Abstract
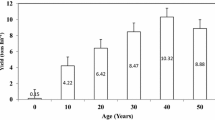
Cover crops significantly affect soil quality, and growth characteristics in apple orchards, but reports are scarce. Therefore, the present study was conducted on a 15-year-old apple orchard (cultivar ‘Red Gold’) at Kashmir valley (32°22′–34°43′N, 73°52′–75°42′E; 1850 m.a.s.l.) to determine the influence of grass (Festuca arundinaceae) and legume (Trifolium pratense) bi-culture (GLBC) on soil properties viz. soil organic carbon (SOC), labile carbon (LC), total nitrogen (TN), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe); and plant growth characteristics like trunk girth (TG), trunk cross-sectional area (TCSA), fruit yield (FY), and yield efficiency(YE), relative to a no cover crop control. GLBC produced 27.9 ± 3.9 and 7.5 ± 0.8 tons/ha green and dry herbage. Plant growth characteristics differed significantly (p < 0.05), with highest TG (38.89 ± 1.54 cm) and TCSA (123.07 ± 9.61 cm2) in GLBC and lowest (36.22 ± 0.97 and 107.11 ± 5.72, respectively) in control. The treatments differed for FY and YE, and maximum FY (30.63 ± 2.81 t/ha) and YE (0.25 ± 0.01 kg/cm2) was recorded in GLBC. Average SOC (12.53 g kg−1), LC (0.90 g kg−1), and TN (0.76 g kg−1) were 20.7, 27.7, and 13.3% greater in GLBC than control at 0–30 cm depth. Relative to control, SOC accumulation in GLBC was 14.15%, and soils sequestered 3.04 Mg C ha−1. For nutrients, differences between treatments were limited for Mg, moderate for P, and Cu; and strong for Mn and K. The findings convey that GLBC adds enough residues to soil to cause measurable changes in SOC and offers potential for C sequestration and soil sustainability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Khan PA, Verma DK, Mir NH, Sharma A, Wani S (2018) Forage production and orchard floor management through grass/legume intercropping in apple based agroforestry systems. Int J Chem Stud 6(1):953–958
Almagro M, de Vente J, Boix-Fayos C, García-Franco N, de Melgares AJ, González D, Solé-Benet A, Martínez-Mena M (2016) Sustainable land management practices as providers of several ecosystem services under rainfed Mediterranean agro-ecosystems. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Chang 21:1029–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-013-9535-2
Álvarez R, Diaz RA, Barbero N, Santaanatoglia OJ, Blotta L (1995) Soil organic carbon, microbial biomass and CO2-C production from three tillage systems. Soil till Res 33:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-1987(94)00432-E
Assaad HI, Hou Y, Zhou L, Carroll RJ, Wu G (2015) Rapid publication-ready MS-Word tables for two-way ANOVA. Springerplus 4:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-0795-z
Blair GJ, Lefroy RDB, Lisle L (1995) Soil C fractions based on their degree of oxidation and the development of a C management index for agriculture system. Aust J Agron Res 46:1459–1466. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9951459
Blake GR, Hartge KH (1986) Bulk density. In: Klute A (ed.) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Agron Monogr. 9. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI. pp 363–375
Busari MA, Kukal SS, Kaur A, Bhatt R, Ally Dulazi A (2015) Conservation tillage impacts on soil, crop and the environment. Int J Soil Water Res 3(2):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.05.002
Coronado AM, Linares C, Gómez-López MD, Zornoza AF (2020) The impact of intercropping, tillage and fertilizer type on soil and crop yield in fruit orchards under Mediterranean conditions: a meta-analysis of field studies. Agri Sys 178:102736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102736
Debasish S, Kukal SS, Bawa SS (2014) Soil organic carbon stock and fractions in relation to land use and soil depth in the degraded Shiwaliks hills of Lower Himalayas. Land Degrad Dev 25:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2151
Demir Z, Tursun N, Işık D (2019) Effects of different cover crops on soil quality parameters and yield in an apricot orchard. Intl J Agric Biol 21:399–408
Gabriel JL, Garrido A, Quemada M (2013) Cover crops effect on farm benefits and nitrate leaching: linking economic and environmental analysis. Agri Syst 121:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2013.06.004
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1992) Particle size analysis. In: Klute A (eds) Methods of soil analysis Part 1. Agron Monogr. 9. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 383–411
Ghimire R, Ghimire B, Mesbah AO, Idowu OJ, O’Neill MK, Angadi SV, Shukla MK (2018) Current status, opportunities and challenges of cover cropping for sustainable dryland farming in the Southern Great Plains. J Crop Improv 32:579–598. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2018.1471432
Gill R, Burke IC, Milchunas DG, Lauenroth WK (1999) Relationship between root biomass and soil organic matter pools in the shortgrass steppe of Eastern Colorado. Ecosystems 2:226–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900070
