Abstract
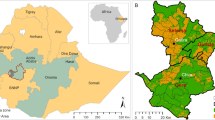
Climate change is one of the extreme factors that threatens biodiversity and affects all organisms and their habitat. Agro-silvopastoral systems with known economic value experience dual pressure due to overexploitation and loss of habitat from rapid climate change effects. Both threats are serious if not managed properly. One strategy for long-term conservation of valuable species and their habitat under changing climate is to identify locations that may sustain suitable habitat conditions for those species. For the argan tree (endemic of Morocco) evaluated in this study, we successfully modeled the habitat suitability of this species for the current and future climate change scenarios (2050 and 2070) by using the Maximum Entropy approach. Predicted future ranges of suitable habitat show that they are site-specific and seem to be highly dependent on climate. The habitat suitability will reduce under each of the future climate scenario (more than 32% of current suitable area will be unsuitable in the future), which tend to have negative consequences for argan ecosystem conservation and provision of functions and services. Given this, predictive maps of suitable habitat elaborated in this study present a powerful tool to include future climate variability in the existing and future restoration and conservation strategies of this valuable agroforestry system.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 May 2018
Unfortunately, in the original publication of the article, the second line arrangement of Table 1 has been listed incorrectly. The correct version of Table 1 is provided below.
Notes
FU: Forage-Unit is equivalent to the average energy produced by 1 kg of barley.
References
Alaoui K (2009) L’arganier ou la richesse d’un patrimoine. Phytothérapie 7:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10298-009-0382-y
Alba-Sánchez F, López-Sáez JA, Nieto-Lugilde D, Svenning J-C (2015) Long-term climate forcings to assess vulnerability in North Africa dry argan woodlands. Appl Veg Sci 18:283–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/avsc.12133
Aouragh M (2012) Dynamique du « paysage-arganeraie » dans le Sud-ouest marocain. Apport des données de télédétection et perspectives de les intégrer dans un SIG. Université Paris Sorbonne-Paris
Araújo MB, Pearson RG, Thuiller W, Erhard M (2005) Validation of species–climate impact models under climate change. Glob Change Biol 11:1504–1513. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.001000.x
Austin M (2007) Species distribution models and ecological theory: a critical assessment and some possible new approaches. Ecol Model 200:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.07.005
Austin MP, Belbin L, Meyers JA et al (2006) Evaluation of statistical models used for predicting plant species distributions: role of artificial data and theory. Ecol Model 199:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.05.023
Benabid A (2000) Flore et écosystèmes du Maroc: Evaluation et préservation de la biodiversité
Benchekroun F, Buttoud G (1989) L’arganeraie dans l’économie rurale du sud-ouest marocain. For Méditerranéenne 2:127–136. http://documents.irevues.inist.fr/bitstream/handle/2042/42141/FM_XI-2_127.pdf?sequ.
Charrouf Z, Guillaume D (2010) Should the amazigh diet (regular and moderate argan-oil consumption) have a beneficial impact on human health? Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50:473–477. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390802544520
De Candolle AP (1844) Prodromus systematis naturalis regni vegetabilis sive enumeratio contracta ordinum, generum specierumque plantarum huc usque cognitarum, juxta methodi naturalis normas digesta, Volume 8 (Latin Edition), Sumptibus Fortin, Masson et Sociorum. Paris
Driouech F, Déqué M, Sánchez-Gómez E (2010) Weather regimes—Moroccan precipitation link in a regional climate change simulation. Glob Planet Change 72:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.03.004
Elith J, Graham CH (2009) Do they? How do they? WHY do they differ? On finding reasons for differing performances of species distribution models. Ecography 32:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2008.05505.x
Elith J, Graham CH, P Anderson R, et al (2006) Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography 29:129–151
Emberger L (1925) Le domaine naturel de l’arganier. Bull Soc Bot Fr 72:770–774. https://doi.org/10.1080/00378941.1925.10832788
Emberger L (1955) Une classification biogéographique des climats, Recueil des Travaux des Laboratoires de Botanique, Géologie et Zoologie de la Faculté des Sciences de L’Université de Montpellier, Série Botanique
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27:861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Feeley KJ, Silman MR (2011) Keep collecting: accurate species distribution modelling requires more collections than previously thought. Divers Distrib 17:1132–1140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2011.00813.x
Fennane M, Ibn Tattou M (2012) Statistiques et commentaires sur l’inventaire actuel de la flore vasculaire du Maroc. Bull de l’Inst Sci Rabat Sect Sci de la Vie 34:1–9
Fick SE, Hijmans RJ (2017) WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5086
Franklin J (2009) Mapping species distributions: spatial inference and prediction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gharby S, Harhar H, El Monfalouti H et al (2011) Chemical and oxidative properties of olive and argan oils sold on the Moroccan market. A comparative study. Mediterr J Nutr Metab 5:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12349-011-0076-5
Graham CH, Elith J, Hijmans RJ et al (2007) The influence of spatial errors in species occurrence data used in distribution models: spatial error in occurrence data for predictive modelling. J Appl Ecol 45:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01408.x
Guisan A, Thuiller W (2005) Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models. Ecol Lett 8:993–1009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00792.x
Guisan A, Zimmermann NE (2000) Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol Model 135:147–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3800(00)00354-9
