammadi, R., & Shamsi, H. (2016). A statistics based digital background calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 51, 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2015.07.014
Mafi, H., Yargholi, M., & Yavari, M. (2018). Statistics-based digital background calibration of residue amplifier nonlinearity in pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 65(12), 4097–4109. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2018.2846647
Wei, J., Zhang, C., & Liu, M. (2022). A 11-Bit 1-GS/s 14.9mW hybrid voltage-time pipelined ADC with gain error calibration. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 69(3), 799–803. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2021.3116591
Panagida, A., & Galton, I. (2009). A 130 mW 100MS/s pipelined ADC with 69 dB SNDR enabled by digital harmonic distortion correction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(12), 3314–3328. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2009.2032637
McNeill, J. A., Coln, M. C., Brown, D. R., & Larivee, B. J. (2009). Digital background-calibration algorithm for ‘“Split ADC”’ architecture. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 56(2), 294–306. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2008.2001830
Montazerolghaem, M. A., Moosazadeh, T., & Yavari, M. (2015). A predetermined LMS digital background calibration technique for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, Express Briefs, 62(9), 841–845. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2015.2435071
Zia, E., Farshidi, E., & Kosarian, A. (2019). A split-based digital background calibration of pipelined analog-to-digital converters by cubic spline interpolation filtering. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 38(10), 4799–4816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01090-5
Shi, L., Zhao, W., Wu, J., & Chen, C. (2012). Digital background calibration techniques for pipelined ADC based on comparator dithering. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 59(4), 239–243. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2012.2188461
Li, J., & Moon, U. K. (2003). Background calibration techniques for multistage pipelined ADC with digital redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog Digital Signal Process, 50(9), 531–538. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2003.816921
Wang, X., Hurst, P. J., & Lewis, S. H. (2004). A 12-Bit 20-Msample/s pipelined analog-to-digital converter with nested digital background calibration. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(11), 1799–1808. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2004.835826
Brooks, L., & Lee, H. S. (2008). Background calibration of pipelined ADCs via decision boundary gap estimation. IEEE Transactions on Cicuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 55(10), 2969–2979. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2008.925373
Rakuljic, N., & Galton, I. (2013). Suppression of quantization-induced convergence error in pipelined ADCs with harmonic distortion correction. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 60(3), 593–602. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215754
Ahmed, I., & Johns, D. A. (2008). An 11-Bit 45 MS/s pipelined ADC with rapid calibration of DAC errors in a multi-bit pipeline stage. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(7), 1626–1637. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2008.923724
Karanicolas, A. N., Lee, H. S., & Bacrania, K. L. (1993). A 15-b 1-Msample/s digitally self-calibrated pipelined ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 28(12), 1207–1215. https://doi.org/10.1109/4.261994
Chuang, S. Y., & Sculley, T. L. (2002). A digitally self-calibrating 14-bit 10-MHz CMOS pipelined ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(6), 674–683. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2002.1004571
Lee, H. S. (1994). A 12-b 600 ks/s digitally self-calibrated pipelined algorithmic ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 29(4), 509–515. https://doi.org/10.1109/4.280701
Chatterjee, S., & Roy, S. (2021). A square wave-based digital foreground calibration algorithm of a pipeline ADC using approximate harmonic sampling. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 68(4), 1068–1072. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2020.3037812
Chiang, S.-H.W., Sun, H., & Razavi, B. (2014). A 10-Bit 800-MHz 19-mW CMOS ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49(4), 935–949. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.2014.2300199
Ravi, C., Rahul, T. & Sahoo, B., (2014). Histogram based deterministic digital background calibration for pipelined ADCs. In 27th International Conference on VLSI Design and 13th International Conference on Embedded Systems, 569–574, Mumbai, India, https://doi.org/10.1109/VLSID.2014.105
Moosazadeh, T., & Yavari, M. (2015). A calibration technique for pipelined ADCs using self-measurement and histogram-test methods. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 62(9), 826–830. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2015.2435851
Wu, T., Wang, N., Wang, J., Xie, L., & Jin, X. (2019). A digital background calibration algorithm of pipelined ADC based on PesudoRandom sequence. In IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China, https://doi.org/10.1109/ELTECH.2019.8839343
Wu, K. C., Wu, M. S., & Hong, H. C. (2019). Multiple correlation estimation based digital background calibration scheme for pipelined ADCs. In IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2019.8702490
Sun, J., Zhang, M., Qiu, L., Wu, J., & Liu, W. (2020). Background calibration of bit weights in pipelined-SAR ADCs using paired comparators. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 28(4), 1074–1078. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2961149
Yang, Z., Yang, P., Yin, X., Li, X., & Yang, H. (2021). Reducing signal swing overheads to only 8% in background 3rd-order inter-stage gain error calibration for pipeline ADCs. In IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Korea. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS51556.2021.9401703
Jiani, M., & Shoaei, O. (2022). Fast background calibration of linear and non-linear errors in pipeline analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 69(3), 884–888. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2021.3135424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KG carried out the modeling and simulations studies, and participated in the drafted of the manuscript. EF participated as supervisor of the study and performed the analysis checking. NAS participated as the advisor of the study and performed the analysis checking.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghanbari, K., Farshidi, E. & Alaei Sheini, N. A new digital background calibration technique for pipeline analog to digital converters using decision points of the voltage transfer characteristics. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 118, 25–35 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-023-02196-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-023-02196-2