Gómez JA, Llewellyn C, Basch G, Sutton PB, Dyson JS, Jones CA (2011) The effects of cover crops and conventional tillage on soil and runoff loss in vineyards and olive groves in several Mediterranean countries. Soil Use Manage 27:502–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2011.00367.x
Guerinot ML (1991) Iron uptake and metabolism in the rhizobia/ legume symbioses. Plant Soil 130:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011874
Gupta PK (1999) Soil, plant, water and fertilizer analysis. Agro Botanica Vyas Nagar. Bikaner, India
Hamidov A, Helming K, Bellocchi G, Bojar W, Dalgaard T, Ghaley BB, Hoffmann C, Holman I, Holzkämper A, Krzeminska D et al (2018) Impacts of climate change adaptation options on soil functions: a review of European case-studies. Land Degrad Dev 29:2378–2389. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3006
Herencia JF, Ruiz JC, Morillo E, Melero S, Villaverde J, Maqueda C (2008) The effect of organic and mineral fertilization on micronutrient availability in soil. Soil Sci 173:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1097/ss.0b013e31815a6676
Hulugalle NR, Weaver TB (2005) Short-term variations in chemical properties of Vertisols as affected by amounts, carbon/nitrogen ratio, and nutrient concentration of crop residues. Commun Soil Sci Plan 36:1449–1464. https://doi.org/10.1081/CSS-200058489
Hussain K, Ilyas A, Wongleecharoen C, Hilger T, Wajid A, Ahmad A (2020) Cadish G (2020) Sustainable land use options for optimum resources use in maize based cropping system on uplands of Western Thailand. Agrofor Syst 94:2289–2300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-020-00550-1
Jobbagy EG, Jackson RB (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol App 10:423–436. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-761(2000)010[0423:TVDOSO]2.0.CO;2
Jokela WE, Grabber JH, Karlen DL, Balser TC, Palmquist DE (2009) Cover crop and liquid manure effects on soil quality indicators in a corn silage system. Agron J 101:727–737. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2008.0191
Köchy M, Hiederer R, Freibauer A (2015) Global distribution of soil organic carbon—part 1: masses and frequency distributions of SOC stocks for the tropics, permafrost regions, wetlands, and the world. Soil 1:351–365. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-1-351-2015
Kuhn BF, Pedersen HL (2009) Cover crop and mulching effects on yield and fruit quality in un-sprayed organic apple Production. Eur J Hort Sci 74:247–253
Kuo S, Sainju UM, Jellum EJ (1997) Winter cover crop effects on soil organic carbon and carbohydrate in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 61:145–152. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100010022x
Lane LA, Ayres JF, Lovett JV (2000) The pastoral significance, adaptive characteristics, and grazing value of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) in dryland environments in Australia: a review. Aust J Exp Agric 40:1033–1046. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA99141
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Locola I, Bassu S, Farina R, Antichi D, Basso B, Bindi M, Marta AD, Danuso F, Doro L, Ferrise R, Giglio L, Ginaldi F, Mazzoncini M, Mula L, Orsini R, Corti G, Pasqui M, Seddaiu G, Tomozeiu R, Ventrella D, Villani G, Roggero PP (2017) Can conservation tillage mitigate climate change impacts in Mediterranean cereal systems? A soil organic carbon assessment using long term experiments. Eur J Agric 90:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2017.07.011
Loveland P, Webb PJ (2003) Is there a critical level of organic matter in the agricultural soils of temperate region. A review. Soil till Res 70:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(02)00139-3
Marques JDO, Luizão FJ, Teixeira WG, Sarrazin M, Ferreira SJF, Beldini TP, Marques EMA (2015) Distribution of organic carbon in different soil fractions in ecosystems of central Amazonia. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 39:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1590/01000683rbcs20150142
Mir NH, Suheel A, Verma DK (2016) Livestock rearing-sectorial status and fodder-feed strategies in Kashmir Himalaya. Ann Biol 32(2):253–259
Nascente SA, Li YC, Crusciol CAC (2013) Cover crops and no-till effects on physical fractions of soil organic matter. Soil till Res 130:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2013.02.008
National Horticulture Board-NHB (2018) Indian production of apple (HSCODE-1040). http://apeda.in/agriexchange/India%20Production/India_Productions.aspx?cat=fruit&hscode=1040- Accessed on 17 June 2021
Novara A, Minacapilli M, Santoro A, Rodrigo-Comino J, Carrubba A, Sarno M, Venezia G, Gristina L (2019) Real cover crops contribution to soil organic carbon sequestration in sloping vineyard. Sci Total Environ 652:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.247
