Abstract
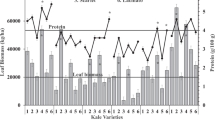
This study has investigated the chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of leaves and stems of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) harvested throughout the growing season. Kenaf (‘Everglades 41’) was planted in June 2011 and harvested at 25, 50 and 75 days after planting (DAP). Crude protein (CP) in leaves was more (P < 0.01) than double than in stems harvested at the same growth stage. Protein concentration in leaves decreased (P < 0.01) as harvesting date was delayed from 50 to 75 DAP, whereas no significant changes in CP were detected in mature stems (75 DAP) as compared to those collected at an earlier stage (50 DAP). Regardless of the maturity stage, cell wall content (NDF and ADF) was higher (P < 0.05) in stems than in leaves. Cell walls were more lignified (P < 0.05) in stems harvested at 50 and 75 DAP and mature leaves (75 DAP) than in young leaves harvested at 25 and 50 DAP. True in vitro dry matter digestibility was lowest (P < 0.05) in mature stems (62%) and highest in leaves harvested at 50 DAP (93%). Conclusively, Kenaf can be grown during the summer season and harvested as a relatively high-quality forage (with high protein content and in vitro digestibility) as early as 50 DAP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson WC, Long FL, Bagby MO (1979) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on yield, composition, and quality of kenaf. Agron J 71:11–14
Alexopoulou E, Christou M, Mardikis M, Chatziathanassiou A (2000) Growth and yield of kenaf varieties in central Greece. Ind Crop Prod 11:163–172
Ammar H, López S, Bochi O, García R, Ranilla MJ (1999) Composition and in vitro digestibility of leaves and stems of grasses and legumes harvested from permanent mountain meadows at different maturity stages. J Anim Feed Sci 8:599–610
Ammar H, López S, González JS, Ranilla MJ (2004a) Seasonal variations in the chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of some Spanish leguminous shrub species. Anim Feed Sci Technol 115:327–340
Ammar H, López S, González JS, Ranilla MJ (2004b) Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of some Spanish browse plant species. J Sci Food Agric 84:197–204
Ammar H, López S, González JS (2005) Assessment of the digestibility of some Mediterranean shrubs by in vitro techniques. Anim Feed Sci Technol 119:323–331
AOAC International (1999) In: Cunniff PA (ed) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International, 16th edn. AOAC International, Arlington, VA
Azizan AR, Md Eusof AJ (1996) From small holders to entrepreneurs in dairy production options and challenges. In: Proceedings of Silver Jubilee Malaysian Society of animal production conference, MSAP, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, pp 118–126
Bañuelos GS, Bryla DR, Cook CG (2002) Vegetative production of kenaf and canola under irrigation in central California. Ind Crop Prod 15:237–245
Basri MHA, Abdu A, Jounejo N, Abdul Hamid H, Ahmed K (2014) Journey of kenaf in Malaysia. A review. Sci Res Essays 9:458–470
Bhangoo MS, Tehrani HS, Henderson J (1986) Effect of planting date, nitrogen levels, row spacing and plant population on kenaf performance in the San Joaquin Valley, CA. Agron J 78:600–604
Carberry PS, Abrecht DG (1990) Germination and elongation of the hypocotyl and radicle of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) in the response to temperature. Field Crop Res 24:227–240
Chantiratikul A, Liang JB, Jelan ZA (2006) Yield and chemical composition of kenaf Hibiscus cannabinus at different stages of maturity. Malays J Anim Sci 11:26–31
Chantiratikul A, Chaikong C, Chinrasri O, Kangkun P (2009) Evaluation of yield and nutritive value of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) at various stages of maturity. Pak J Nutr 8:1055–1058
Cosentino SL, Copani V (2003) Vegetal fibres as multipurpose material. Agroindustria 2:137–145
Danalatos NG, Archontoulis SV (2004) Potential growth and biomass productivity of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under central Greek conditions: II. The influence of variety, sowing time and plant density. In: Proceedings of the 2nd world conference on biomass for energy, industry and climate protection, ETA-Florence, Italy and WIP-Munich, Germany, pp 319–322
Diaz-Mendoza M, Velasco-Arroyo B, Santamaría ME, González-Melendi P, Martínez M, Diaz I (2016) Plant senescence and proteolysis: two processes with one destiny. Genet Mol Biol 39:329–338
Fall-Toure S, Michalet-Doreau B (1995) Nitrogen partition in cell structures of tropical browse plants compared with temperate forages: influence on their in situ degradation pattern. Anim Feed Sci Technol 51:65–72