Guisan A, Tingley R, Baumgartner JB et al (2013) Predicting species distributions for conservation decisions. Ecol Lett 16:1424–1435. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12189
Hallegatte S, Fay M, Bangalore M et al (2015) Shock waves: managing the impacts of climate change on poverty. World Bank Publications, Washington, DC
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Hernandez PA, Graham CH, Master LL, Albert DL (2006) The effect of sample size and species characteristics on performance of different species distribution modeling methods. Ecography 29:773–785. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0906-7590.2006.04700.x
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL et al (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1965–1978. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1276
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ et al (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 486:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11118
IPCC (2013) climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Working Group II contribution to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
Kriegler E, O’Neill BC, Hallegatte S et al (2012) The need for and use of socio-economic scenarios for climate change analysis: a new approach based on shared socio-economic pathways. Glob Environ Change 22:807–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2012.05.005
Lybbert TJ, Aboudrare A, Chaloud D et al (2011) Booming markets for Moroccan argan oil appear to benefit some rural households while threatening the endemic argan forest. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:13963–13968. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106382108
M’hirit O, Benzyane M, Benchekroune F, et al (1998) L’Arganier: Une espece fruitiere-forestiere a usages multiples. Belgique, Pierre Mardaga
MDCE (2016) La Troisième Communication Nationale à la Convention Cadre des Nations Unies sur le Changement Climatique. Ministre de l’environnement, Rabat (MAR)
Merow C, Smith MJ, Silander JA (2013) A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: what it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography 36:1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2013.07872.x
Miller RG (1974) The jackknife-a review. Biometrika 61:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/61.1.1
Moss RH, Edmonds JA, Hibbard KA et al (2010) The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 463:747–756. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08823
Moukrim S, Lahssini S, Mharzi Alaoui H et al (2018) Modélisation de la distribution spatiale des espèces endémiques pour leur conservation: cas de l’argania spinosa (L.) Skeels. Rev D’Ecologie Terre Vie 73:153–166. http://hdl.handle.net/2042/66102
Msanda F, El Aboudi A, Peltier JP (2005) Biodiversité et biogéographie de l’arganeraie marocaine. Cah Agric 14:357–364. doi: http://revues.cirad.fr/index.php/cahiers-agricultures/article/view/30528/30288
Naggar M, M’hirit O (2006) L’arganeraie: un parcours typique des zones arides et semi-arides marocaines. Sécheresse 17:314–317. http://www.jle.com/download/sec-270111-larganeraie_un_parcours_typique_des_zones_arides_et_semi_arides_marocaines–WsxwDn8AAQEAAGUMmlQAAAAK-a.pdf
NFI (2005) National Forest Inventory; High Commission for Water, Forests and Combating Desertification, Morocco
Nouaim R (2005) L’Arganier au Maroc: entre mythes et réalités: une civilisation née d’un arbre. Editions L’Harmattan
Nouaim R, Chaussod R, El Aboudi A, et al (1991) L’arganier. Essai de synthèse des connaissances sur cet arbre. Physiol Arbres Arbustes En Zones Arid Semi Arid Groupe D’Étude L’Arbre Eds John Libbey Eurotex Paris Fr 373–388
OECD (2012) Environmental Outlook to 2050 The Consequences of Inaction. OECD Publishing, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264122246-en
Pearson RG (2007) Species’ distribution modeling for conservation educators and practitioners. Lessons Conserv 3:54–89. https://www.amnh.org/our-research/center-for-biodiversity-conservation/resources-and-publications/lessons-in-conservation/lessons-in-conservation-volume-iii
Peterson AT, Soberón J (2012) Species distribution modeling and ecological niche modeling: getting the concepts right. Nat Conserv 10:102–107. https://doi.org/10.4322/natcon.2012.019
Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008) Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography 31:161–175
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol Model 190:231–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.03.026
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Dudík M et al (2017) Opening the black box: an open-source release of Maxent. Ecography. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.03049
Rocher P (1926) L’arganier. Ann Géogr 35:259–267. https://doi.org/10.3406/geo.1926.8452
Smedmark JE, Swenson U, Anderberg AA (2006) Accounting for variation of substitution rates through time in Bayesian phylogeny reconstruction of Sapotoideae (Sapotaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:706–721
Stride G, Nylinder S, Swenson U (2014) Revisiting the biogeography of Sideroxylon (Sapotaceae) and an evaluation of the taxonomic status of Argania and Spiniluma. Aust Syst Bot 27:104–118
Weigel AP, Knutti R, Liniger MA, Appenzeller C (2010) Risks of model weighting in multimodel climate projections. J Clim 23:4175–4191. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3594.1
Acknowledgements
We thank forest manager for providing valuable field assistance and support. In addition, we thank anonymous reviewers and editor for providing helpful comments. Finally, we thank Mrs. Amina Sena and Dr. Adnane Labbaci for their proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: Table 1 was updated.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moukrim, S., Lahssini, S., Rhazi, M. et al. Climate change impacts on potential distribution of multipurpose agro-forestry species: Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels as case study. Agroforest Syst 93, 1209–1219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-018-0232-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-018-0232-8