Pearson T, Walker S, Brown S (2005) Source book for land use, land-use change and forestry. VA, USA: Projects Winrock International
Ram SN, Kumar S, Roy MM, Baig MJ (2006) Effect of legumes and fertility levels on buffel grass (Cenchrus ciliaris) and Annona (Annona squamosa) grown under horti-pasture system. Ind J Agron 51(4):278–282
Ramzan S, Kirmani AN, Rasool R (2014) Fractionation of zinc and their association with soil properties in soils of Kashmir Himalayas. Int J Agric Soil Sci 2(8):132–142
Reicosky DC (1997a) Tilage-methods induced Co2 emission from soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 49:273–285. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009766510274
Reicosky DC (1997b) Tillage methods and carbon dioxide loss: fall versus spring tillage. In: Lal R (ed) Management of carbon sequestration in Soil. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 99–111
Rovira P, Ramon VV (2002) Labile and recalcitrant pools of carbon and nitrogen in organic matter decomposing at different depths in soil: an acid hydrolysis approach. Geoderma 107:109–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(01)00143-4
Sanchez EE, Giayetto AA, Cichon L, Fernandez D, Aruani MC, Curetti M (2007) Cover crops influence soil properties and tree performance in an organic apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) orchard in northern Patagonia. Plant Soil 292:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9215-7
Shackelford GE, Kelsey R, Dicks LV (2019) Effects of cover crops on multiple ecosystem services: ten meta-analyses of data from arable farmland in California and the Mediterranean. Land Use Pol 88:104204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104204
Shunfeng GE, Zhanling ZHU, Ling P, Qian C, Yuanmao J (2018) Soil nutrient status and leaf nutrient diagnosis in the main apple producing regions in China. Hortic Plant J 4(3):89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2018.03.009
Sofi JA, Dar IH, Chesti MH, Bisati IA (2018) Effect of nitrogen fixing cover crops on fertility of apple (Malus domestica Borkh) orchard soils assessed in a chronosequence in North-West Himalaya of Kashmir Valley, India. Leg Res 41(1): 7–94. https://doi.org/10.18805/LR-3508
Soil Survey Staff (2003) Keys to soil taxonomy. United States Department of Agriculture. Natural Resource Conservation Service, Ninth 2003.
Sturludottir E, Brophy C, Belanger G, Gustavsson AM, Jørgensen M, Lunnan T (2013) Benefits of mixing grasses and legumes for herbage yield and nutritive value in Northern Europe and Canada. Grass Forage Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/gfs.12037
TerAvest D, Smith JL, Carpenter-Boggs L, Hoagland L, Granatstein D, Reganold JP (2010) Influence of orchard floor management and compost application timing on nitrogen partitioning in apple trees. Hort Sci 45:637–642. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.45.4.637
Wendling M, Büchi L, Amossé C (2016) Influence of root and leaf traits on the uptake of nutrients in cover crops. Plant Soil 409:419–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2974-2
Westwood MN, Reimer FC, Quackenbush VL (1963) Long term yield as related to ultimate tree size of three pears varieties grown on rootstocks of five Pyrus species. Proc Am Soc Hort Sci 82:103–108
Widdup KH, Purves RG, Black AD, Jarvis P, Lucas RJ (2001) Nitrogen fixation by caucasian clover and white clover in irrigated ryegrass pastures. Proc NZ Grass Ass 63:171–175
Yang J, Zhang T, Zhang R, Huang Q, Li H (2019) Long-term cover cropping seasonally affects soil microbial carbon metabolism in an apple orchard. Bioengineered 10(1):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2019.1622991
Zheng W, Zhao Z, Gong Q, Zhai B (2018) Li Z (2018) Effects of cover crop in an apple orchard on microbial community composition, networks, and potential genes involved with degradation of crop residues in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 54:743–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1298-1
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance received under Young Scientist Startup Grant (DST/SERB/337-2014) from Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India is highly acknowledged. Assistance in soil analysis provided by staff of Soil Science Laboratory, Central Institute of Temperate Horticulture, Srinagar is highly appreciated. Appreciations are also to farmers for sharing their thoughts and knowledge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dad, J.M., Dand, S.A. & Pala, N.A. The effect of bi-culture cover crops on soil quality, carbon sequestration, and growth characteristics in apple orchards of North Western Himalayas. Agroforest Syst 95, 1745–1758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00687-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00687-7