García-López R, Vinent E, Herrera J (2006) Green protein in 60 days, kenaf (Hibiscus cannabiscus), an alternative for cattle rearing. Cuban J Agric Sci 40:143–146
Goering HK, Van Soest PJ (1970) Forage fiber analysis (apparatus, reagents, procedures and some applications). Agriculture handbook N° 379. Agriculture Research Service USDA, Washington DC
González-Valenzuela EA, Ávila-Curiel JM, Ortega-Santos JA, González-Padrón MA, Muir JP (2008) Harvesting interval changes yield and nutritive value of kenaf in a dry tropical climate. Agron J 100:938–941
Killinger GB (1969) Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus), a multi-use crop. Agron J 61:734–736
Kim BW, Sung KI, Nejad JG, Shin JS (2012) Nutritive value and fermentation quality of the silage of three Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinas L.) cultivars at three different growth stages. J Korean Soc Grassl Forage Sci 32:353–360
Kobiasy M, Tellez MR, Webber CL, Dayan FE, Schrader KK, Wedge DE (2001) Phytotoxic and fungitoxic activities of the essential oil of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) leaves and its composition. J Agric Food Chem 49:3768–3771
López RG, Serrano EV, López ES, González-Medina MR (2016) Protein foliage (kenaf and cassava) in rations of sugarcane without urea, for dairy cows. Pastos y Forrajes 39:203–207
Manzanares M, Tenorio J, Ayerbe L (1997) Sowing time, cultivar, plant population and application of N fertilization on kenaf in Spain’s central plateau. Biomass Bioenerg 12:263–271
Meints PD, Smith CA (2003) Kenaf seed storage duration on germination, emergence, and yield. Ind Crop Prod 17:9–14
Muir JP (2002) Effect of dairy compost application and plant maturity on forage kenaf cultivar fiber concentration and in sacco disappearance. Crop Sci 42:248–254
Oh S, Mbiriri DT, Ryu C, Lee K, Cho S, Choi NJ (2018) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) as a roughage source for beef cattle. J Anim Sci 31:1598–1603
Petrini C, Bazzocchi R, Montalti P (1994) Yield potential and adaptation of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) in north-central Italy. Ind Crop Prod 3:11–15
Phillips WA, Rao SR, Von Tungeln DL, Fitch GQ (1996) Digestibility of freshly harvested, ensilage and mature kenaf by sheep. Prof Anim Sci 12:99–104
Phillips WA, McCollum FT, Fitch GQ (1999) Kenaf dry matter production, chemical composition and in situ disappearance when harvested at different intervals. Prof Anim Sci 15:34–39
Phillips WA, Rao SR, Fitch JQ, Mayeux H (2002a) Digestibility and dry matter intake of diets containing alfalfa and kenaf. J Amin Sci 80:2989–2995
Phillips WA, Reuter RR, Brown MA, Fitch GQ, Rao SR, Mayeux H (2002b) Growth and performance of lambs fed a finishing diet containing either Alfalfa or Kenaf as the roughage source. Small Rumin Res 46:75–79
Robinson PH, Old CA (2014) Brief history of California alfalfa hay TDN equation. Feedstuffs 2014:16–17
Rude BJ, Baldwin BS, Hanson KC (2002) Performance of and nutrient utilization by steers consuming kenaf, pearl millet, or mixed grass. Prof Anim Sci 18:74–78
SGS Agri-Food Laboratories (2013) Forage news from SGS Agrifood Laboratories: Feed and forage calculations. http://agtest.com/articles/forage/SGS-New%20services.pdf. Accessed 28 June 2019
Shayo CM, Udén P (1999) Nutritional uniformity of crude protein fraction in some tropical browse plants estimated by two in vitro methods. Anim Feed Sci Technol 78:141–151
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill International, Singapore
Suriyajantratong W, Tucker RE, Sigafus RE, Mitchell GE Jr (1973) Kenaf and rice straw for sheep. J Anim Sci 37:1251–1254
Swingle RS, Urias AR, Doyle JC, Voigt RL (1978) Chemical composition of Kenaf forage and its digestibility by lambs and in vitro. J Anim Sci 46:1346–1350
Van Soest PJ (1994) Nutritional ecology of the ruminant, 2nd edn. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fibre and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74:3583–3597
Webber CL III (1993) Yield components of five kenaf cultivars. Agron J 85:533–535
Ziblim AI, Agyapong RA, Aikins TK (2015) Assessing the biomass production and nutritive value of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) at various stages of growth. UDS Int J Dev 2:26–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ammar, H., Ismaïl, Y., Lehiani, M.A. et al. Biomass production and nutritive value of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) at various stages of growth. Agroforest Syst 94, 1171–1178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00420-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-019-00420-5